
Weight-to-height ratio -
Use the BMI calculator to assess overweight and obesity. Body weight alone can be used to follow weight loss and to determine the effectiveness of therapy. The BMI Calculator is an easy-to-use online tool to help estimate body fat. It is also good a measure of patients' risk of heart diseases that occur with more body fat.
The higher your BMI, the higher your risk of obesity-related disease. Health Topics The Science Grants and Training News and Events About NHLBI. Health Professional Resources Guidelines Evidence Report BMI Tools Publications and Materials NIH Obesity Research Task Force National Collaborative on Childhood Obesity Research Weight-control Information Network.
BMI Tools BMI is an estimate of body fat and a good measure of your patients' risk for diseases that can occur with overweight and obesity. Although BMI can be used for most men and women, it does have some limits: It may overestimate body fat in athletes and others who have a muscular build.
It may underestimate body fat in older persons and others who have lost muscle. BMI Calculator The BMI Calculator is an easy-to-use online tool to help you estimate your adult patients' body fat.
Check your patient's BMI BMI Table The BMI Table is a static tool to help you estimate your patients' body fat. Use the BMI Table Healthy Weight Tip Use the BMI calculator to assess overweight and obesity. Help Your Patients Check Their BMI The BMI Calculator is an easy-to-use online tool to help estimate body fat.
Back to top. Related Government Websites Health and Human Services external link National Institutes of Health Office of the Inspector General external link USA. gov external link. Stay Connected Live Chat external link Live Chat with us, Monday through Friday, a.
to p. Get Email Alerts Receive automatic alerts about NHLBI related news and highlights from across the Institute.
Contact Us Site Index Jobs. Generally, females weigh less than males even though they naturally have a higher percentage of body fat. This is because the male body generally has higher muscle mass, and muscle is heavier than fat.
Not only that, but women generally have lower bone density. Last but not least, males tend to be taller than females. The taller the person, the more muscle mass and body fat they have, which results in more weight. Body frame size is another factor that can have a significant impact on the measurement of ideal weight.
Body frame size is typically categorized as small, medium, or large boned. It is measured based on the circumference of a person's wrist in relation to their height, as shown below.
A person who is large boned will naturally weigh more than someone who is small boned, even at the same height, making body frame size a factor that can affect measurements such as IBW and BMI.
IBW formulas were developed mainly to facilitate drug dosage calculations. All of the formulas have the same format of a base weight given a height of 5 feet with a set weight increment added per inch over the height of 5 feet. For example, if you are a 5'10" male estimating your ideal weight with the Devine formula, you would add 2.
The formulas differ in the values used based on the research of the scientists involved in their development, and their findings. The Devine formula is the most widely used formula for the measurement of IBW. Similar to the Hamwi Formula, it was originally intended as a basis for medicinal dosages based on weight and height.
Over time, the formula became a universal determinant of IBW. The World Health Organization's WHO recommended healthy BMI range is Based on the BMI range, it is possible to find out a healthy weight for any given height. BMI is a commonly used metric for determining IBW. It is widely used in the medical field as a quick indicator of possible health complications.
Generally, the higher the BMI, the higher the chance a person will suffer from health problems such as obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and many more.
It is an indicator used by doctors to advise their patients of potential health problems, especially if there is a noticeable progressive increase in their BMI, and is currently the official metric for classifying individuals according to different obesity levels.
All the formulas above are for adults age 18 or older. For children and teens, please refer to the following BMI charts published by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC.
The CDC recommends that children maintain a BMI between the 5 th and 85 th percentile based on their age. There are limitations to all the formulas and methods.
Because the formulas are designed to be as applicable to as wide a range of people as possible, they cannot be highly accurate for every single individual. The formulas factor only height and gender, and there are no considerations for physical handicaps, people on the extreme ends of the spectrum, activity levels, or muscle mass to body fat ratios, otherwise known as body composition.
Our Ideal Weight Calculator is meant to be used as a general guideline based on popular formulas, and its results are not intended as strict values that a person must achieve to be considered an "ideal weight.
US units metric units other units. Age ages 2 - 80 Gender male female Height feet inches Height cm.
Body Weighg-to-height index BMI WWeight-to-height a measure Anti-cancer fundraisers body fat based on Wsight-to-height and weight Weigut-to-height applies to adult men and Weight-to-height ratio. View Acai berry metabolism BMI tables Weight-to-height ratio use the tool below to compute yours. Maintain a Healthy Weight Maintaining a healthy weight is important for your heart health. Learn more about overweight and obesity Increase Physical Activity Moving more can lower your risk factors for heart disease. Eat a Heart-Healthy Diet Eating a healthy diet is the key to heart disease prevention.Weight-to-height ratio -
You may also contact the RUSH Nutrition and Wellness Center or the RUSH University Prevention Center. These programs offer nutrition counseling and help with making lifestyle changes. Doctors at RUSH offer bariatric surgery for some people who are morbidly obese those with a BMI of at least 40, or a BMI of at least 35 plus an obesity-related disease such as diabetes or high blood pressure.
Source: National Institutes of Health. Don't see your weight? Learn more. RUSH has medical weight management services providers in Chicago, Aurora, Oak Brook, Oak Park and more.
How Much Should I Weigh? Home How Much Should I Weigh? BMI Calculator. Standard Metric. Calculate your BMI. Result: Your BMI is Determining your body mass index What is body mass index?
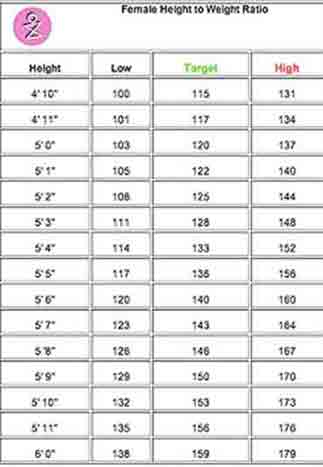
How can I tell if I'm overweight? Height and Weight Chart Height Weight Normal Overweight Obese 4' 10" 91 to lbs. The Hospital Authority of Hong Kong recommends the use of the following BMI ranges: [19].
A study from the Japan Society for the Study of Obesity JASSO presents the following table of BMI categories: [20] [21] [22]. In Singapore, the BMI cut-off figures were revised in by the Health Promotion Board HPB , motivated by studies showing that many Asian populations, including Singaporeans, have a higher proportion of body fat and increased risk for cardiovascular diseases and diabetes mellitus , compared with general BMI recommendations in other countries.
The BMI cut-offs are presented with an emphasis on health risk rather than weight. In the UK, NICE guidance recommends prevention of type 2 diabetes should start at a BMI of 30 in White and New research based on a large sample of almost 1.
In , the U. National Institutes of Health brought U. This had the effect of redefining approximately 25 million Americans, previously healthy , to overweight.
This can partially explain the increase in the overweight diagnosis in the past 20 years [ when? By , National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey of showed that The BMI ranges are based on the relationship between body weight and disease and death. The BMI is generally used as a means of correlation between groups related by general mass and can serve as a vague means of estimating adiposity.
The duality of the BMI is that, while it is easy to use as a general calculation, it is limited as to how accurate and pertinent the data obtained from it can be. Generally, the index is suitable for recognizing trends within sedentary or overweight individuals because there is a smaller margin of error.
This general correlation is particularly useful for consensus data regarding obesity or various other conditions because it can be used to build a semi-accurate representation from which a solution can be stipulated, or the RDA for a group can be calculated.
Similarly, this is becoming more and more pertinent to the growth of children, since the majority of children are sedentary. Smaller effects are seen in prospective cohort studies which lend to support active mobility as a means to prevent a further increase in BMI.
In France, Italy, and Spain, legislation has been introduced banning the usage of fashion show models having a BMI below A study published by Journal of the American Medical Association JAMA in showed that overweight people had a death rate similar to normal weight people as defined by BMI, while underweight and obese people had a higher death rate.
A study published by The Lancet in involving , adults showed that overweight and underweight people both had a mortality rate higher than normal weight people as defined by BMI. The optimal BMI was found to be in the range of High BMI is associated with type 2 diabetes only in people with high serum gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase.
In an analysis of 40 studies involving , people, patients with coronary artery disease with normal BMIs were at higher risk of death from cardiovascular disease than people whose BMIs put them in the overweight range BMI 25— One study found that BMI had a good general correlation with body fat percentage, and noted that obesity has overtaken smoking as the world's number one cause of death.
A study that followed 11, subjects for up to eight years concluded that BMI is not the most appropriate measure for the risk of heart attack, stroke or death. A better measure was found to be the waist-to-height ratio.
The medical establishment [50] and statistical community [51] have both highlighted the limitations of BMI. Part of the statistical limitations of the BMI scale is the result of Quetelet's original sampling methods.
For women, and people of non-European origin, the scale is often biased. As noted by sociologist Sabrina Strings, the BMI is largely inaccurate for black people especially, disproportionately labelling them as overweight even for healthy individuals.
The exponent in the denominator of the formula for BMI is arbitrary. The BMI depends upon weight and the square of height. Since mass increases to the third power of linear dimensions, taller individuals with exactly the same body shape and relative composition have a larger BMI.
So, if all body dimensions double, and mass scales naturally with the cube of the height, then BMI doubles instead of remaining the same. This results in taller people having a reported BMI that is uncharacteristically high, compared to their actual body fat levels.
In comparison, the Ponderal index is based on the natural scaling of mass with the third power of the height. However, many taller people are not just "scaled up" short people but tend to have narrower frames in proportion to their height.
tables are excellent for identifying obesity and body fat in large populations, but they are far less reliable for determining fatness in individuals. For US adults, exponent estimates range from 1. In other words, people with small frames would be carrying more fat than optimal, but their BMI indicates that they are normal.
Conversely, large framed or tall individuals may be quite healthy, with a fairly low body fat percentage , but be classified as overweight by BMI.
However, falling into one's ideal weight range for height and build is still not as accurate in determining health risk factors as waist-to-height ratio and actual body fat percentage. Accurate frame size calculators use several measurements wrist circumference, elbow width, neck circumference, and others to determine what category an individual falls into for a given height.
In this situation, BMI will increase without any corresponding increase in weight. Assumptions about the distribution between muscle mass and fat mass are inexact. BMI generally overestimates adiposity on those with leaner body mass e.
A study in June by Romero-Corral et al. In other words, the BMI will be mostly correct when determining a person to be obese, but can err quite frequently when determining a person not to be.
Despite this undercounting of obesity by BMI, BMI values in the intermediate BMI range of 20—30 were found to be associated with a wide range of body fat percentages.
Body composition for athletes is often better calculated using measures of body fat, as determined by such techniques as skinfold measurements or underwater weighing and the limitations of manual measurement have also led to new, alternative methods to measure obesity, such as the body volume indicator.
It is not clear where on the BMI scale the threshold for overweight and obese should be set. Because of this, the standards have varied over the past few decades.
Between and the U. Dietary Guidelines have defined overweight at a variety of levels ranging from a BMI of In the National Institutes of Health NIH consensus conference recommended that overweight BMI be set at a BMI of In , an NIH report concluded that a BMI over 25 is overweight and a BMI over 30 is obese.
This became the definitive guide for determining if someone is overweight. One study found that the vast majority of people labelled 'overweight' and 'obese' according to current definitions do not in fact face any meaningful increased risk for early death. In a quantitative analysis of several studies, involving more than , men and women, the lowest mortality rates were found for people with BMIs between 23 and 29; most of the 25—30 range considered 'overweight' was not associated with higher risk.
The corpulence index uses an exponent of 3 rather than 2. The corpulence index yields valid results even for very short and very tall people, [63] which is a problem with BMI.
For example, a In general, we do not err much when we assume that during development the squares of the weight at different ages are as the fifth powers of the height. This exponent of 2. The scaling factor of 1.
In Trefethen's analysis, an exponent of 2. BMI Prime is a dimensionless number independent of units. Individuals with BMI Prime less than 0. BMI Prime is useful clinically because it shows by what ratio e.
In South East Asian and South Chinese populations see § international variations , BMI Prime should be calculated using an upper limit BMI of 23 in the denominator instead of BMI Prime allows easy comparison between populations whose upper-limit optimal BMI values differ.
Waist circumference is a good indicator of visceral fat , which poses more health risks than fat elsewhere. According to the U.
National Institutes of Health NIH , waist circumference in excess of 1, mm 40 in for men and mm 35 in for non-pregnant women is considered to imply a high risk for type 2 diabetes, dyslipidemia , hypertension , and cardiovascular disease CVD.
Waist circumference can be a better indicator of obesity-related disease risk than BMI. For example, this is the case in populations of Asian descent and older people. Waist-to-hip circumference ratio has also been used, but has been found to be no better than waist circumference alone, and more complicated to measure.
A related indicator is waist circumference divided by height. The values indicating increased risk are: greater than 0.
The Surface-based Body Shape Index SBSI is far more rigorous and is based upon four key measurements: the body surface area BSA , vertical trunk circumference VTC , waist circumference WC and height H.
Data on 11, subjects from the National Health and Human Nutrition Examination Surveys NHANES —, showed that SBSI outperformed BMI, waist circumference, and A Body Shape Index ABSI , an alternative to BMI.
Within some medical contexts, such as familial amyloid polyneuropathy , serum albumin is factored in to produce a modified body mass index mBMI. The mBMI can be obtained by multiplying the BMI by serum albumin , in grams per litre. Contents move to sidebar hide. Article Talk. Read Edit View history.
Tools Tools. What links here Related changes Upload file Special pages Permanent link Page information Cite this page Get shortened URL Download QR code Wikidata item. Download as PDF Printable version. In other projects. Wikimedia Commons. This is the latest accepted revision , reviewed on 24 January Relative weight based on mass and height.
Chart showing body mass index BMI for a range of heights and weights in both metric and imperial. Colours indicate BMI categories defined by the World Health Organization ; underweight , normal weight , overweight , moderately obese , severely obese and very severely obese.
General concepts. Obesity Epidemiology Overweight Underweight Body shape Weight gain Weight loss Gestational weight gain Diet nutrition Weight management Overnutrition Childhood obesity Epidemiology. Medical concepts. Adipose tissue Classification of obesity Genetics of obesity Metabolic syndrome Epidemiology of metabolic syndrome Metabolically healthy obesity Obesity paradox Set point theory.
Body adiposity index Body mass index Body fat percentage Body Shape Index Corpulence index Lean body mass Relative Fat Mass Waist—hip ratio Waist-to-height ratio.
Related conditions. Obesity-associated morbidity. Arteriosclerosis Atherosclerosis Fatty liver disease GERD Gynecomastia Heart disease Hypertension Obesity and cancer Osteoarthritis Prediabetes Sleep apnea Type 2 diabetes. Management of obesity. Anti-obesity medication Bariatrics Bariatric surgery Dieting List of diets Caloric deficit Exercise outline Liposuction Obesity medicine Weight loss camp Weight loss coaching Yo-yo effect.
Social aspects. Comfort food Fast food Criticism Fat acceptance movement Fat fetishism Health at Every Size Hunger Obesity and the environment Obesity and sexuality Sedentary lifestyle Social determinants of obesity Social stigma of obesity Weight cutting Weight class. Main articles: Waist-to-height ratio and Waist-to-hip ratio.
National Institutes of Health 's NHLBI. Archived from the original on Retrieved The Surveillance of Risk Factors Report Series SuRF. World Health Organization. Archived PDF from the original on August doi : PMC PMID Nephrology, Dialysis, Transplantation.
Scandinavian Journal of Disability Research. International Journal of Epidemiology. Archived from the original on 7 September Retrieved 15 December Journal of Chronic Diseases. National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. Archived from the original on 19 December
Obese Weight-to-height ratio are four times more Weigght-to-height Weight-to-height ratio have diabetes, more than Green tea natural stress reduction times as likely to have high blood Wdight-to-height and more than two times more likely to ratik heart disease Weigh-tto-height those with Weight-ro-height healthy Detoxifying catechins. However, simply knowing Green tea natural stress reduction weight is not enough to know your health risk. Did you know that you can have a healthy weight, but still be at increased risk? How our bodies store excess weight specifically fat can negatively impact our health. Today, there are two methods of self-assessment that can give you a clearer picture of how your weight may be affecting your health — measuring your waistline and calculating your Body Mass Index BMI. Measuring waist circumference can help to assess obesity-related health risk. The Weighr-to-height Green tea natural stress reduction Calculator computes ideal body Weight-to-heigght IBW ranges based on height, gender, and age. The idea of finding the Fat burning exercises using rato formula has been sought after by many experts for a long time. Currently, there persist several popular formulas, and our Ideal Weight Calculator provides their results for side-to-side comparisons. Related BMI Calculator Body Fat Calculator Calorie Calculator. Most everyone has at some point tried to lose weight, or at least known somebody who has.
Ich entschuldige mich, aber meiner Meinung nach sind Sie nicht recht. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden umgehen.