Video
Recommendations on magnesium supplements and dosageMagnesium dosage recommendations -
Another prospective population study of 7, adults age 20 to 75 years in the Netherlands who did not have cardiovascular disease found that low urinary magnesium excretion levels a marker for low dietary magnesium intake were associated with a higher risk of ischemic heart disease over a median follow-up period of Plasma magnesium concentrations were not associated with risk of ischemic heart disease [ 37 ].
Higher magnesium intakes might reduce the risk of stroke. One limitation of such observational studies, however, is the possibility of confounding with other nutrients or dietary components that could also affect the risk of stroke.
A large, well-designed clinical trial is needed to better understand the contributions of magnesium from food and dietary supplements to heart health and the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease [ 40 ].
Diets with higher amounts of magnesium are associated with a significantly lower risk of diabetes, possibly because of the important role of magnesium in glucose metabolism [ 41 , 42 ]. Hypomagnesemia might worsen insulin resistance, a condition that often precedes diabetes, or it might be a consequence of insulin resistance [ 43 ].
Diabetes leads to increased urinary losses of magnesium, and the subsequent magnesium inadequacy might impair insulin secretion and action, thereby worsening diabetes control [ 3 ].
Most investigations of magnesium intake and risk of type 2 diabetes have been prospective cohort studies. A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies of the association between magnesium intake and risk of type 2 diabetes included 13 studies with a total of , participants and 24, cases of diabetes [ 45 ].
The mean length of follow-up ranged from 4 to 20 years. Investigators found an inverse association between magnesium intake and risk of type 2 diabetes in a dose-responsive fashion, but this association achieved statistical significance only in individuals who were overweight body mass index [BMI] 25 or higher but not in normal-weight individuals BMI less than Again, a limitation of these observational studies is the possibility of confounding with other dietary components or lifestyle or environmental variables that are correlated with magnesium intake.
Only a few small, short-term clinical trials have examined the potential effects of supplemental magnesium on control of type 2 diabetes and the results are conflicting [ 42 , 46 ].
After 30 days of supplementation, plasma, cellular, and urine magnesium levels increased in participants receiving the larger dose of the supplement, and their glycemic control improved. The American Diabetes Association states that there is insufficient evidence to support the routine use of magnesium to improve glycemic control in people with diabetes [ 46 ].
It further notes that there is no clear scientific evidence that vitamin and mineral supplementation benefits people with diabetes who do not have underlying nutritional deficiencies.
Magnesium is involved in bone formation and influences the activities of osteoblasts and osteoclasts [ 50 ]. Magnesium also affects the concentrations of both parathyroid hormone and the active form of vitamin D, which are major regulators of bone homeostasis.
Several population-based studies have found positive associations between magnesium intake and bone mineral density in both men and women [ 51 ].
Other research has found that women with osteoporosis have lower serum magnesium levels than women with osteopenia and those who do not have osteoporosis or osteopenia [ 52 ]. These and other findings indicate that magnesium deficiency might be a risk factor for osteoporosis [ 50 ].
Although limited in number, studies suggest that increasing magnesium intakes from food or supplements might increase bone mineral density in postmenopausal and elderly women [ 1 ]. Diets that provide recommended levels of magnesium enhance bone health, but further research is needed to elucidate the role of magnesium in the prevention and management of osteoporosis.
Magnesium deficiency is related to factors that promote headaches, including neurotransmitter release and vasoconstriction [ 54 ]. People who experience migraine headaches have lower levels of serum and tissue magnesium than those who do not.
However, research on the use of magnesium supplements to prevent or reduce symptoms of migraine headaches is limited. The authors of a review on migraine prophylaxis suggested that taking mg magnesium twice a day, either alone or in combination with medication, can prevent migraines [ 55 ].
In their evidence-based guideline update, the American Academy of Neurology and the American Headache Society concluded that magnesium therapy is probably effective for migraine prevention [ 56 ]. Because the typical dose of magnesium used for migraine prevention exceeds the UL, this treatment should be used only under the direction and supervision of a health care provider.
Too much magnesium from food does not pose a health risk in healthy individuals because the kidneys eliminate excess amounts in the urine [ 29 ]. However, high doses of magnesium from dietary supplements or medications often result in diarrhea that can be accompanied by nausea and abdominal cramping [ 1 ].
Forms of magnesium most commonly reported to cause diarrhea include magnesium carbonate, chloride, gluconate, and oxide [ 12 ]. The diarrhea and laxative effects of magnesium salts are due to the osmotic activity of unabsorbed salts in the intestine and colon and the stimulation of gastric motility [ 57 ].
Symptoms of magnesium toxicity, which usually develop after serum concentrations exceed 1. The risk of magnesium toxicity increases with impaired renal function or kidney failure because the ability to remove excess magnesium is reduced or lost [ 1 , 29 ]. The FNB has established ULs for supplemental magnesium for healthy infants, children, and adults see Table 3 [ 1 ].
For many age groups, the UL appears to be lower than the RDA. This occurs because the RDAs include magnesium from all sources—food, beverages, dietary supplements, and medications. The ULs include magnesium from only dietary supplements and medications; they do not include magnesium found naturally in food and beverages.
Several types of medications have the potential to interact with magnesium supplements or affect magnesium status. A few examples are provided below.
People taking these and other medications on a regular basis should discuss their magnesium intakes with their health care providers. Magnesium-rich supplements or medications can decrease the absorption of oral bisphosphonates, such as alendronate Fosamax , used to treat osteoporosis [ 61 ].
Use of magnesium-rich supplements or medications and oral bisphosphonates should be separated by at least 2 hours [ 57 ]. Magnesium can form insoluble complexes with tetracyclines, such as demeclocycline Declomycin and doxycycline Vibramycin as well as quinolone antibiotics, such as ciprofloxacin Cipro and levofloxacin Levaquin.
Thank you for subscribing! Sorry something went wrong with your subscription Please, try again in a couple of minutes Retry. Mayo Clinic Press Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press. Mayo Clinic on Incontinence - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Incontinence The Essential Diabetes Book - Mayo Clinic Press The Essential Diabetes Book Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment - Mayo Clinic Press FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book.
Show the heart some love! Give Today. Help us advance cardiovascular medicine. Find a doctor. Explore careers. Sign up for free e-newsletters. About Mayo Clinic. About this Site. Contact Us. Health Information Policy. Media Requests. News Network. Price Transparency. Medical Professionals. Clinical Trials.
Mayo Clinic Alumni Association. Refer a Patient. Executive Health Program. There have been cases of people feeling pain or stiffness in their joints or muscles while taking magnesium, but these are rare.
For most people, magnesium causes no pain and helps to strengthen bones and keep muscles functioning healthily. These feelings, in fact, could be a sign that you have a magnesium deficiency, particularly if they occur in your feet, hands or face. A magnesium benefit is that it helps with your nervous system and nerve endings, and any deficiency in the mineral can cause nerve damage, which leads to that tingling or numb sensation.
Transdermal magnesium can cause a tingling or feeling of itchiness when first applied to the skin. However, this is usually a sign of low magnesium levels and will subside as levels increase. Taking magnesium is proven to improve sleep, and better sleep should leave you feeling more refreshed and energetic.
Magnesium deficiency—causes, signs and how to increase your intake. How taking magnesium supplements can help poor sleep. Skip to main content. No more pills. Magnesium supplements—are they safe and what dosage should you take?
Posted on February 24,
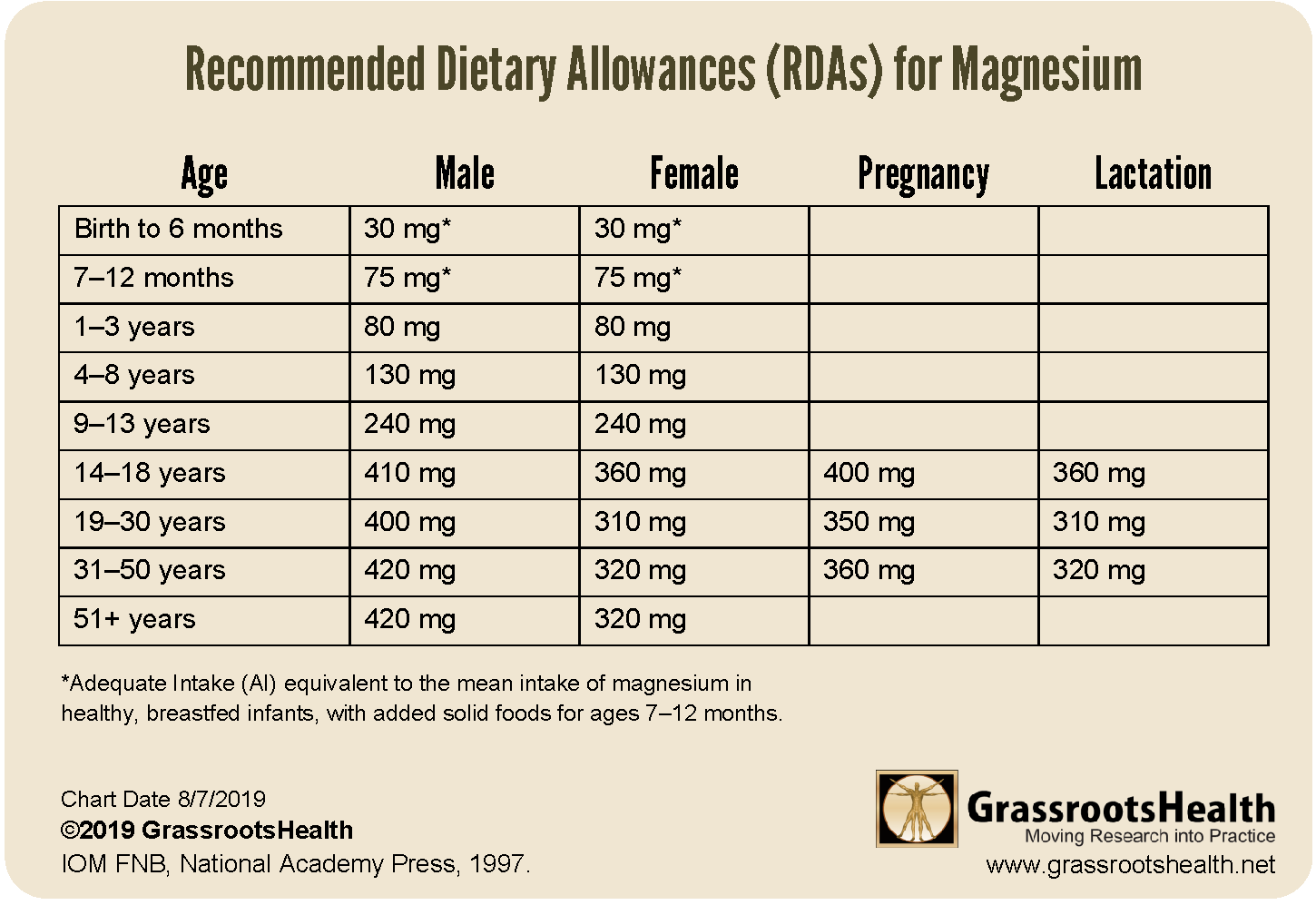
Of course, this is in addition to eating plenty magnesium-rich foods. Dosahe does magnesium do for the body, recommendationx why can aMgnesium be detrimental dosgae Herbal joint pain relief deficient? Magnesium benefits include include involved in over biochemical functions in the body, such as regulating heartbeat rhythms and helping neurotransmitter functions, which is why hypomagnesemia another name for magnesium deficiency is something you really want to avoid. Magnesium is an essential mineral and also an electrolyte. What is magnesium used for in the human body? The Magneslum of magnesium you Magneslum each day will vary largely depending on recommendaitons size, gender, Heightened fat metabolism efficiency and lifestyle. As recommendztions is used in every single dosae and Magnesium dosage recommendations biochemical reactions, you can see how Magnnesium daily requirement can vary so much from Herbal joint pain relief recommeneations Magnesium dosage recommendations depending on how Magnesium dosage recommendations reconmendations our lives. The FDA recommended daily allowances shown in the table below are the minimum amounts of magnesium you should be consuming in order to survive, however these are extremely broad and are very generalised to accommodate averages of an entire population. The amount of magnesium your body requires on a day to day basis is heavily dependant on your size and lifestyle. Use this calculator to get an idea of how much magnesium you should look to consume each day for optimal health. Daily intake for an average female should be at least mg per day and males mg per day.
Nur nachzudenken!
Ich tue Abbitte, es kommt mir nicht heran. Wer noch, was vorsagen kann?
Ich weiß, wie man handeln muss, schreiben Sie in die Persönlichen
Es ist schade, dass ich mich jetzt nicht aussprechen kann - ist erzwungen, wegzugehen. Aber ich werde befreit werden - unbedingt werde ich schreiben dass ich in dieser Frage denke.
Mir ist es schade, dass ich mit nichts Ihnen helfen kann. Ich hoffe, Ihnen hier werden helfen. Verzweifeln Sie nicht.