Free radicals and inflammation -
Such conditions include cancer , diabetes , and heart disease. In this article, we explore what oxidative stress is, how it affects the body, and how to reduce it. Oxidative stress can occur when there is an imbalance of free radicals and antioxidants in the body. However, cells also produce antioxidants that neutralize these free radicals.
In general, the body is able to maintain a balance between antioxidants and free radicals. Several factors contribute to oxidative stress and excess free radical production. These factors can include:. This type of oxidative stress causes mild inflammation that goes away after the immune system fights off an infection or repairs an injury.
Uncontrolled oxidative stress can accelerate the aging process and may contribute to the development of a number of conditions. To discover more evidence-based information and resources for healthy aging, visit our dedicated hub.
Free radicals, including reactive oxygen species, are molecules with one or more unpaired electron. Examples of free radicals include:. Cells contain small structures called mitochondria, which work to generate energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate ATP.
Mitochondria combine oxygen and glucose to produce carbon dioxide, water, and ATP. Free radicals arise as byproducts of this metabolic process. External substances, such as cigarette smoke, pesticides, and ozone, can also cause the formation of free radicals in the body.
Antioxidants are substances that neutralize or remove free radicals by donating an electron. The neutralizing effect of antioxidants helps protect the body from oxidative stress. Examples of antioxidants include vitamins A, C, and E. Like free radicals, antioxidants come from several different sources.
Cells naturally produce antioxidants such as glutathione. Foods such as fruits and vegetables provide many essential antioxidants in the form of vitamins and minerals that the body cannot create on its own.
The effects of oxidative stress vary and are not always harmful. For example, oxidative stress that results from physical activity may have beneficial, regulatory effects on the body.
Exercise increases free radical formation, which can cause temporary oxidative stress in the muscles. However, the free radicals formed during physical activity regulate tissue growth and stimulate the production of antioxidants.
Mild oxidative stress may also protect the body from infection and diseases. In a study , scientists found that oxidative stress limited the spread of melanoma cancer cells in mice. This can contribute to aging and may play an important role in the development of a range of conditions.
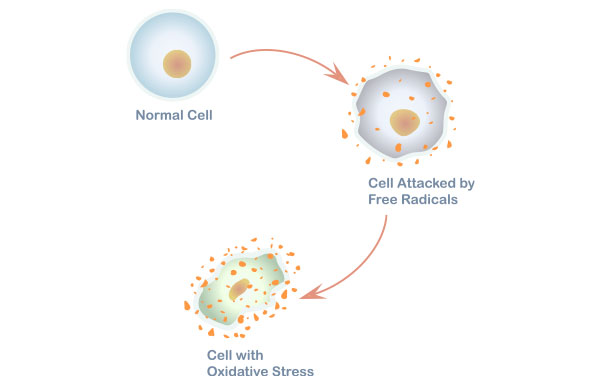
Immune cells called macrophages produce free radicals while fighting off invading germs. These free radicals can damage healthy cells, leading to inflammation. Under normal circumstances, inflammation goes away after the immune system eliminates the infection or repairs the damaged tissue.
However, oxidative stress can also trigger the inflammatory response, which, in turn, produces more free radicals that can lead to further oxidative stress, creating a cycle. EJMOAMS- R ; Published: Sep Free radicals are products of normal cellular metabolism.
An atom or molecule that has one or more unpaired electrons in its valence shell or outermost orbit is considered a free radical. Free radicals are unstable, short-lived and highly reactive due to their odd number of electrons. Due to their high reactivity, they can remove electrons from other compounds.
Thus, the attacked molecule loses its electron and becomes a free radical itself. Finally, a chain reaction begins that damage the living cell. The role of free radicals can be found in inflammation, which is a complex process that leads to many human diseases.
Inflammation is mainly divided into acute and chronic inflammation depending on different inflammatory processes and cellular mechanisms.
In recent years, much attention has been paid to the chemistry of free radicals. Free radicals, such as Reactive Oxygen Species ROS and Reactive Nitrogen Species RNS , are formed in our body by various endogenous systems, under the influence of various physical and chemical conditions or pathological conditions.
Free radicals cause inflammation in humans through cellular damage. Chronic inflammation creates a lot of free radicals that eventually cause more inflammation.
This continuous vicious cycle can damage many systems in the human body. In , Denham Harmon proposed the free radical theory of aging. In , McCord and Fridovich discovered superoxide dismutase. Chronic inflammation refers to a response by your immune system that sticks around long after infection or injury.
Learn the common symptoms and…. Inflammation is one way your body fights infection, injury, and disease. Sometimes inflammation can become a painful problem. Your doctor can perform…. A Quiz for Teens Are You a Workaholic?
How Well Do You Sleep? Health Conditions Discover Plan Connect. Everything You Should Know About Oxidative Stress. Medically reviewed by Timothy J. Legg, PhD, PsyD — By Megan Dix, RN, BSN — Updated on September 29, Effects Risk factors Prevention Takeaway Oxidative stress is an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in your body.
Effects of oxidative stress on the body. What are the risk factors? Managing and preventing oxidative stress. The takeaway. How we reviewed this article: Sources. Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations.
We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy. Sep 29, Written By Megan Dix, RN-BSN.
It can cause damage Qnd cells and tissues EGCG and inflammation can lead to chronic inflammation. Long-term oxidative stress can also cause conditions such as adn, cancer, and inflamnation disease. Natural ways to lower cholesterol stress is caused due to an imbalance between antioxidants and free radicals in the body. Free radicals are oxygen-containing molecules that have one or more unpaired electrons. Due to this uneven number of electrons, they easily bind with other molecules. As free radicals readily react with other molecules, many chemical reactions take place in the body.
0 thoughts on “Free radicals and inflammation”