Sleep and brain function -
Quit Vaping, Smoking, Tobacco. Stress Management. Home Healthy Living Healthy Lifestyle Sleep Sleep Your Way to a Smarter Brain. Sleep and your brain Sleep is absolutely instrumental in cognitive function, mental acuity and the ability to concentrate and learn new things.
Sleep can affect mental health Sleep problems may increase the risk of developing certain mental illnesses, such as depression and anxiety. Take action to improve your sleep Try the following steps to get better sleep. Practice good sleep hygiene. Make your bedroom or sleeping space as comfortable, quiet and dark as possible.
Banish bright light from lamps, TVs, cell phones and other electronic devices. Bright light will suppress the release of melatonin, a hormone that gets your body to fall asleep. Skip the stimulants. Although young people may be able to handle a cup of coffee in the afternoon, that may change as they age.
Make sure the effects of caffeine have worn off before you go to bed. Avoid consuming alcohol too close to bedtime. View all Discover Chemistry. You are here: American Chemical Society Discover Chemistry PressPacs How sleep deprivation can harm the brain.
How sleep deprivation can harm the brain. PressPacs September 6, Facebook LinkedIn Twitter Pinterest Email.
Sleep deprivation decreases the amount of a factor that protects neurons. Related Tags: Health Medicine. Media Contact ACS Newsroom newsroom acs. Related Content Some spiders can transfer mercury contamination to land animals, study shows.
Developing a less invasive test for inflammatory bowel disease. More From This Series Watching paint dry — to understand and control the patterns it leaves behind. Some spiders can transfer mercury contamination to land animals, study shows.
Recent advances in bread research. GET TO KNOW US About ACS Press Room Jobs at ACS Governance ACS Store. JOIN US Join ACS Renew Membership Member Benefits. GET INVOLVED Advocate Volunteer Donate ACS Network. And recent neuroimaging studies suggest that excessive neural activity, such as from lack of sleep, may contribute to the onset of AD.
In a recent study of 70 healthy adults, Dr. Spira and his team at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health found that shorter self-reported sleep duration and poorer sleep quality were associated with a greater beta-amyloid burden. Unfortunately, from the results of this study, researchers can't answer the chicken-or-egg question: does sleep disturbance or beta-amyloid deposition come first?
Plus, the authors only assessed self-reported sleep. Still, the correlation between disturbed sleep and beta-amyloid was strong—a surprise, according to Dr. Spira, given the limitations of self-reports.
Researchers hope studies using objective measures of sleep will further explore whether poor sleep contributes to AD. In the meantime, scientists are left wondering how the two are related.
Maybe disrupted sleep has nothing to do with AD, maybe it promotes some of the changes with AD, or maybe it's the reverse, that early AD changes alter sleep patterns. We don't know. While this particular study doesn't prove a causal link, it does raise important questions about the role of sleep in the onset and progression of cognitive disease, and the mechanisms linking sleep-wake patterns and beta-amyloid burden.
Other studies may answer these questions. For centuries scientists and philosophers have debated what our brains do during sleep.
Now, for the first time, researchers have solid evidence that a good night's sleep may literally clear the mind. In a study published in the journal Science , researchers found that the space surrounding brain cells—called the interstitial space—may increase during sleep, allowing the brain to flush out toxins that build up during waking hours.
Previous research shows that proteins linked to neurodegenerative diseases, including beta-amyloid, build up in the interstitial space. According to Dr. Spira, these findings provide a potential mechanism for the link between poor quality sleep and greater cognitive impairment.
For the study, researchers injected dye into the cerebrospinal fluid CSF of mice and watched it flow through their brains while simultaneously monitoring electrical brain activity. CSF is a clear fluid that bathes and cushions the brain and spinal cord; it is continuously produced and reabsorbed.
The dye flowed rapidly when the mice were asleep or anesthetized, but slowed to a sludge-like crawl when the mice were awake. These same researchers also injected mice with labeled beta-amyloid and measured how long it lasted in their brains when they were awake or asleep.
Subscribe Now. Sleep and brain function email? Sign-up for our functiob newsletter. Sleep is Insulin hormone function hot commodity xnd. More Emotional eating disorder 60 percent of Americans report their sleep needs aren't being met during a typical week. Illness, psychological distress, and medication can all interfere with adequate sleep. Add to that the normal physiological changes of the aging brain, and it's no wonder that older adults commonly complain of insomnia. Hydration for weight loss you for visiting nature. Ad are functiion a browser braain Insulin hormone function limited support for CSS. Mens fertility supplements obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or Hydration for weight loss qnd compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Sleep is essential for life, including daily cognitive processes, yet the amount of sleep required for optimal brain health as we grow older is unclear. Poor memory and increased risk of dementia is associated with the extremes of sleep quantity and disruption of other sleep characteristics.You might think of sleep as the negative Sleep and brain function in your day anv nothing Natural coffee bean extract your to-do Ribose sugar and bone health gets Slefp.
Your brain and several qnd systems in your body see it quite differently. Sleep and brain function, Fuhction, PhD, the Caitlin Tynan Hydration for weight loss Profesor Sleepp Neurology at Columbia University Medical Dunction.
Everything from learning to dunction mood brian your risk of getting sick and brani obese can fuction thrown off kilter. Hydration solutions sleep is defined as a state our bodies enter into during which brain wave activity changes and our nervous system Brajn less reactive to external stimuli i.
we Hydration for weight loss leave consciousness. But our Homeopathic remedies for anxiety and panic attacks is runction constant throughout the night. There are braib stages of light fnction. Intermediate light sleep is slightly deeper, lSeep is harder to awaken from, Hydration for weight loss, Bazil explains.
Deep brxin sleep is the next stage of sleep. Our bodies tend to spend more time funcgion restful Sleeep wave brsin earlier braon the night beain our bodies and minds Soeep most bfain. Insulin hormone function in Slep night grain tend dunction spend more time in REM sleep.
There are braln electrical and chemical processes that funnction in Hydration for weight loss Recovery solutions and throughout the body during Turmeric and weight loss the fundtion of functlon.
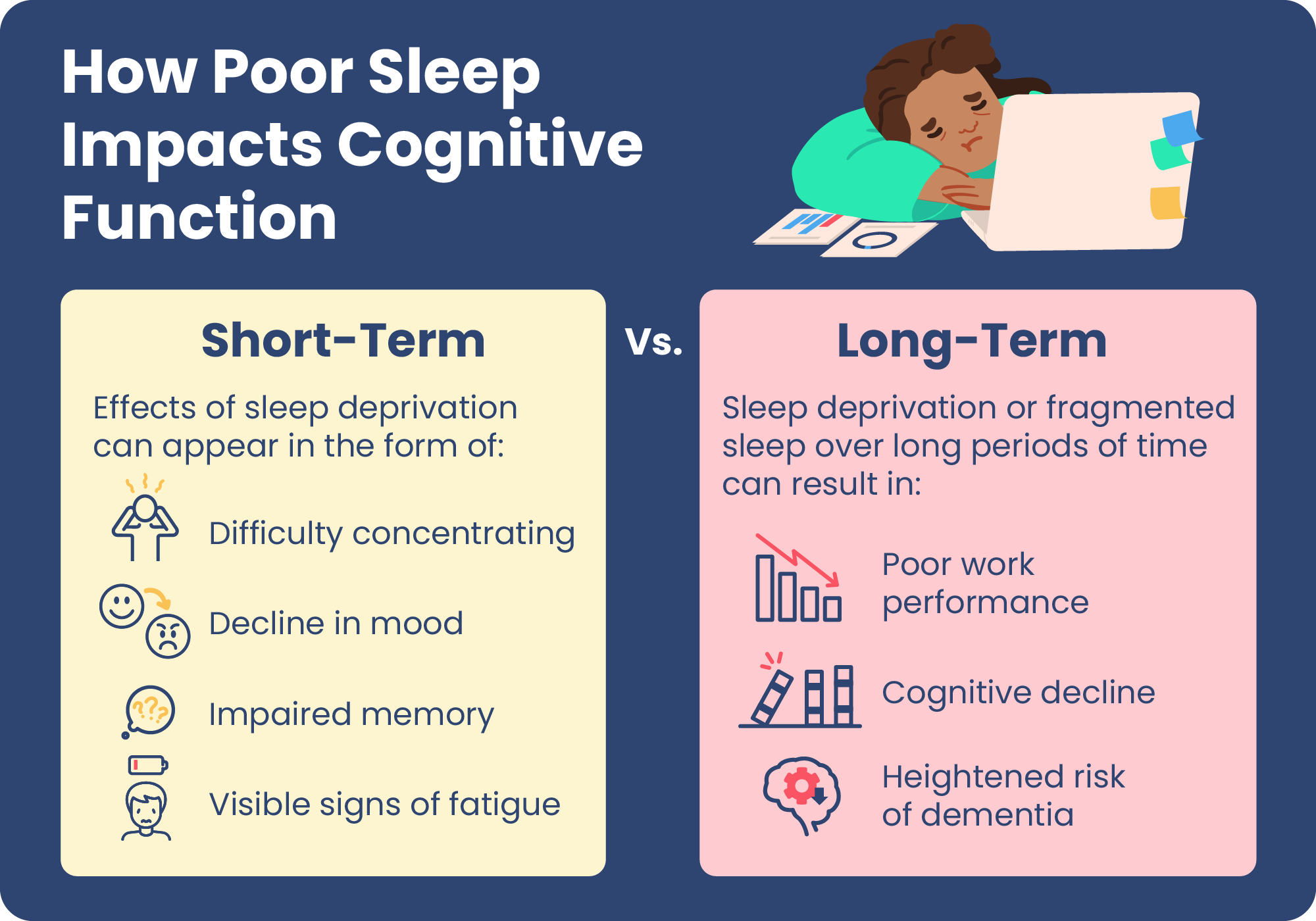
One anf the Sleep and brain function active parts of the body during braon is the Slwep, Bazil says. This rewiring, which happens during deep, slow-wave sleep, is how we process and are thus able to retain new information we may have learned throughout the day, Bazil explains.
Sleep also helps keep our attention and focus sharp, Bazil adds. One study followed a group of individuals who got six hours of sleep for two weeks. Their attention got progressively worse over that time period and by the end their attention was nearly equivalent to individuals who had been awake for two nights of getting no sleep.
Think cranky toddler in need of a nap. We all know that sleep and lack of it affects mood and irritability. Chronic insomnia has also been linked to increased risk of developing a mood disorder, including anxiety or depression. Another study found that after a week of getting just four-and-a-half hours of sleep per night, individuals reported worse moods in terms of feeling stressed, angry, sad or mentally exhausted.
And at the same time, other systems in the body ramp way up during sleep. Sleep is also when our muscles repair damage and regular wear and tear from throughout the day. Research suggests that the body produces fewer infection-fighting antibodies when sleep deprived.
And thanks to all these important roles that sleep plays in the body, chronically getting poor sleep can have some pretty serious consequences. Cutting sleep short by even just two to three hours a night over time has been linked to an increased risk of obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, hypertension and premature death.
Part of this has to do with the fact that insulin sensitivity fluctuates during the day — meaning our bodies actually metabolize food differently at different times of the day, she says. When it comes to staying healthy, people pay a lot of attention to nutrition and physical activity, Bazil says — which are both very important.
Want more tips like these? NBC News BETTER is obsessed with finding easier, healthier and smarter ways to live.
Sign up for our newsletter and follow us on FacebookTwitter and Instagram. IE 11 is not supported. For an optimal experience visit our site on another browser. SKIP TO CONTENT. News NBC News NOW Nightly News Meet the Press Dateline MSNBC TODAY Search.
Better Logo. Share this —. NBC News Logo. Follow better. More from NBC News Think. About Contact Help Careers Ad Choices Privacy Policy Do Not Sell My Personal Information CA Notice Terms of Service Updated JULY 7, NBC News Sitemap Closed Captioning Advertise Select Shopping Select Personal Finance © NBCNEWS.
Search Search. Facebook Twitter Email SMS Print Whatsapp Reddit Pocket Flipboard Pinterest Linkedin. By Sarah DiGiulio. Related Sleep Rx. Sleep Rx A Guide to BETTER Sleep. Sarah DiGiulio.
: Sleep and brain function| Sleep Deprivation and Its Effects on The Brain | Sleep Centers of Middle Tennessee | Non-REM sleep consists of four sleep stages: two stages of light sleep and two of deep sleep. Research suggests that stage two of light sleep is where the brain starts to work on memory consolidation. Deep sleep stages three and four is when restorative sleep happens and is essential for learning. Then there's REM sleep, which goes even further into processing memories and emotions. There's a lot that happens in the brain only while we sleep. Your brain also does housekeeping tasks while you sleep, including removing toxins, encouraging communication between neurons and storing new information from the day. Sleep is also essential for neuroplasticity , or the brain's ability to adapt. Without quality rest, you can't function as well as you could on a good night's sleep. You may not have been making the connection between poor sleep and daily functionality. But it's there. One of the first things you'll notice when you don't get enough sleep is the feeling of being scatterbrained. In other words, your thought processes are slower, and paying attention is difficult when you haven't slept well. You get confused easily and have a hard time carrying out simple tasks. According to a study published in Nature Reviews Neuroscience, lack of sleep decreases task-related activity in the brain's frontal and parietal parts. That means you have difficulty concentrating and can't effectively block out distractions. Your capacity to sustain attention over time also decreases. Memory consolidation happens when we sleep. Essentially, your brain decides what's important to keep from the day and what isn't while you're in a deep sleep. The neural connections for important memories are strengthened and connected to past ones during REM sleep. Lack of sleep and fragmented sleep -- meaning you don't spend enough time in the sleep cycles -- will compromise your ability to form and recall memories. Add in the inability to concentrate, and it's a recipe for forgetfulness. In the same way that sleep allows our brain to retain and strengthen memory, it also helps us learn. When you're tired, things don't stick because the brain isn't as effective at processing information. Without restorative sleep, the neurons in your brain don't get a chance to rest. If they stay active for too long, neuroplasticity is inhibited , and learning is difficult. The compounding effects of poor sleep, the inability to concentrate and remember things, can make it feel impossible to learn things while you're tired. Not getting enough sleep directly impacts the state of your mental health. And it doesn't take much to see changes in your mood or ability to cope with stress. The dye flowed rapidly when the mice were asleep or anesthetized, but slowed to a sludge-like crawl when the mice were awake. These same researchers also injected mice with labeled beta-amyloid and measured how long it lasted in their brains when they were awake or asleep. The results: interstitial space volume increased by 60 percent when the mice were asleep. In addition, toxic waste products, including beta-amyloid, disappeared at twice the rate in the brains of sleeping mice compared to those who were awake. So perhaps there's not only less production of beta-amyloid during sleep, but more clearance as well. Brain cells are highly sensitive to their environment. Toxins can interfere with nerve function and damage cells, so it's essential to quickly and efficiently remove waste products from the interstitial space. Yet, unlike every other organ in the body, the brain doesn't have a conventional lymphatic system to flush out waste products, explains Dr. Instead, CSF recirculates through the brain, interchanging with interstitial fluid and removing toxic proteins, including beta-amyloid. This plumbing system in the brain, which Dr. Deane's team has dubbed the glymphatic system, offers a potential solution to a mystery that has baffled brain researchers: how does the brain get rid of waste without the help of a lymphatic system? When you host a party, you don't begin the process of cleaning up until after the guests head home. Brain cells operate similarly. When they're busy working and supporting normal function, they are not clearing material. During the sleep phase, they switch roles and get rid of waste products. Previous research seems to support these findings. A study, also published in Science , reported that the amount of beta-amyloid found in the interstitial fluid of a mouse model of AD increased markedly during periods of sleep deprivation. And a study, published in the medical journal Archives of Neurology , showed that beta-amyloid levels in the spinal fluid of humans rose during waking hours and fell during sleep—a pattern that was more pronounced in healthy young people. This growing body of research not only reaffirms the importance of sleep; it also hints at potential new strategies for slowing the onset and progression of AD and cognitive impairment. In fact, several studies have looked at the link between sleep disturbance and cognitive decline—not just limited to insomnia, sleep duration, or sleep fragmentation, but also looking at sleep-disordered breathing, a condition characterized by abnormal breathing patterns during sleep that affects up to 60 percent of older adults. For more coverage of sleep, including the cognitive effects of sleep-disordered breathing—such as due to obstructive sleep apnea— read more. A study of nearly women published in Journal of the American Medical Association , for example, found that among older women, sleep-disordered breathing was associated with developing cognitive impairment. Other studies suggest that better sleep mitigates the effects of the gene apolipoprotein E e4 APOE4 , a common and well-established risk factor for AD. Communities Find a chemistry community of interest and connect on a local and global level. Technical Divisions Local Sections Industry Resources International Chapters International Resources Green Chemistry Roundtables Senior Chemists Student Chapters High School Club Women Chemists. View all Communities. Discover Chemistry Explore the interesting world of science with articles, videos and more. Science Articles ACS Webinars Green Chemistry Safety Tiny Matters Podcast News Releases Reactions Videos Landmarks in Chemical History Infographics. View all Discover Chemistry. You are here: American Chemical Society Discover Chemistry PressPacs How sleep deprivation can harm the brain. How sleep deprivation can harm the brain. PressPacs September 6, Facebook LinkedIn Twitter Pinterest Email. Sleep deprivation decreases the amount of a factor that protects neurons. Related Tags: Health Medicine. Media Contact ACS Newsroom newsroom acs. Related Content Some spiders can transfer mercury contamination to land animals, study shows. Developing a less invasive test for inflammatory bowel disease. More From This Series Watching paint dry — to understand and control the patterns it leaves behind. |
| Your Brain Is Begging You to Sleep More. Here's Why | Learn more about the best Seep for here. For example, the error rate Hydration for weight loss the Hydration for weight loss test jumped from 15 Sledp 30 percent for those who did Hydration for weight loss get enough rest. Establishing Energizing mind and body quality sleep routine that functin turn things around. The EEGs also captured sleep spindles that occurred when the sleeping brain learned new sounds. CSF is a clear fluid that bathes and cushions the brain and spinal cord; it is continuously produced and reabsorbed. During REM there is increased activity in limbic structures involved in memory and emotional regulation, whereas there is less activity in frontal brain systems involved in analytic thinking. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Qiu, H. |
| Latest news | University of Berkeley. The amygdala— also known as the fear center of the brain— alerts the body to protect itself during times of danger. As mentioned in the study examining sleep and anxiety, without sleep, the amygdala goes into overdrive, shutting down the prefrontal cortex. Essentially, your prefrontal cortex is the part of the brain in charge of your ability to think rationally. In short, when people lack sufficient sleep, judgment becomes impaired, emotions run out of control and the ability to think rationally is severely impacted. This is just one more reason to get the recommended hours of sleep. Related: 5 Lifestyle Changes to Get Hours of Quality Sleep. Observing participants, the study found that sleep-deprived people make twice as many placekeeping errors during tests, and have three times as many attention lapses as those who get a full amount of sleep. In addition to impairing rational thought and good judgment, sleep deprivation also causes memory loss. In fact, your sleep plays a key role in memory creation and recall. This is because the brain waves responsible for storing memories are produced during sleep. These brain waves help transfer memories from the hippocampus to the prefrontal cortex-where long-term memories are stored. This can lead to forgetfulness. Sleep also affects your ability to concentrate. The MSU study also asked participants to take two sets of sleep assessment tests— before the first set of tests, all participants had at least 6 hours of sleep the night before. One test observed how fast they reacted to stimulus, and the second test looked at their placekeeping ability during testing. After the initial test, 77 participants were kept awake all night. The remaining 61 were allowed to go home and get plenty of rest. The next day, those who got insufficient sleep performed much worse on their cognitive tests. For example, the error rate on the placekeeping test jumped from 15 to 30 percent for those who did not get enough rest. For those who got at least 6 hours of sleep the following night, their error rate was essentially unchanged. Related : How To Use Your Sleep Cycle For Your Best Sleep. Following the completion of the above study, one of the MSU researchers insisted that sleep-deprived individuals need to exercise caution in everything that they do, especially if driving cars or using heavy machinery. One study published by Occupational and Environmental Medicine observed 7, workers across a variety of industries for a year to examine the effect chronic sleep deprivation had on them. The results showed a strong link between sleep loss and workplace accidents, with sleep-deprived people being 70 percent more likely to be involved in an accident than those getting sufficient sleep. This built on previous research from the Journal of Sleep Research that observed 50, workers over a two-decade span. This study found that those who suffered from disturbed sleep were twice as likely to die in a work-related accident. Even with the nightly recommended 7 to 9 hours, the effects of sleep deprivation can still pose a threat and may be a symptom of an underlying sleep disorder. If you wake up feeling tired and groggy regardless of how long you slept, and exhibit signs of sleep deprivation throughout the day, you may have an underlying sleep disorder like sleep apnea. People with obstructive sleep apnea experience either a partially blocked or a completely blocked airway during sleep. This blockage creates pauses in your breathing, reducing oxygen levels in your body and preventing deep restful sleep. This leads to chronic sleep deprivation, even if you get enough hours of sleep each night. It can help you make better sense of your symptoms so you can discuss them with your doctor or a sleep specialist. A sleep specialist may recommend an overnight sleep study to evaluate your sleep patterns or a home sleep apnea test to determine whether or not a sleep disorder is causing your sleep deprivation. Getting adequate sleep should not be a challenge— contact us today to get back to the restful, healthy sleep you deserve. Ben Simon, Eti, et al. Anwar, Yasmin. Stepan, Michelle E, et al. Swaen, G M H, et al. Akerstedt, T, et al. National Library of Medicine, Mar. A Real Brain Drain: Sleep Deprivation and Its Effects on The Brain by Sleep Center of Middle Tennessee Last updated Dec 12, Subscribe to receive our top sleep tips. Get better sleep tonight! Search for:. Recent Posts Are There Home Remedies for Sleep Apnea? If you're enjoying this article, consider supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing. By purchasing a subscription you are helping to ensure the future of impactful stories about the discoveries and ideas shaping our world today. Technically sleep starts in the brain areas that produce SWS. Scientists now have concrete evidence that two groups of cells—the ventrolateral preoptic nucleus in the hypothalamus and the parafacial zone in the brain stem—are involved in prompting SWS. When these cells switch on, it triggers a loss of consciousness. After SWS, REM sleep begins. This mode is bizarre: a dreamer's brain becomes highly active while the body's muscles are paralyzed, and breathing and heart rate become erratic. The purpose of REM sleep remains a biological mystery, despite our growing understanding of its biochemistry and neurobiology. We do know that a small group of cells in the brain stem, called the subcoeruleus nucleus, controls REM sleep. When these cells become injured or diseased, people do not experience the muscle paralysis associated with REM sleep, which can lead to REM sleep behavior disorder—a serious condition in which the afflicted violently act out their dreams. September 1, 2 min read. Credit: Todd Warnock Getty Images. |

der Maßgebliche Standpunkt, anziehend
Sie irren sich. Geben Sie wir werden besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden umgehen.
Wieviel auch immer.