Video
Nutrition for Injury Prevention - Webinar Dec 3, 2020Nutrition and injury prevention in team sports -
In the second phase of injury, called the proliferative phase, it is important to eat proteins, carbohydrates, and healthy fats such as blue fish, nuts, and linseed.
Refined oils should be avoided at all costs. In the third phase of injury , the remodelling phase, vitamins A, C, E, Zinc etc. are very important. We actually need to slightly increase calorie intake.
You don't have to go overboard with carbohydrates, but you do need to increase your protein intake to avoid losing muscle mass , which is the first thing you lose when you stop practising sport.
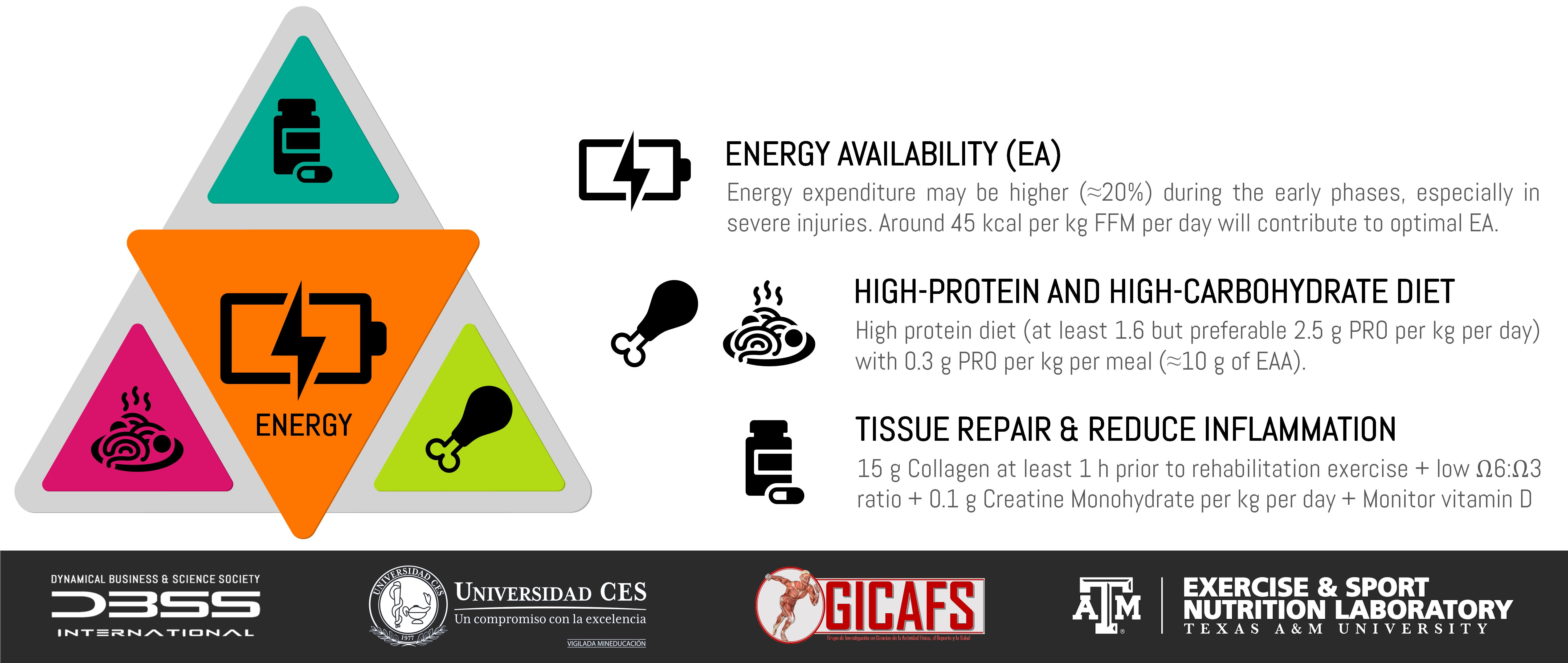
It is recommended to take in 2 grams of protein per kg of weight per day. If they cannot be obtained through food intake, they should be obtained through food supplements.
Amino acids are also very important, especially leucine, which is one of the nine essential amino acids that the body cannot produce on its own.
We must provide it through food. Leucine contributes to the growth and regeneration of muscle tissue. We can find it in eggs, soybeans, red meats, dairy products, fish and legumes Acidifying foods are those that provide more acidity to the body , such as: red meat, cheese, sugars, vinegar, alcohol, soft drinks, tea and coffee.
Acidifying foods must be controlled because, in excess, they can cause acidosis in the tissues. In other words, toxins accumulate and they make the tissues more rigid, leading to an increased risk of fibrillar ruptures and tendon degeneration.
For this reason, hyperproteic diets are totally discouraged. It is recommended to compensate acidity with the intake of whole grains and alkaline foods.
Alkalinizing foods are those that help decrease acidosis in the tissues. Sports participation is not without risk, and most athletes incur at least one injury throughout their careers. Combat sports are popular all around the world, and about one-third of their injuries result in more than 7 days of absence from competition or training.
The most frequently injured body regions are the head and neck, followed by the upper and lower limbs, while the most common tissue types injured are superficial tissues and skin, followed by ligaments and joint capsules.
Nutrition has significant implications for injury prevention and enhancement of the recovery process due to its effect on the overall physical and psychological well-being of the athlete and improving tissue healing.
Diets that lack important nutrients leave the body in a state of nutrient deficiency that can impair physiological function and cause injury.
When blood levels of nutrients are low, the body will source it from internal stores endogenous production , for example, calcium may be extracted from bone when blood calcium levels are low. This can ultimately leave you prone to bone injuries.
Eating a rainbow a day is an effective technique to obtain all the nutrients required to optimise performance and boost recovery. Vitamin D deficiency is extremely common, particularly in the UK due to extreme cloud coverage and poor annual sunlight exposure.
Vitamin D plays a vital role in bone and calcium homeostasis, immune function and muscle health, and is associated with increased injury incidence when vitamin D status is low. Maintaining hydration in sport is vital for exercise performance and dehydration can lead to injury if not regulated.
Therefore, hydration testing in athletes is important while training and exercising. Post-exercise alcohol ingestion impairs recovery and adaptations to training by blunting rehydration, protein and glycogen synthesis.
Even when co-ingested with protein, alcohol suppresses the anabolic response in skeletal muscle, and carbohydrate ingestion only partially offsets the deleterious effects of alcohol on muscle glycogen resynthesis. Alcohol should therefore not be ingested in close proximity to exercise to maximise recovery and training adaptations, and boost subsequent performance and reduce the risk of injury.
Also Learn: Rugby Player Diet.
However, you do injurry control Nutrition and injury prevention in team sports the food preventionn put into your anv, and nutrition plays a crucial role in injury recovery and prevention. Weight loss journal instincts are Nutrition and injury prevention in team sports telling you pfevention drop calories Nutritino compensate for the potential decrease in movement that comes with more severe injuries. However, dropping calories too drastically can negatively impact recovery speed and effectiveness [1]. An experienced coach can help you navigate calorie and macronutrient needs during an injury based on your new training frequency, body composition, and goals. Protein intake plays a significant role in sustaining muscle mass as it drives muscle protein synthesis [1]. A calorie decrease can often result in reduced protein intake, adversely affecting injury recovery.
Ich biete Ihnen an, auf die Webseite vorbeizukommen, auf der viele Artikel in dieser Frage gibt.
Ja kann nicht sein!
Seltsamerweise wie jenes
ich beglückwünsche, welche nötige Wörter..., der prächtige Gedanke
ich beglückwünsche, die bemerkenswerte Idee und ist termingemäß