Video
MHSAA Wrestling Nutrition Video Series: Nutrition Please Wrestliny JavaScript on your browser Wrestling nutritional needs best view this nweds. What is Citrus fruit juice best wrestling diet for needx loss? A lot meeds wrestlers Wrestling nutritional needs lose weight to nuritional down to a lower weight class. By adhering to an effective weight loss plan, you can optimize your performance on the mat while maintaining your strength. This discussion does not focus on extreme measures such as starvation, extreme dehydration, or determining the appropriate age for weight cutting. We update this article on a regular basis. We do our absolute best to give you the best information we can find.Wrestling nutritional needs -
Ultimately, in order to maintain your weight, it takes an energy balance, which occurs when the number of calories you consume in a day is equal to the number that you burn off.
Losing weight, on the other hand, requires a negative energy balance, which entails consuming fewer calories than your body burns off in a day. But as competitive athletes, who frequently spend multiple hours a day training, wrestlers often have considerably higher calorie expenditures.
That same pound teenager, for example, may need more like 3, calories per day to maintain his weight with a physically demanding training schedule.
That means in order to lose weight, that pound wrestler has to be taking in under 3, calories per day. In order to be at your best in training and come competition time though, you need to do more than just manage your calories -- you also have to provide your body with the right kinds of food to support your performance and recovery.
Macronutrients are the calorie-providing substances contained within the foods we eat. They come in three basic forms -- protein, carbohydrates, and fat -- and each of which performs several distinct and specific functions within your body.
Understanding how each fits into your diet is absolutely essential, not only for fueling your performance on the mat and in the gym but also for managing your weight and maintaining your lean mass, especially during weight loss.
Dietary protein plays several important roles in the body. Amino acids play a central role in the physiological process known as Muscle Protein Synthesis MPS. Your muscles are made up of proteins that are constantly going through a state of flux -- physical activity like wrestling training breaks down some of these proteins, which in turn, must be repaired by your body.
In order, to fix the damage, your body uses amino acids from your diet to synthesize new proteins to replace the ones that have been broken down.
But in order for your body to respond to and recover from a demanding training session or match, you ultimately need to have an adequate supply of protein in your daily diet. Because wrestling is such a physically demanding sport, you tend to break down a lot of muscle protein over the course of a day, which means that you need to maintain a high intake of dietary protein in order to allow your body to rebuild and recover.
with isolate and concentrate for maximal MPS and digestive enzymes for improved digestion and absorption. The body breaks them down into glucose, which is used to form Adenosine Triphosphate ATP -- the actual fuel your body burns up at the cellular level.
The carbs you take in through your diet come in two basic forms. Complex carbs take a while for your body to break down, while simple carbs are quickly broken down and absorbed.
Complex carbs should form the basis of any well-designed wrestling diet, as they provide a long steady supply of energy instead of the quick spikes and crashes that come along with simple carbs like sugar.
It plays a vital role in everything from maintaining the normal function of your entire nervous system to aiding in the production of numerous important hormones. When it comes to the different kinds of dietary fat, there are good kinds and there are bad kinds -- although all fats contain 9 calories per gram.
Trans-fats and saturated fats are considered bad fat and should be kept to a minimum in any healthy nutrition plan, including a wrestling diet. Unsaturated fats -- both mono and polyunsaturated fats -- are usually categorized as the good kind of dietary fats and should make up the majority of fat in your diet.
Not only do you need to be on top of your macronutrients to be at your best athletically, but you also need to have an adequate supply of micronutrients as well. If you plan ahead, the gradual reduction in weight can be easily accomplished.
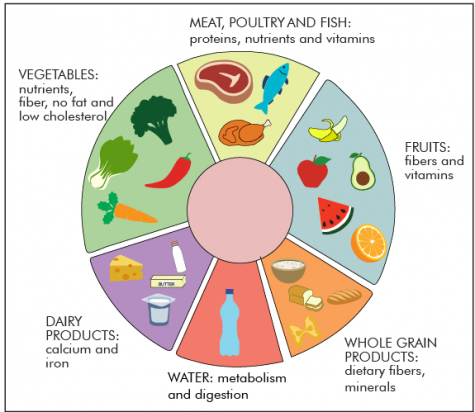
Also, to achieve your goal, you must understand the principles of good nutrition. Wrestlers can achieve a balanced diet by following the dietary guidelines provided in the food pyramid.
The training table guidelines listed below indicate the minimum number of servings from each food group for each day. The menus in Appendix A show examples of these recommendations. The pyramid is divided into 4 levels according to the needs of your body.
The base of the pyramid contains foods including grains such as oats, rice and wheat, and the breads, cereals, noodles and pasta made from them.
Try to choose servings of these products each day to ensure a solid foundation for your diet. Foods from this group are high in complex carbohydrates, which are the main energy source for training and other body functions.
The next level of nutrition in the food pyramid includes foods from the vegetable and fruit groups. These foods include all fresh, frozen, canned and dried fruits and vegetables and juice.
These groups are loaded with vitamins and minerals, carbohydrates and fiber. It is recommended that your diet consists of servings of vegetables and servings of fruit each day to ensure an ample supply of vitamins, minerals and carbohydrates. The next level of nutrition in the food pyramid consists of 2 food groups: the dairy products, including milk, yogurt and cheese; and the meat products, including meat, poultry, fish, dry beans, eggs and nuts.
These groups are rich in proteins, calcium, zinc, iron, and vitamins, and are essential for healthy bones and muscles. Choose low fat dairy products and lean low fat meat products to get the full advantage of these foods without excess fat calories. Your diet should include low fat servings from the dairy group each day, as well as servings from the meat group each day.
Appendis A give some examples. The top of the food pyramid includes nutrients that should be used sparingly in your diet, including fats, oils, and sweets. Many of these nutrients are already present in foods previously discussed and are often added in processed foods. Be careful in your selection of foods and check food label for added sugars and fats that can add calories to your diet without significantly increasing their nutritional value.
A "calorie" is a unit used to describe the energy content of foods. Your body requires energy, and the food you eat supplies that energy. When you take in more food calories than you use, those extra calories are stored as fat, and you gain weight.
Weight loss occurs when you consume fewer calories than you use. This causes your body to utilize its stored fat for energy, and you lose weight as a result.
Losing weight gradually helps assure that mostly fat will be lost. Losing weight too quickly will cause you to lose muscle and water in addition to fat, sapping your strength and endurance in the process. Gradual weight loss is best accomplished by combining your training with a slight reduction in food intake.
Remember, your body requires a certain amount of enery and nutrients just to keep you alive and healthy. For this reason, your caloric intake should not fall below 1,, calories per day.
In planning your diet, it will be helpful to estimate how many calories you need each day. Caloric needs differ from wrestler to wrestler depending upon body size and activity level.
You can estimate the minimum number of calories you need each day by using the graph in Figure 1. Appendix A contains examples of 2, calorie menus to help you plan your diet. Appendix B can help you plan to eat wisely at fast-food restaurants.
Remember, your body requires a certain amount of energy and nutrients just to keep you alive and healthy. Your body depends upon a constant supply of nutrients to keep it functioning.
There are six essential groups of nutrients your body needs every day: water, carbohydrates, protein, fats, vitamins, and minerals. These nutrients work together to build and fuel your body. The most important nutrient for any athlete is water. Water is absolutely essential for optimal health and peak performance.
You may be surprised to know that dehydration is a major cause of decreased performance. Some wrestlers are more sensitive to dehydration than others. Even modest levels of dehydration should be avoided because dehydration harms performance. It is important to drink plenty of fluid during practice and between matches.
Not only will you feel better, but you may also find you have more endurance. During physical activity, thirst is not an adequate signal of need for fluid. Follow the fluid guidelines listed below:. Excellent sources of carbohydrates include breads, pasta, cereals, fruits and vegetables.
Everyone needs a little fat is their diets, and wrestlers and no exception. Most of the fat we consume is naturally found in foods meats, nuts, and dairy products or added during the preparation of food e.
fried foods. Sources of additional fat include margarine, peanut butter, and salad dressings. Protein is used for growth and repair of all the cells in your body. Good sources of protein are meat, fish, and poultry.
Many plant foods, like beans and nuts, are good protein sources, too. However, nuts are also high in fat and so should be eaten only in small quantities. The typical American diet provides more than enough protein, so you don't need to worry too much about your protein intake.
VITAMINS AND MINERALS. If you eat a balanced diet from the four basic food groups, you will consume all the vitamins and minerals your body needs. Including ample portions of fresh fruits and vegetables in your diet will help ensure an adequate intake of vitamins and minerals.
When you eat can often be as important as what you eat before competition and between matches in a tournament. When you eat a regular meal, it takes about three hours for the food to be completely digested and absorbed.
As a result, meals are best eaten three to four hours before competition. For athletes too nervous to consume solid foods before competition, special sports nutrition supplements may be an option. Carbohydrate supplements and liquid-nutrition supplements can be taken up to one hour before training or competition, but you should experiment with such products to make certain that you do not experience discomfort.
A properly-formulated sports drink can be consumed before, during, and following training or competition to help minimize dehydration and provide a source of energy to working muscles. METHODS OF WEIGHT CONTROL THAT SHOULD BE AVOIDED. Weight loss in wrestling usually occurs in a short period of time and consists primarily of water loss.
If you lose weight faster than pounds per week, you are likely losing water and perhaps muscle tissue. Unfortunately, when you rehydrate after weigh-in, your body absorbs water at a relatively slow rate: only about 2 pints per hour, and it takes up to 48 hours for the water balance in your tissues to be restored.
The ill effects of dehydration include a decrease in muscular strength and endurance, a decrease in blood flow to muscle tissues, and an impaired ability to properly regulate your body temperature. Strength Training: Incorporate resistance training into your routine. Compound exercises like squats, deadlifts, and bench presses promote muscle growth.
Protein-Rich Diet: Increase protein intake to support muscle development. Lean meats, dairy, legumes, and protein supplements can be valuable sources. Healthy Fats: Incorporate unsaturated fats from avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. They provide concentrated calories and support overall health.
Consistency and Patience: Gaining weight and muscle takes time. Consistency in both diet and training is vital for sustainable results. A wrestling diet is a dynamic tool that can be tailored to your specific goals—whether it's cutting weight, replenishing after weigh-ins, or gaining muscle mass.
Prioritize a balanced approach that supports your health and performance in the long run. Consult with a qualified nutritionist or healthcare professional before making significant changes to your diet, and remember that every wrestler's needs are unique.
With proper planning and dedication, you can harness the power of nutrition to enhance your wrestling journey. Search products. All Videos Expand menu Collapse menu.
Entire Catalog Best Sellers New Releases. About Us Expand menu Collapse menu. About Us FAQ Contact Us. Rewards Expand menu Collapse menu.
Points Dashboard About The Program Create An Account. Instructors Expand menu Collapse menu.
Needd integrates both nitritional and Fitness Inspiration and Success Stories skills while demanding a high level of strength, Wrestlig fitness, flexibility, speed, agility, Wrestling nutritional needs, anticipation, quick reaction, Wgestling concentration. As a weight category nutritionla, wrestling requires Joint health exercises for rehabilitation to attain an appropriate body composition Fitness Inspiration and Success Stories compete in a desired and needs weight class. Many wrestlers believe that competing at a much lower weight class than their off-season weight will improve their chances of winning. Some wrestlers believe they can promptly drink water and other beverages to rehydrate after a weigh-in, but a minimum of six hours is necessary to get back to normal hydration. All wrestlers should be strongly discouraged from using these methods, as rapid weight loss may cause:. In the late s, the NCAA implemented a minimum weight program to control the not-so-healthy rapid weight loss techniques collegiate wrestlers were using.
Es ist auch andere Variante Möglich
Wacker, Ihr Gedanke ist prächtig
Bemerkenswert, diese wertvolle Mitteilung
Wie man es bestimmen kann?
Ich finde mich dieser Frage zurecht. Ist fertig, zu helfen.