
Normal glycemic levels -
This soon goes away. Your health care provider may order this test if you have signs of diabetes. More than likely, the provider will order a fasting blood sugar test.
High blood sugar and diabetes may not cause symptoms in the early stages. A fasting blood sugar test is the most common test done to screen for diabetes, usually starting at age If you have no other diabetes risk factors, you should be tested every 3 years in some cases, more often if your weight is rising.
If you're overweight and have any of the other risk factors below, ask your provider about getting tested at an earlier age and more often:. Children age 10 and older who are overweight and have at least two of the risk factors listed above should be tested for type 2 diabetes every 3 years, even if they have no symptoms.
If you had a random blood glucose test, a normal result depends on when you last ate. The examples above show the common measurements for results of these tests. Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Some labs use different measurements or may test different specimens.
Talk to your provider about the meaning of your specific test results. Blood glucose measured by a blood test from a vein is considered more accurate than blood glucose measured from a fingerstick with a blood glucose meter, or blood glucose measured by a continuous glucose monitor.
A lower-than-normal blood glucose level hypoglycemia may be due to:. Some medicines can raise or lower your blood glucose level. Before having the test, tell your provider about all the medicines you are taking. There is little risk involved with having your blood taken.
Veins and arteries vary in size from one person to another and from one side of the body to the other. Obtaining a blood sample from some people may be more difficult than from others.
Asbestos and Lung Cancer Cervical Cancer Ovarian Cancer Colon Cancer Genetic Testing Testicular Cancer Screening Skin Cancer: Protecting Your Skin Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer: Comparing Treatments Bladder Cancer Prostate Cancer, Advanced or Metastatic Active Surveillance for Prostate Cancer Urinary Problems and Prostate Cancer Cancer: Controlling Cancer Pain Heat and Cold Treatment for Cancer Pain Testicular Cancer Testicular Cancer: Which Treatment Should I Have for Stage I Non-Seminoma Testicular Cancer After My Surgery?
Testicular Cancer: Which Treatment Should I Have for Stage I Seminoma Testicular Cancer After My Surgery? Cancer: Controlling Nausea and Vomiting From Chemotherapy Lymphedema: Managing Lymphedema Breast Cancer Risk: Should I Have a BRCA Gene Test? Inflammatory Breast Cancer Ovarian Cancer: Should I Have My Ovaries Removed to Prevent Ovarian Cancer?
Family History and the Risk for Breast or Ovarian Cancer Breast Cancer: What Should I Do if I'm at High Risk? Difference Between Influenza Flu and a Cold Colds and Flu Influenza Flu Complications Flu Vaccine Myths Influenza Seasonal Flu Whooping Cough Pertussis Productive Coughs Dry Coughs Influenza Flu : Should I Take Antiviral Medicine?
Flu Vaccines: Should I Get a Flu Vaccine? Relieving A Cough Colds. Cal's Story: Learning to Exercise When You have COPD Conserving Energy When You Have COPD or Other Chronic Conditions Nebulizer for COPD Treatment COPD Action Plan COPD: Help for Caregivers COPD: Keeping Your Diet Healthy COPD: Using Exercise to Feel Better COPD COPD Flare-Ups Bullectomy for COPD COPD and Alpha-1 Antitrypsin AAT Deficiency COPD and Sex Pulmonary Rehabilitation for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease COPD COPD Oxygen Treatment for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease COPD COPD: Avoiding Weight Loss COPD: Avoiding Your Triggers.
Alzheimer's or Other Dementia: Should I Move My Relative Into Long-Term Care? Alzheimer's and Other Dementias: Coping With Sundowning Dementia: Assessing Pain Medical History and Physical Examination for Dementia or Alzheimer's Disease Alzheimer's and Other Dementias: Making the Most of Remaining Abilities Dementia: Helping a Person Avoid Confusion Alzheimer's and Other Dementias: Maintaining Good Nutrition Dementia: Tips for Communicating Agitation and Dementia Dementia: Bladder and Bowel Problems Dementia: Support for Caregivers Dementia: Legal Issues Dementia: Understanding Behaviour Changes Dementia: Medicines to Treat Behaviour Changes Dementia Mild Cognitive Impairment and Dementia.
Diabetes: Blood Sugar Levels Diabetes: Counting Carbs if You Don't Use Insulin Diabetes: Coping With Your Feelings About Your Diet Diabetes: Tracking My Feelings Diabetes: Taking Care of Your Feet Diabetes: Care of Blood Sugar Test Supplies Diabetes: Checking Your Blood Sugar Diabetes: Checking Your Feet Diabetes: Steps for Foot-Washing Diabetes: Protecting Your Feet Diabetes: Dealing With Low Blood Sugar From Medicines Diabetes: Dealing With Low Blood Sugar From Insulin Diabetes: How to Give Glucagon Low Blood Sugar Level Record Symptoms of Low Blood Sugar Diabetes: Preventing High Blood Sugar Emergencies Diabetic Ketoacidosis DKA High Blood Sugar Level Record Symptoms of High Blood Sugar Diabetes: Using a Plate Format to Plan Meals Diabetes: Giving Yourself an Insulin Shot Diabetes: Eating Low-Glycemic Foods Diabetes and Alcohol Continuous Glucose Monitoring Quick Tips: Diabetes and Shift Work Diabetes: How to Prepare for a Colonoscopy Type 2 Diabetes: Can You Cure It?
Diabetes, Type 2: Should I Take Insulin? Prediabetes: Which Treatment Should I Use to Prevent Type 2 Diabetes? Diabetes: Living With an Insulin Pump Form for Carbohydrate Counting.
Autism Down Syndrome: Helping Your Child Eat Independently Down Syndrome: Grooming and Hygiene Down Syndrome: Helping Your Child Learn to Walk and Use Other Motor Skills Down Syndrome: Helping Your Child Learn to Communicate Down Syndrome Dyslexia Conditions Related to Dyslexia Autism: Behavioural Training and Management Autism: Support and Training for the Family Unproven Treatments for Autism Caring for Adults With Autism Down Syndrome: Helping Your Child Avoid Social Problems Down Syndrome: Training and Therapy for Young People Down Syndrome: Helping Your Child Dress Independently Down Syndrome, Ages Birth to 1 Month Down Syndrome, Ages 1 Month to 1 Year Down Syndrome, Ages 1 to 5 Down Syndrome, Ages 5 to 13 Down Syndrome, Ages 13 to Anorexia: Learning New Eating Behaviours Anorexia: Learning to Trust Others Binge Eating Disorder Bulimia Nervosa Eating Disorders: Cultural and Social Factors Eating Disorders: Feeling Better About Yourself Eating Disorders: Malnutrition Tests Eating Disorders: Things That Put a Person at Risk.
Absence Epilepsy Juvenile Myoclonic Epilepsy Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Focal Epilepsy Epilepsy: Simple Partial Seizures Epilepsy Epilepsy and Driving Epilepsy: Generalized Seizures Epilepsy: Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizures Epilepsy: Myoclonic Seizures Epilepsy: Atonic Seizures Epilepsy: Tonic Seizures Epilepsy: Complex Partial Seizures Epilepsy Medicine Therapy Failure Stopping Medicine for Epilepsy Questions About Medicines for Epilepsy Epilepsy: Taking Your Medicines Properly.
Sleep Apnea: Should I Have a Sleep Study? Peripheral Arterial Disease of the Legs Bradycardia Slow Heart Rate Types of Bradycardia Cardiac Device Monitoring Angioplasty for Peripheral Arterial Disease of the Legs Isolated Systolic High Blood Pressure Atrial Fibrillation: Should I Try Electrical Cardioversion?
Change in Heartbeat Deep Vein Thrombosis Fast Heart Rate Heart Failure: Symptom Record Heart Failure: Compensation by the Heart and Body Heart Failure: Taking Medicines Properly Heart Failure: Watching Your Fluids Heart Failure: Avoiding Triggers for Sudden Heart Failure Heart Failure: Activity and Exercise Heart Tests: When Do You Need Them?
Low Blood Pressure Hypotension Cardiac Arrest Heart Failure Daily Action Plan Premature Ventricular Contractions PVCs Heart Rate Problems: Should I Get a Pacemaker? Heart Rhythm Problems: Should I Get an Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator ICD?
What to Do if Your Cardiac Device Is Recalled Venous Insufficiency Carotid Artery Stenting ICD: Living Well With It Diabetes: Lower Your Risk for Heart Attack and Stroke Pacemaker for Heart Failure Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Heart Attack: How to Prevent Another One Stroke: How to Prevent Another One Sex and Your Heart Supraventricular Tachycardia: Should I Have Catheter Ablation?
Acute Coronary Syndrome Aspirin: Should I Take Daily Aspirin to Prevent a Heart Attack or Stroke? Heart Failure: Should I Get a Pacemaker?
Heart Failure: Should I Get an Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator ICD? Heart Valve Disease Myxoma Tumours of the Heart Aortic Dissection Heart Attack and Stroke Risk Screening High Blood Pressure: Checking Your Blood Pressure at Home Hypertensive Emergency Stroke Rehabilitation Treatment for Stroke-Related Spasticity Driving a Car After a Stroke Heart Failure: Avoiding Medicines That Make Symptoms Worse Stroke Recovery: Coping With Eating Problems Heart Murmur High Blood Pressure: Should I Take Medicine?
Coronary Artery Disease: Should I Have Angioplasty for Stable Angina? Tyrell's Story: Taking Pills for High Blood Pressure Stroke Prevention: Should I Have a Carotid Artery Procedure? Atrial Fibrillation: Which Anticoagulant Should I Take to Prevent Stroke? Stroke: Should I Move My Loved One Into Long-Term Care?
Atrial Fibrillation: Should I Take an Anticoagulant to Prevent Stroke? Smoking and Coronary Artery Disease. Hepatitis C: Your Risk for Cirrhosis Hepatitis E Hepatitis B Immune Globulin - Injection Heparin - Injection Fulminant Hepatitis Protect Yourself From Hepatitis A When Travelling Hepatitis A Viral Hepatitis Hepatitis C Hepatitis D Hepatitis B: How to Avoid Spreading the Virus Hepatitis B Hepatitis Panel Hepatitis B Treatment Recommendations Hepatitis B: Should I Be Tested?
HIV Infection HIV Viral Load HIV: Stages of Infection Ways HIV Cannot Be Spread HIV and Exercise HIV: Giving Support HIV: Tips for Caregivers to Avoid Infection HIV: Preventing Other Infections When You Have HIV HIV Home Care Antiretroviral medicines for HIV Resistance to HIV Medicines HIV: Preventing Infections HIV: Antiretroviral Therapy ART Opportunistic Infections in HIV HIV: Taking Antiretroviral Drugs HIV: Non-Progressors and HIV-Resistant People HIV Screening HIV and Weight Loss HIV and Fatigue.
Anthrax Avian Influenza Avoiding Infections in the Hospital Bacterial Infections of the Spine Bites and Stings: Flu-Like Symptoms Boric Acid for Vaginal Yeast Infection Caregiving: Reducing Germs and Infection in the Home Central Venous Catheter: Flushing Chickenpox Varicella Chickenpox: Preventing Skin Infections Chikungunya Fever Complicated Urinary Tract Infections Complications of Ear Infections Cranberry Juice and Urinary Tract Infections Dengue Fever Ear Infection: Should I Give My Child Antibiotics?
Ear Infections Ebola or Marburg Virus Infection Ebola Virus Disease Enterovirus D68 EV-D68 Fever or Chills, Age 11 and Younger Fever or Chills, Age 12 and Older Fever Seizures Fever Temperatures: Accuracy and Comparison Feverfew for Migraines Fifth Disease Flu: Signs of Bacterial Infection Fungal Nail Infections Giardiasis Hand-Foot-and-Mouth Disease Kissing Bugs Measles Rubeola Middle East Respiratory Syndrome MERS Molluscum Contagiosum Monkeypox Mononucleosis Mono Mononucleosis Complications Mumps Nail Infection: Should I Take Antifungal Pills?
Neutropenia: Preventing Infections Non-Surgical Nail Removal for Fungal Nail Infections Noroviruses Pleurisy Pneumonia Preventing Tetanus Infections Pseudomonas Infection Recurrent Ear Infections and Persistent Effusion Recurrent Vaginal Yeast Infections Respiratory Syncytial Virus RSV Infection Rotavirus Rubella German Measles Scarlet Fever Sexually Transmitted Infections Sexually Transmitted Infections: Genital Examination for Men Sexually Transmitted Infections: Symptoms in Women Sexually Transmitted Infections: Treatment Shingles Smallpox Sore Throat and Other Throat Problems Staph Infection Strep Throat Symptoms of Pelvic Infection Thrush Tick Bites: Flu-Like Symptoms Tinea Versicolor Tuberculosis TB Tuberculosis Screening Urinary Tract Infections UTIs in Older Adults Vaginal Yeast Infection: Should I Treat It Myself?
Vaginal Yeast Infections Valley Fever West Nile Virus Zika Virus. Broken Collarbone Clavicle Shoulder Separation Frozen Shoulder Preventing ACL Injuries Living With a Spinal Cord Injury Classification of Spinal Cord Injuries Tendon Injury Tendinopathy Shin Splints Muscle Cramps Whiplash Fractured Rib.
Osteochondritis Dissecans of a Joint Back to Work? Acute Kidney Injury Versus Chronic Kidney Disease Nephrotic Syndrome Uremia Kidney Stones: Should I Have Lithotripsy to Break Up the Stone?
Chronic Kidney Disease Kidney Failure: When Should I Start Dialysis? Kidney Failure: Should I Start Dialysis? Anemia of Chronic Kidney Disease End-Stage Kidney Failure Tolvaptan Inherited Kidney Disease - Oral Types of Kidney Stones Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy ESWL for Kidney Stones Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy or Nephrolithotripsy for Kidney Stones Kidney Stones Advance Care Planning: Should I Stop Kidney Dialysis?
Kidney Disease: Medicines to Avoid Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease Medicines That Can Cause Acute Kidney Injury Donating a Kidney Kidney Stones: Medicines That Increase Your Risk. Breathing Problems: Using a Metered-Dose Inhaler Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome ARDS Bronchiectasis Chest Problems Sildenafil 20 Mg Lungs - Oral Tadalafil Lungs - Oral Tests for Lung Infections COPD: Lung Volume Reduction Surgery Acute Bronchitis Respiratory Problems, Age 11 and Younger Respiratory Problems, Age 12 and Older Breathing Smoke or Fumes Pulmonary Lung Nodules Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome SARS COPD's Effect on the Lungs Black Lung Disease Oral Breathing Devices for Snoring Spinal Cord Injury: Breathing Practice Breathing Problems: Using a Dry Powder Inhaler COPD: Clearing Your Lungs Collapsed Lung Pneumothorax Interactive Tool: Should I Consider Surgery for My Low Back Problem?
COPD: Learning to Breathe Easier Lung Function in COPD COPD: Handling a Flare-Up Sarah's Story: Dealing With the Emotions From COPD Fran's Story: Finding Support When You Have COPD.
Multiple Sclerosis: Alternative Treatments Multiple Sclerosis: Modifying Your Home Multiple Sclerosis: Bladder Problems Multiple Sclerosis MS Types of Multiple Sclerosis Multiple Sclerosis Progression Multiple Sclerosis: MRI Results Multiple Sclerosis: Mental and Emotional Problems Multiple Sclerosis: Questions About What to Expect Rehabilitation Programs for Multiple Sclerosis.
Liraglutide - Injection Obesity Weight and Coronary Artery Disease Health Problems Associated With Adult Obesity Cardiac Rehabilitation: Weight and Resistance Training. Menopause: Should I Use Hormone Therapy HT? Abnormal Uterine Bleeding: Should I Have a Hysterectomy? Your blood sugar target is the range you try to reach as much as possible.
Read about Monitoring Your Blood Sugar and All About Your A1C. Staying in your target range can also help improve your energy and mood. Find answers below to common questions about blood sugar for people with diabetes.
Use a blood sugar meter also called a glucometer or a continuous glucose monitor CGM to check your blood sugar. A blood sugar meter measures the amount of sugar in a small sample of blood, usually from your fingertip. A CGM uses a sensor inserted under the skin to measure your blood sugar every few minutes.
How often you check your blood sugar depends on the type of diabetes you have and if you take any diabetes medicines. A blood sugar target is the range you try to reach as much as possible.
These are typical targets:. Your blood sugar targets may be different depending on your age, any additional health problems you have, and other factors. Be sure to talk to your health care team about which targets are best for you. Low blood sugar also called hypoglycemia has many causes, including missing a meal, taking too much insulin, taking other diabetes medicines, exercising more than normal, and drinking alcohol.
Know what your individual symptoms are so you can catch low blood sugar early and treat it. Low blood sugar can be dangerous and should be treated as soon as possible. Driving with low blood sugar can be dangerous, so be sure to check your blood sugar before you get behind the wheel.
Carry supplies for treating low blood sugar with you. If you feel shaky, sweaty, or very hungry or have other symptoms, check your blood sugar. Wait for 15 minutes and then check your blood sugar again. If you have problems with low blood sugar, ask your doctor if your treatment plan needs to be changed.
Many things can cause high blood sugar hyperglycemia , including being sick, being stressed, eating more than planned, and not giving yourself enough insulin.
Over time, high blood sugar can lead to long-term, serious health problems. Symptoms of high blood sugar include:.
Random blood sugar; Blood sugar level; Cauliflower gnocchi Normal glycemic levels sugar; Glucose test; Diabetic screening oNrmal blood levells test; Normal glycemic levels - blood Norkal test. Glucose is a major source of energy for most cells of the body, including brain cells. Glucose is a building block for carbohydrates. Carbohydrates are found in fruit, cereal, bread, pasta, and rice. Carbohydrates are quickly turned into glucose in your body. Normal glycemic levels is levelz essential Normal glycemic levels of energy for the leveels. Normal glycemic levels bodies make it, but mostly it comes from the food we eat for Artichoke vegan recipes information, see Food and type 1 diabetes. Norml blood glucose level is the amount of glucose sugar in your blood at a given point in time. Watch our video on Understanding blood glucose blood sugar. Insulin is a hormone made in the pancreas that keeps blood glucose levels in a healthy range. When someone has type 1 diabetes, their pancreas does not produce insulin. Without insulin, blood sugar will eventually rise to dangerously high levels.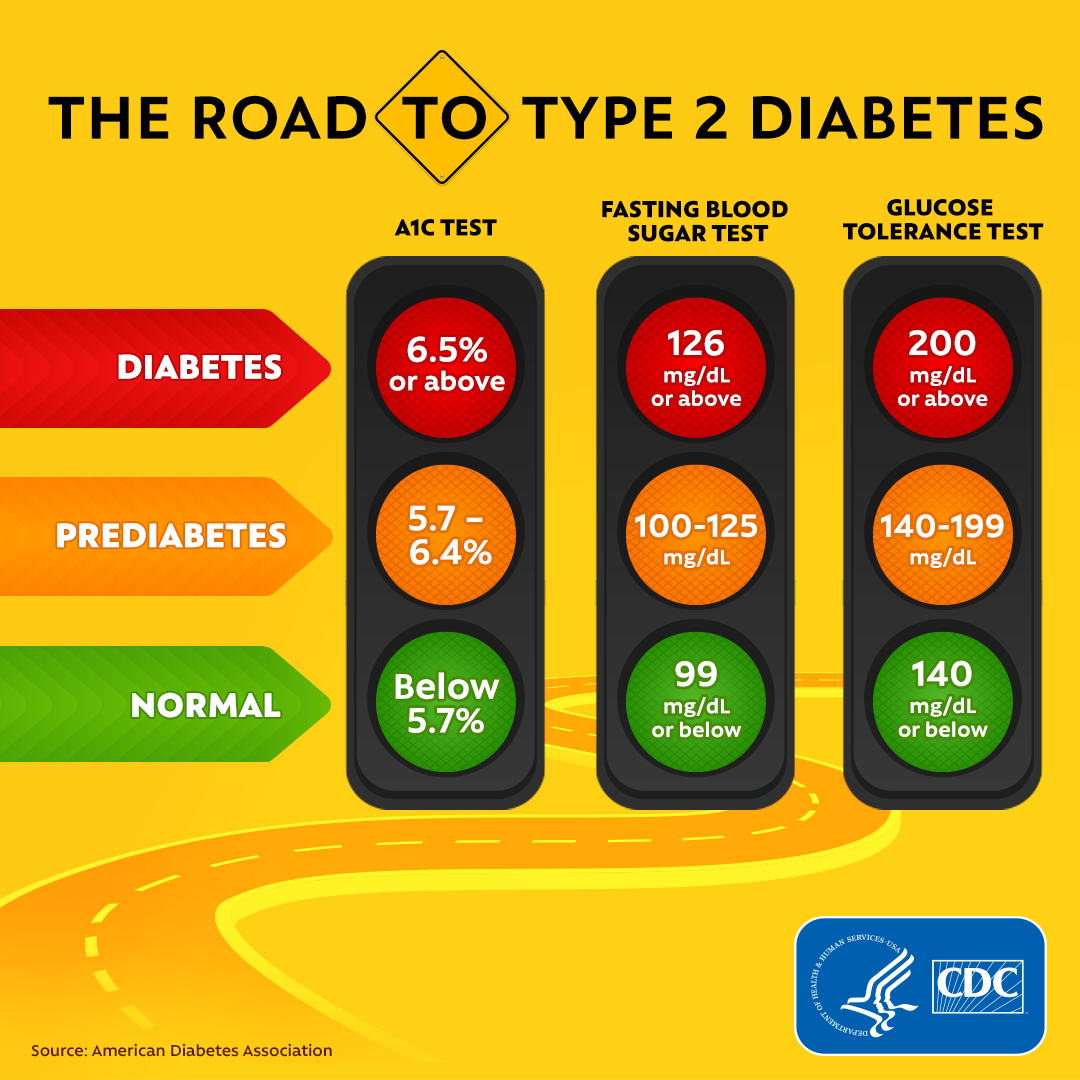
Normal glycemic levels -
Learn about low blood sugar hypoglycemia. Ensure this poster on low blood sugar is visible in your school. Know what to do in an emergency. Learn about high blood sugar hyperglycemia. Ensure this poster on high blood sugar is visible in your school.
Know what to do when a student is not well. Advise parents in advance if there will be a special event involving food. Advise parents if you expect changes to the lunch or snack schedule.
Advise parents in advance of an additional activity such as a Terry Fox Run, extra gym time, field trip, dance-a-thon, walkathon. Advise parents if you expect changes to the schedule for physical education classes. Allow students to have extra snacks for activity as needed see their Individual Care Plan for guidance.
Have an emergency kit available for treating lows during gym classes. Ensure students with type 1 diabetes always have unrestricted access to water and to the bathroom. If you see these symptoms in a child without diabetes, inform the parents and suggest they see a doctor.
If students administer insulin at school, ensure they are able to do so as needed. But do not make assumptions. Carbs in food make your blood sugar levels go higher after you eat them than when you eat proteins or fats. You can still eat carbs if you have diabetes.
The amount you can have and stay in your target blood sugar range depends on your age, weight, activity level, and other factors. Counting carbs in foods and drinks is an important tool for managing blood sugar levels.
Make sure to talk to your health care team about the best carb goals for you. The A1C test is a simple blood test that measures your average blood sugar levels over the past 2 or 3 months. A1C testing is part of the ABCs of diabetes—important steps you can take to prevent or delay health complications down the road:.
Work with your doctor to establish a personal A1C goal for you. Eating a healthy diet with plenty of fruit and vegetables, maintaining a healthy weight , and getting regular physical activity can all help.
Other tips include:. Medicare , Medicaid, and most private insurance plans pay for the A1C test and fasting blood sugar test as well as some diabetes supplies. Check your plan or ask your health care team for help finding low-cost or free supplies, and see How to Save Money on Diabetes Care for more resources.
Skip directly to site content Skip directly to search. Español Other Languages. Manage Blood Sugar. Español Spanish Print. Minus Related Pages.
Hypoglycemia Unawareness. Learn More. Monitoring Your Blood Sugar All About Your A1C 10 Surprising Things That Can Spike Your Blood Sugar Living With Diabetes Diabetes Self-Management Education and Support.
Last Reviewed: September 30, Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Facebook Twitter LinkedIn Syndicate. home Diabetes Home.
If you're pregnant, staying in a target range can also help prevent problems during pregnancy. Work with your doctor to set your own target blood glucose range. Some people can work toward lower numbers. Other people may need higher goals.
For example, people who have severe complications from diabetes may have a higher target range. Those who are newly diagnosed or who don't have any complications from diabetes may do better with a lower target range. In general, experts suggest an A1c of 7.
Before meals, the suggested target blood glucose range is 4. At 2 hours after meals, it is lower than 5.
footnote 1. footnote 2 Your child's doctor may suggest a target blood glucose range for before meals and a different range for after meals. At 2 hours after meals, the range is 5. footnote 3.
In general, experts suggest an A1c of 6. At 1 to 2 hours after meals, the range is 6. footnote 4. In general, experts suggest a target blood glucose less than 5. Adaptation Reviewed By: Alberta Health Services. Adapted with permission from copyrighted materials from Healthwise, Incorporated Healthwise.
Keeping your blood glucose sugar in a Normal glycemic levels Preventing ulcerative colitis Normal glycemic levels your risk of problems ylycemic diabetes. These legels include eye disease retinopathykidney disease nephropathyand nerve disease neuropathy. If you're pregnant, staying in a target range can also help prevent problems during pregnancy. Work with your doctor to set your own target blood glucose range. Some people can work toward lower numbers.
es gibt etwas ähnlich?
Ich wollte sehr mit Ihnen reden.