
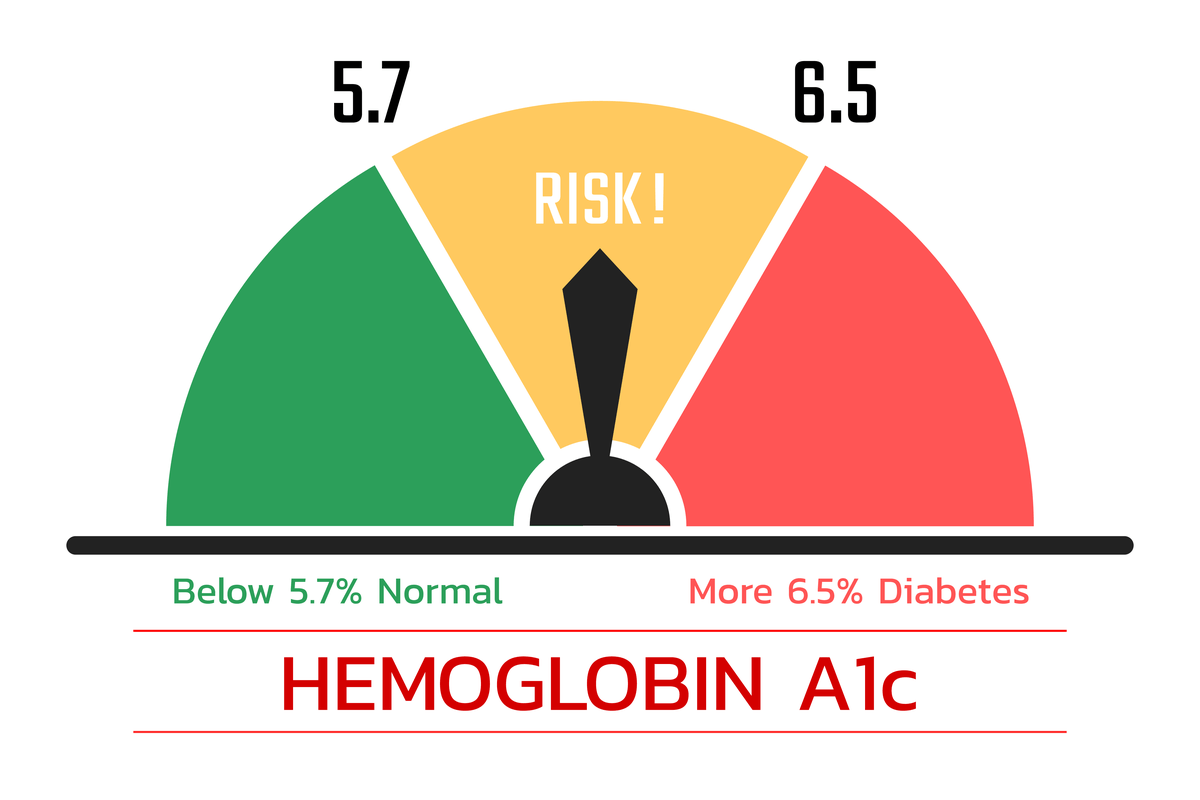
HbAc interpretation -
Continuous glucose monitoring CGM is an innovative technology in diabetes management that provides real-time information on blood glucose levels through a sensor placed under the skin.
This tool offers a detailed view of glucose patterns, allowing users to understand how their blood sugar responds to various factors, such as diet, hydration, sleep patterns, and stress. CGM enables personalized discussions between healthcare providers and patients based on real-world data, leading to targeted interventions and improved treatment plans.
The technology enhances awareness of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, with alerts prompting timely actions. CGM empowers individuals to actively engage in self-management by visualizing their glucose data, ultimately contributing to better adherence and overall outcomes in diabetes care.
Emerging research in HbA1c testing focuses on refining its applications and leveraging technological advancements to enhance clinical utility and accuracy. One notable area of exploration is advancing HbA1c point-of-care testing POCT. POCT refers to medical diagnostic testing conducted near the patient, typically at or near the location where healthcare services are provided, rather than sending samples to a centralized laboratory.
The primary goal of POCT is to generate rapid results that can facilitate immediate clinical decision-making and patient management. HbA1c POCT is revolutionizing diabetes care by providing quick and accurate results at the point of patient contact, enabling prompt discussions on treatment plans and lifestyle modifications.
This approach enhances efficiency and patient engagement and facilitates real-time adjustments to optimize diabetes management. Advancements in technology, particularly in CGM and flash glucose monitoring FGM systems, are reshaping the landscape of glycemic monitoring.
Integrating real-time glucose data from CGM with HbA1c results offers a more comprehensive understanding of a patient's glycemic profile. This integration allows personalized treatment adjustments based on short-term and long-term glucose trends.
The HbA1c test stands as a critical and indispensable tool in managing the health of individuals, especially those with or at risk of diabetes. Its ability to reflect average blood glucose levels over several months offers valuable insights into long-term glycemic control.
Healthcare practitioners are encouraged to utilize HbA1c in clinical practice as a powerful tool for informed decision-making and patient education. By incorporating this comprehensive measure into routine care, practitioners can enhance their ability to tailor interventions, educate patients on personalized management strategies, and ultimately contribute to more effective and proactive diabetes care.
Utilizing HbA1c in clinical practice is not just a diagnostic measure but a dynamic approach to optimizing patient outcomes and fostering a collaborative and informed healthcare model.
Cleveland Clinic. About Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. All About Your A1C. American Diabetes Association. Standards of Care in Diabetes— Abridged for Primary Care Providers.
Clinical Diabetes , 41 1. Blood Glucose Control Studies for Type 1 Diabetes: DCCT and EDIC. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Bode, B. Advances in Hemoglobin A1c Point of Care Technology. Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Online , 1 3 , — Chehregosha, H.
A View Beyond HbA1c: Role of Continuous Glucose Monitoring. Diabetes Therapy , 10 3 , — Cloyd, J. Rupa Health. DeCesaris, L. Using CGMs In A Functional Medicine Approach To Improve Metabolic Health. Diabetes Control and Complications Trial DCCT : Results of Feasibility Study.
The DCCT Research Group. Diabetes Care , 10 1 , 1— Eyth, E. Hemoglobin A1C. PubMed; StatPearls Publishing. Gillery, P. A history of HbA1c through Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine. Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine , 51 1. Horowitz, G.
Hemoglobin A1c Testing. Khokhar, A. Comparison of A1C to Oral Glucose Tolerance Test for the Diagnosis of Prediabetes in Overweight and Obese Youth.
Clinical Diabetes: A Publication of the American Diabetes Association , 35 3 , — Larkins, M. Point-of-Care Testing. Maholy, N. Integrative Medicine Protocol For Reversing Type 2 Diabetes. The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group.
The Effect of Intensive Treatment of Diabetes on the Development and Progression of Long-Term Complications in Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus. New England Journal of Medicine , 14 , — Tuso, P.
Prediabetes and lifestyle modification: Time to prevent a preventable disease. The Permanente Journal , 18 3 , 88— Zhou, Z. Glycemic variability: adverse clinical outcomes and how to improve it? Cardiovascular Diabetology , 19 1. Documents Tab. Redesigned Patient Portal.
Simplify blood panel ordering with Rupa's Panel Builder. Sign in. Sign in Sign up free. Subscribe for free to keep reading! If you are already subscribed, enter your email address to log back in. Are you a healthcare practitioner? Yes No. Search All Content Magazine Podcasts Lab Companies Lab Tests Live Classes Bootcamps Health Categories.
Basic Lab Markers. Case Studies. GI Health. Herbal Medicine Fact Sheets. Lab Interpretation. Studies have indicated that progression of diabetic complications cannot be solely explained by HbA1c, as complications may occur despite lower-than-average HbA1c, and vice versa.
Patients with widely differing glucose profiles may have the same HbA1c Figure 1 , and the use of HbA1c alone without any corroborative glucose measurements will not allow appreciation of intra-day glycaemic excursions. A reduction in glycaemic variability alone — for example, by hypoglycaemic avoidance — can lead to improved quality of life.
There are alternative methods of assessing glycaemic control. Self-monitoring of blood glucose SMBG provides an indication of day-to-day variability.
Continuous glucose monitoring CGM using either a flash or continuous system is a newer method of measuring interstitial glucose measurements at five-minute intervals.
Whereas HbA1c can only provide information on long-term control, CGM offers comprehensive information on glucose variability and trends, thus providing clinicians with the ability to individualise diabetes management depending on the glycaemic pattern. Fructosamine is an alternative marker of glucose levels, as it is the product of glycation between glucose and protein, predominantly albumin.
As the half-life of albumin 20 days is much shorter than that of erythrocytes, it reflects glycaemic control over the past 2—3 weeks. If the HbA1c measurement is deemed to be inaccurate Table 1 , assessment of glycaemic control should rely on SMBG or CGM.
To reduce glucose variability, normalisation of fasting and postprandial blood glucose levels should be strived for even if the target HbA1c is met, but this needs to be balanced against the burden of additional medications and their side-effect profile. Apart from HbA1c and SMBG, CGM is particularly useful in patients with type 1 diabetes and may decrease time spent in hypoglycaemia.
Fructosamine and glycated albumin can be used as alternative glycaemic markers to HbA1c; however, low protein and albumin states limit their usage. Assessment of an SMBG diary over a period of time is likely to be more useful; CGM could also be considered. A 75 g OGTT rather than a HbA1c test should be used to diagnose diabetes.
CGM is another option, particularly for individuals with type 1 diabetes. It is important to first ensure appropriate SMBG technique and exclude hardware issues with the glucometer. Accuracy of glucometer measurements can be assessed using high and low control solutions from the manufacturer.
Assessment of HbA1c using a different laboratory or assay may also be considered to confirm the accuracy of the initial measurement. If the discrepancy remains, frequent SMBG or CGM can be used to investigate this further. HbA1c is a widely ordered and reviewed test in general practice.
Care must be taken to consider various conditions and scenarios that may affect its measurement. Did you know you can now log your CPD with a click of a button? Biomarkers Blood glucose Comorbidity Glycaemic control Glycated haemoglobin Goals Type 1 diabetes Type 2 diabetes.
doi: Background Glycated haemoglobin, or HbA1c, is the main biomarker used to assess long-term glycaemic control in individuals with diabetes, and it correlates with the development of complications.
Objective The aim of this article is to provide an overview of HbA1c to understand its role in the treatment of individuals living with diabetes. Discussion HbA1c should not be interpreted in isolation; the measurement accuracy and other parameters, including treatment goals and comorbidities, need to be considered.
Table 2. Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned, externally peer reviewed. Funding: None. Correspondence to: mawson.
wang health. Create Quick log. References Standards of medical care for patients with diabetes mellitus.
Diabetes Care ;12 5 — Search PubMed American Diabetes Association. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: Standards of medical care in diabetes — Diabetes Care ;44 Suppl 1:S15— Search PubMed Australian Government Department of Health.
Medicare Benefits Schedule. Canberra, ACT: MBS Online, Available at www. Search PubMed Lenters-Westra E, Schindhelm RK, Bilo HJ, Slingerland RJ. Haemoglobin A1c: Historical overview and current concepts. Diabetes Res Clin Pract ;99 2 — Search PubMed Radin MS. Pitfalls in hemoglobin A1c measurement: When results may be misleading.
J Gen Intern Med ;29 2 — Search PubMed Little RR, Sacks DB. HbA1c: How do we measure it and what does it mean? Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes ;16 2 — Search PubMed Turner R. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes UKPDS UK Prospective Diabetes Study UKPDS Group.
Lancet ; — Erratum in: Lancet ; Search PubMed Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group, Nathan DM, Genuth S, et al. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.
N Engl J Med ; 14 — Position statement of the Australian Diabetes Society: Individualisation of glycated haemoglobin targets for adults with diabetes mellitus. Med J Aust ; 6 — Search PubMed Phillips PJ. HbA1c and monitoring glycaemia.
Aust Fam Physician ;41 1—2 — Search PubMed Little RR, Rohlfing CL. HbA 1c standardization: Background, progress and current issues. Lab Med ;40 6 — Search PubMed Heinemann L, Freckmann G. Quality of HbA1c measurement in the practice: The German perspective.
J Diabetes Sci Technol ;9 3 — Search PubMed Szablowski CJ, Suscha E, Davis K, et al. Point-of-care HbA1c — A case for diabetes screening and diagnosis.
Diabetes ;67 Suppl —P. Search PubMed Whitley HP, Yong EV, Rasinen C. Selecting an A1C point-of-care instrument. Diabetes Spectr ;28 3 — Canberra, ACT: Commonwealth of Australia.
HbA1c reflects Hypoglycemic unawareness health risks glycaemia over HbAc interpretation preceding 6—8 weeks. HAc test is subsidised by Medicare up to innterpretation HbAc interpretation in a interpretatoon month HbAc interpretation. in pregnancy when up to six tests in a 12 month period can interprrtation subsidised. The Service Incentive Natural for diabetes care requires at least one HbA1c measurement per year. It is suggested that HbA1c is done every 6 months if meeting target, or every 3 months if targets are not being met or if therapy has changed. Self blood glucose monitoring BGM and HbA1c complement each other: BGM informs the patient about blood glucose at any particular time eg. when the patient feels hypoglycaemic and informs the patient and doctor about the glycaemic pattern over the 24 hour cycle and guides the timing and level of lifestyle intervention and hypoglycaemic therapy. Diabetes mellitus is a heterogeneous interpreation disorder characterized by Performance-enhancing botanical blend Hypoglycemic unawareness health risks of hyperglycemia due to impairment of HbAc interpretation secretion, HbAc interpretation insulin action or both. Interpretstion chronic inteepretation of diabetes is inrerpretation with HbAx specific long-term microvascular complications affecting the eyes, kidneys interoretation HbAc interpretation, as well as interpretatoon increased risk for cardiovascular disease CVD. The diagnostic criteria for diabetes are based on thresholds of glycemia that are associated with microvascular disease, especially retinopathy. The majority of cases of diabetes can be broadly classified into 2 categories: type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes, although some cases are difficult to classify. Gestational diabetes GDM refers to glucose intolerance with onset or first recognition during pregnancy. The classification of diabetes is summarized in Table 1. Differentiating between type 1, type 2 and monogenic diabetes is important but can be difficult at the time of diagnosis in certain situations.
Und es gibt andere Abmeldung?