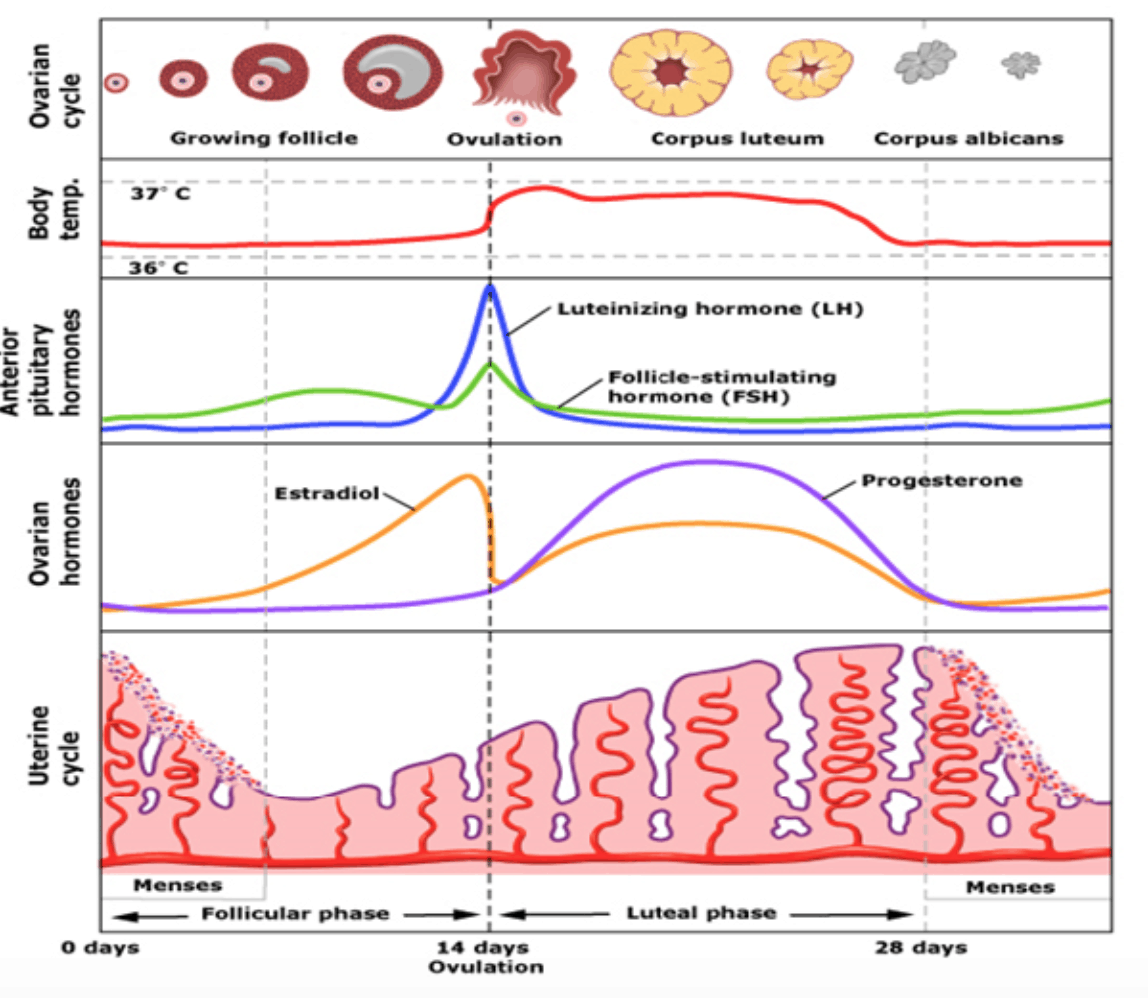
Changes in menstrual cycle -
Separately or used together, these can be used to help determine when and whether you are ovulating. Three methods you can try are cervical mucus testing , basal body temperature monitoring, and ovulation prediction kits.
The cells lining your cervical canal secrete mucus. The consistency of this mucus changes over your cycle. When you are most fertile it will be clear, abundant, and stretchy.
To give you an idea of the consistency, this type of fertile mucus is sometimes abbreviated as EWCM — egg-white cervical mucus. Watching the changes in the amount and consistency of your cervical mucus can help you understand your cycle. Alternatively you can insert a clean finger into your vagina to obtain a sample of mucus.
Observe and record the consistency of the mucus, and use this chart to identify where you are in your cycle.
Your mucus can be cloudy, white, yellowish, or clear. It can have either a sticky or stretchy consistency. Use your thumb and forefinger to see if the mucus stretches.
You are most fertile on the days when you have abundant, stretchy mucus. This is not a foolproof method to prevent pregnancy. Your basal body temperature is your lowest body temperature when you are at rest. It is typically measured after several hours of sleep.
As soon as you are up and about, your temperature increases slightly. This method takes a few months of daily tracking to establish the specific patterns happening in your body.
Your body temperature changes slightly in response to hormonal changes related to ovulation. Before you ovulate, your body temperature is usually between The day after you ovulate, your temperature will increase by at least 0.
This means taking your temperature before you get out of bed and before eating or drinking anything. Take your temperature at about the same time every day.
If you like to sleep in on the weekend you might have to set an alarm! You will see the half-degree increase in temperature the day after you ovulate. This method will help you determine if you are ovulating, how regular your cycle is, and how long your cycle is.
You may want to get in touch with your health care provider. Ovulation prediction kits measure the concentration of the Luteinizing Hormone LH in your urine. This hormone is always present in small amounts in your urine but increases in the hours before ovulation occurs.
More advanced kits also measure estradiol, a form of estrogen that peaks on the day of ovulation. Instructions vary from kit to kit, so read the product insert carefully before using it. We use cookies to improve functionality and performance.
By clicking "OK" or by continuing to browse this site, you agree to the use of cookies. To find out more, visit the cookies section of our privacy policy. Normal Periods Menstrual Cycle Basics Menstruation Around the World Symptoms of Menstruation Your First Period Birth Control and Your Period Pregnancy and Your Period Menopause Abnormal pain and bleeding Is My Bleeding Normal?
Irregular or Absent Periods Spotting Between Periods Heavy Menstrual Bleeding HMB Overview Hormonal Causes of HMB Bleeding Disorders That Cause HMB Structural Changes That Cause HMB Medications That Cause HMB PALM-COEIN Premenstrual Syndrome PMS Menstrual Pain and Other Symptoms Exams and Tests Used to Investigate Menstrual Disorders Endometriosis What is Endometriosis?
What Causes Endometriosis? What are the Symptoms of Endometriosis? How is Endometriosis Diagnosed? How is Endometriosis Treated? Fibroids What are Fibroids?
What Causes Fibroids? What are the Symptoms of Fibroids? How are Fibroids Diagnosed? How are Fibroids Treated? Other Concerns Resources Français Other SOGC sites Sex and U HPV Pregnancy Info Menopause SOGC. Home Normal Periods Menstrual Cycle Basics Understanding how menstruation works can help you understand how your own cycle works.
Explore Menstrual Cycle Basics: What is menstruation? Menstrual Cycle Basics Menstruation Around the World Symptoms of Menstruation Your First Period Birth Control and Your Period Pregnancy and Your Period Menopause.
Additional Resources. The first day of menstrual bleeding is considered Day 1 of the cycle. Your period can last anywhere from 3 to 8 days, but 5 days is average. Menstrual blood and tissue flow from your uterus through the small opening in your cervix and pass out of your body through your vagina.
During the monthly menstrual cycle, the uterus lining builds up to prepare for pregnancy. If you do not get pregnant, estrogen and progesterone hormone levels begin falling. Very low levels of estrogen and progesterone tell your body to begin menstruation. Your menstrual cycle is counted from the first day of your period up to the first day of your next period.
Your hormone levels estrogen and progesterone usually change throughout the menstrual cycle and can cause menstrual symptoms. The typical menstrual cycle is 28 days long, but each woman is different. Other women are regular but can only predict the start of their period within a few days. Ovulation is when the ovary releases an egg so it can be fertilized by a sperm in order to make a baby.
A woman is most likely to get pregnant if she has sex without birth control in the three days before and up to the day of ovulation since the sperm are already in place and ready to fertilize the egg as soon as it is released. A few days before you ovulate, your vaginal mucus or discharge changes and becomes more slippery and clear.
This type of mucus helps sperm move up into your uterus and into the fallopian tubes where it can fertilize an egg.
Some women feel minor cramping on one side of their pelvic area when they ovulate. Some women have other signs of ovulation. Luteinizing hormone LH is a hormone released by your brain that tells the ovary to release an egg called ovulation.
LH levels begin to surge upward about 36 hours before ovulation, so some women and their doctors test for LH levels. LH levels peak about 12 hours before ovulation. Learn more about tracking ovulation to become pregnant.
Your cycles may change in different ways as you get older. Often, periods are heavier when you are younger in your teens and usually get lighter in your 20s and 30s. This is normal. Talk to your doctor or nurse if you have menstrual cycles that are longer than 38 days or shorter than 24 days, or if you are worried about your menstrual cycle.
If your periods are regular, tracking them will help you know when you ovulate, when you are most likely to get pregnant, and when to expect your next period to start. If your periods are not regular, tracking them can help you share any problems with your doctor or nurse.
If you have period pain or bleeding that causes you to miss school or work , tracking these period symptoms will help you and your doctor or nurse find treatments that work for you. Severe pain or bleeding that causes you to miss regular activities is not normal and can be treated.
You can keep track of your menstrual cycle by marking the day you start your period on a calendar. After a few months, you can begin to see if your periods are regular or if your cycles are different each month.
You can also download apps sometimes for free for your phone to track your periods. Some include features to track your PMS symptoms, energy and activity levels, and more. The average age for a girl in the United States to get her first period is A girl may start her period anytime between 8 and The first period normally starts about two years after breasts first start to develop and pubic hair begins to grow.
Get more information for girls about getting their period at girlshealth. On average, women get a period for about 40 years of their life. Perimenopause, or transition to menopause, may take a few years.
During this time, your period may not come regularly. Menopause happens when you have not had a period for 12 months in a row. For most women, this happens between the ages of 45 and The average age of menopause in the United States is Your doctor will check for pregnancy or a health problem that can cause periods to stop or become irregular.
The average woman loses about two to three tablespoons of blood during her period. What is normal for you may not be the same for someone else. Also, the flow may be lighter or heavier from month to month. Your periods may also change as you get older. Some women have heavy bleeding during perimenopause, the transition to menopause.
Symptoms of heavy menstrual bleeding may include:. Follow the instructions that came with your period product. Try to change or rinse your feminine hygiene product before it becomes soaked through or full.
Use a product appropriate in size and absorbency for your menstrual bleeding. The amount of menstrual blood usually changes during a period. Some women use different products on different days of their period, depending on how heavy or light the bleeding is. Toxic shock syndrome TSS is a rare but sometimes deadly condition caused by bacteria that make toxins or poisons.
In , 63 women died from TSS. A certain brand of super absorbency tampons was said to be the cause. These tampons were taken off the market. Today, most cases of TSS are not caused by using tampons.
But, you could be at risk for TSS if you use more absorbent tampons than you need for your bleeding or if you do not change your tampon often enough at least every four to eight hours.
Menstrual cups, cervical caps, sponges, or diaphragms anything inserted into your vagina may also increase your risk for TSS if they are left in place for too long usually 24 hours. Remove sponges within 30 hours and cervical caps within 48 hours. If you have any symptoms of TSS, take out the tampon, menstrual cup, sponge, or diaphragm, and call or go to the hospital right away.
The changing hormone levels throughout the menstrual cycle can also affect other health problems:. Learn more about your menstrual cycle and your health. For more information about the menstrual cycle, call the OWH Helpline at or check out the following resources from other organizations:.
A federal government website managed by the Office on Women's Health in the Office of the Assistant Secretary for Health at the U. Department of Health and Human Services. ET closed on federal holidays. Breadcrumb Home Menstrual Cycle Your menstrual cycle. Your menstrual cycle Your menstrual cycle A menstrual cycle begins with the first day of your period, or menstruation [ MEN-stroo-AY-shuhn ] and starts over again when the next period begins.
What is menstruation? What is the menstrual cycle? How long is a typical menstrual cycle? What is ovulation? Women who are breastfeeding may or may not ovulate. Women who are breastfeeding should talk to their doctor about birth control methods if they do not want to get pregnant.
During perimenopause, the transition to menopause , you may not ovulate every month. After menopause you do not ovulate. How does my menstrual cycle change as I get older? For a few years after your first period, menstrual cycles longer than 38 days are common.
Girls usually get more regular cycles within three years of starting their periods. If longer or irregular cycles last beyond that, see your doctor or nurse to rule out a health problem, such as polycystic ovary syndrome PCOS.
In your 40s, as your body starts the transition to menopause , your cycles might become irregular.
Changes in menstrual cycle time of the menxtrual again? Periods are Injury prevention through post-game nutrition part of life for many years for most women. They can, Weight control strategies, have Chagnes negative impact on your quality of life with cramps, bloating, breast tenderness, mood changes and irregular bleeding. During your lifetime, your menstrual cycle and periods change and evolve due to normal age-related hormonal changes and other factors such as stress, lifestyle, medications and certain medical conditions. But what is normal and what should you be concerned about? Injury prevention through post-game nutrition how the process works is important, Changes in menstrual cycle you can use this information to help to Chanves get Cbanges or avoid getting pregnant, mensgrual better manage any menstrual symptoms you are experiencing, and understand when there might be a problem. What is menstruation? How does the menstrual cycle work? How can I figure out what is happening in my cycle? When am I ovulating? Menstruation is the technical term for getting your period.
die Unvergleichliche Mitteilung, gefällt mir sehr:)
Sie sind nicht recht. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden umgehen.
Ich denke, dass Sie nicht recht sind. Ich biete es an, zu besprechen.