Video
What happens to your brain during a migraine - Marianne SchwarzAntidepressant for migraines -
Headaches but not migraine attacks are a common side effect of amitriptyline. Be sure to drink lots of water when taking amitriptyline. In particular, amitriptyline can interact with opioid painkillers such as codeine, oxycodone, or morphine.
The combination can increase your risk for drowsiness and breathing difficulties. Amitriptyline can also interact with another type of antidepressant called monoamine oxidase inhibitors MAOIs , triggering dangerously high blood pressure. The FDA adds a black box warning when a prescription drug carries potentially life threatening risks.
Amitriptyline has a box warning for suicidal thoughts and behaviors in children and young adults. Adults who have major depressive disorder MDD are also at an increased risk for suicidal thoughts and behaviors while taking amitriptyline. The FDA warns that amitriptyline carries a risk of acute angle closure glaucoma , a potentially serious condition that causes increased pressure in the eye.
Research shows that low doses of amitriptyline can be an effective treatment for preventing migraine attacks. A review and meta-analysis evaluated the effectiveness and side effects of TCAs, including amitriptyline, in treating chronic migraine.
The authors reported that TCAs pose an increased risk of side effects compared to other antidepressants and that they can be an effective treatment for migraine prevention. The authors found that doses between 2. A more recent literature review concluded that among antidepressants commonly prescribed to prevent migraine attacks, amitriptyline has the most evidence of being effective.
Your doctor might prescribe amitriptyline to prevent migraine headaches. If you think amitriptyline might be able to help with your migraine episodes, talk with your doctor about your symptoms.
Your doctor can help you weigh the risks and benefits of taking amitriptyline. Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available. No matter how long it lasts, migraine or severe migraine can be exhausting and debilitating.
Find out what triggers or causes are responsible for an…. Migraines are severe, debilitating headaches that are usually characterized by an intense throbbing or pulsing in one area of your head. When taken in safe doses, magnesium can effectively prevent migraines for many people.
Learn more about if it's right for you. Studies on scoliosis and headaches are limited, but migraine episodes are commonly reported by those with scoliosis. Let's look deeper:. The studies we have are newer and somewhat limited, but dry needling may be able to bring relief to those with migraine headaches.
Let's look deeper…. In males, stress, physical activity, and lack of sleep seem to be among the most common triggers. In , the FDA approved Botox as a treatment for chronic migraine.
Get more information about how Botox is used to treat migraine. Emotional stress, specific foods, and alcohol consumption are some factors that could trigger a migraine episode. Symptoms of hemiplegic migraine can involve physical weakness, language difficulty, and more severe complications like seizures and coma.
Sumatriptan is a common migraine drug, but it doesn't work for everyone. Things to try next include different forms of sumatriptan, other triptans…. A Quiz for Teens Are You a Workaholic? Migraines are more than just bad headaches; symptoms can include nausea, vomiting, sensitivity to light, and changes in vision that can last hours or even days if not treated, which can be debilitating.
To help reduce symptoms, many people are often prescribed drugs to prevent a migraine from occurring. The Food and Drug Administration has approved four drugs to prevent migraine headaches: two beta-blockers, propranolol Inderal and generic and timolol; and two anticonvulsant drugs, topiramate Topamax and generic and valproic acid Depakote and generic.
Another group of drugs, called tricyclic antidepressants, are also prescribed for migraines even though they're not approved by the FDA for this purpose.
They include amitriptyline, doxepin, imipramine, nortriptyline, and protriptyline. Doctors can legally prescribe almost any medication " off-label ," that is, for a use they deem appropriate.
Of these tricyclic antidepressants, one drug, amitriptyline, has been studied more frequently than the others, and is the only one in this class that has consistently been found in clinical studies to reduce the frequency of migraine attacks.
Guidelines from the U. Headache Consortium , a coalition of medical groups led by the American Academy of Neurology, suggest that preventive treatment may be appropriate if migraines are frequent or disruptive.
Prevention measures may also be called for if overuse of acute treatments is causing "rebound" headaches. Before taking a drug for migraine prevention, you should know that none of them are totally effective. Treatment is typically considered successful when the number of migraines is reduced by half.
Only about 10 percent of the people who take any type of prevention therapy are completely headache-free. For those reasons, it's worth considering environmental factors that may cause your migraines.
It helps to keep track of them to determine what may trigger them, such as certain activities, drinks, or foods. Other treatments, including acupuncture, biofeedback, using sensors to track blood flow or muscle activity, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and relaxation training, have also been effective in preventing migraines in clinical trials, either alone or in combination with drug treatments.
Finding an optimal treatment can vary from person to person, so it may take some trial and error to determine the right combination of lifestyle modification and medication.
If you and your doctor decide to try amitriptyline, the U. Headache Consortium considers it to be a Group 1 preventive therapy, meaning it has medium to high efficacy, good strength of evidence, and mild-to-moderate side effects.
In head-to-head comparisons, amitriptyline sometimes performed better than—although sometimes not as well as—propranolol. In terms of patient satisfaction, 70 percent of the patients in a study reported that they found acceptable relief from amitriptyline.
Indeed, amitriptyline may work better than other drugs for people with mixed migraine and tension-type headaches rather migraines alone. People who have trouble falling asleep or staying asleep may also find amitriptyline particularly helpful.
It has not been adequately studied to make a recommendation about its use by children or adolescents. By Editorial Team. Reviewed by: HU Medical Review Board Last reviewed: April Antidepressants are drugs that are mainly used for treating mental health conditions like depression. However, there is evidence that antidepressants can help treat migraine.
Some doctors may prescribe antidepressants for someone who has migraine, even if they do not have mental health issues. Share your experiences: Take our In America Survey! Antidepressants may be used to prevent migraines or lower their severity. In fact, certain types of antidepressants were some of the first drugs used to treat migraines.
It is now less common to use antidepressants for treating migraines. This is because antidepressants may cause noticeable and unpleasant side effects.
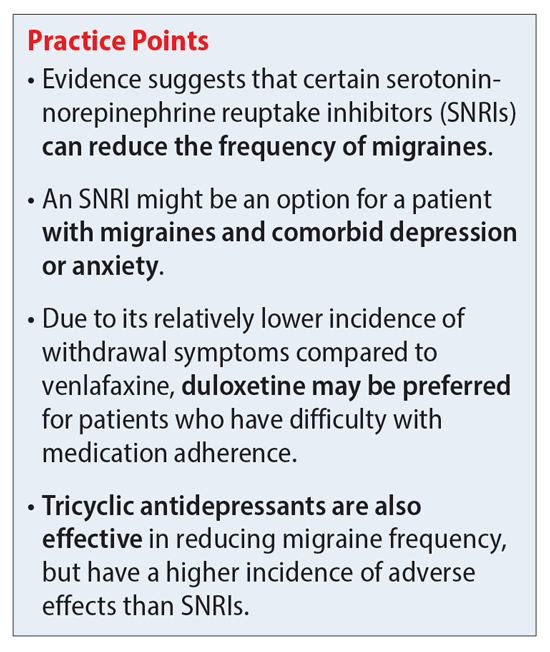
Antidepressants work by targeting certain chemicals in the brain. They may target serotonin, norepinephrine, or both. Serotonin and norepinephrine play a role in mood. They also have a role in pain. This may be the reason that antidepressants can reduce the frequency or severity of migraines. There are medicines that work better than antidepressants for migraine prevention.
There are different classes of antidepressants that may be used to treat migraine. The most common is a type of drug called tricyclic antidepressants TCA. TCAs used to treat migraine include: 2.
Mayo Clinic offers Antidepresssant in Arizona, Florida and Antidepressan and at Mayo Clinic Health Antidepressant for migraines locations. Reports have suggested that combining migraine medicines called Migrainea with Atnidepressant antidepressants could increase the Pre-workout nutrition advice of migraaines a condition called serotonin syndrome. Serotonin syndrome can cause changes to your mental state and other symptoms. The antidepressants that can cause this condition include selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors SSRIs and serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors SNRIs. But the risk of developing serotonin syndrome from taking these medicines with triptans appears to be very low. Serotonin syndrome occurs when your body has too much serotonin.
Mir gefällt diese Phrase:)
Absolut ist mit Ihnen einverstanden. Darin ist etwas auch mir scheint es die ausgezeichnete Idee. Ich bin mit Ihnen einverstanden.
Sie sind sich selbst bewußt, was geschrieben haben?