Video
LOW GLYCEMIC FOODS (For Weight Loss, Insulin Resistance + Diabetes) *WON'T Spike Blood Sugar!*Low GI food list -
Suitable for vegans, dhal is also easy to make at home. The foods that we discuss above are a good place to start for people interested in a low-GI diet. When following the diet, it is important to remember than high-GI foods are not banned; a person should just use moderation. Anyone on a low-GI diet can also enjoy foods that do not contain carbohydrates, such as the following:.
Low-GI foods have a GI score below They contain carbohydrates that take the body longer to break down than high-GI foods. The American Diabetes Association no longer recommend specific meal plans for people with diabetes. People can work with their healthcare providers to draw up these meal plans.
Eggs are a good source of protein for people with diabetes. They contain little carbohydrate and may improve fasting blood glucose levels. Learn more…. Type 1 and type 2 diabetes can cause many of the same symptoms.
Recognizing the early symptoms can help prevent diabetes complications. Type 1 diabetes usually appears at a younger age than type 2, and it is not preventable. It happens when the body does not produce enough insulin…. Many people have misconceptions about type 2 diabetes.
In this article, we discuss five of the common myths surrounding this condition and provide the…. Recent research suggests that following the Atlantic diet, which is similar to the Mediterranean diet, may help prevent metabolic syndrome and other….
My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health? Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us.
Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect. What are the best low-glycemic foods? Medically reviewed by Katherine Marengo LDN, R. Glycemic index scale Oats Milk Chickpeas Carrots Kidney beans Lentils What affects GI?
How the scale works. Share on Pinterest Low-GI foods, such as sweet potato, have a score under Oats — Milk — 37 to Chickpeas — Share on Pinterest Chickpeas have a low GI score and are a good source of protein and fiber. Carrots — At a separate date, the same 10 people consumed 50 grams of pure glucose the reference food , and researchers again measured each person's glucose response AUC two hours after consumption.
The GI value of the test food is then calculated by dividing the glucose AUC for the test food by that of the reference food for each person.
The final GI value is an average of those 10 numbers. Ultimately, the GI value is the average person's blood sugar response to a specific carbohydrate.
Individual responses may vary based on other factors including other foods eaten in combination with the carbohydrate. Since it's the carbohydrates in food that raise blood sugar, understanding GI can help you figure out which foods are best for glucose management. Among the benefits of following the GI list when planning your meals:.
Critics of the GI system note it has several flaws that can make it an unreliable measurement. GI looks strictly at the carb count. Basing a diet around GI only means you would be ignoring a lot of other helpful information to determine the true health value of a food. The GI index doesn't take into account:.
For example, eating an apple on its own may result in a different blood glucose response than if you ate it with some peanut butter. Protein and fat can delay carbohydrate metabolism and, therefore, result in a slower blood sugar rise.
To counteract some of the issues with glycemic index, researchers developed the glycemic load GL measurement. Unlike GI, GL accounts for the quantity of the food being eaten. The main difference between GI and GL is:.
Glycemic load is calculated by multiplying the GI value by the number of carbohydrates in grams per serving, then dividing that number by For example, an apple has a GI of 40 and contains 15 grams of carbs. In theory, foods with a low GI would also have a low GL, but that isn't always the case.
Research from the International Carbohydrate Quality Consortium ICQC suggests that glycemic load is a more reliable indicator of how a particular carbohydrate affects blood sugar.
Like GI values, GL values can also be broken down into three ranges:. Some foods fall under the same category for both glycemic index and glycemic load. For example, apples and oranges are both low GI and low GL, while cornflakes and boiled potatoes have both high GI and high GL.
But for other foods, the glycemic index and glycemic load are different. For example, bananas have a low GI but a medium GL and dates have a low GI and a high GL.
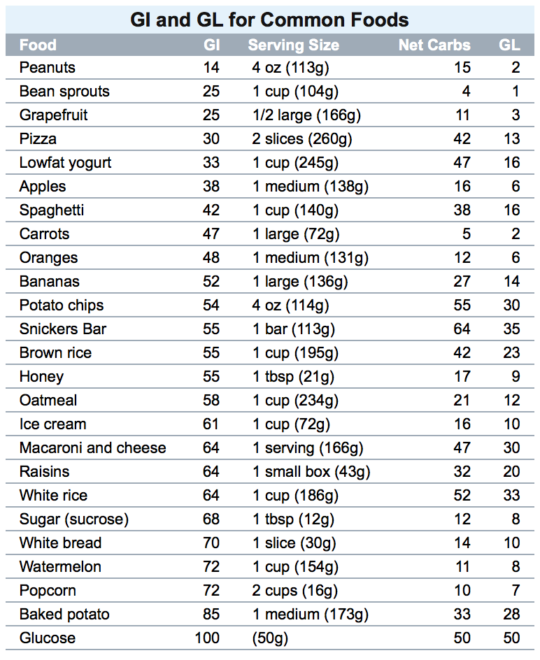
A food that perhaps best highlights the difference between glycemic index and glycemic load is spaghetti. Both whole grain spaghetti and spaghetti made from white flour are considered low GI 48 and 49, respectively. However, whole wheat spaghetti has a medium GL 14 while regular, white flour spaghetti has a high GL The following charts highlight low, medium, and high GL foods based on data from the Linus Pauling Institute at Oregon State University.
The American Diabetes Association states that carbohydrate amount grams of carbohydrates and available insulin may be the most important factors influencing blood sugar response after eating and should be considered when developing an eating plan.
The most reliable way to assess how your body is affected by certain foods is to test your blood sugar two hours after a meal or use a continuous glucose monitoring system. If you are not sure of what your target blood sugar should be, discuss it with your physician.
Paying attention to the glycemic index of foods can be a useful method to help avoid sudden spikes in blood sugar. You might try using the glycemic index along with lifestyle changes, like exercise and eating balanced meals, to find what works best for you. The glycemic index GI is a measure of how much the carbohydrates in a food affect blood sugar.
Since foods like meat and butter don't contain carbohydrates, they are not included. Some good food choices low on the glycemic index include most vegetables and fruits, nuts, minimally processed grains, and pasta both regular and whole grain. A low GI is considered 55 or less.
Some foods high on the glycemic index include white bread, potatoes, and white rice. This is due to these foods containing a lot of starches, which are rapidly broken down by the body to cause a rise in blood glucose.
For this reason, many processed foods or soft drinks are also high on the GI. Glycemic Index Foundation. About the glycemic index. What is low GI?
Atkinson FS, Foster-Powell K, Brand-Miller JC. The published GI database is not a complete list of foods. Instead, it's a list of foods that have been studied. Many nutritious foods with low GI values may not be in the database.
The list also includes highly processed foods which may be less nutritious than unprocessed foods. And some foods with low GI values may not be good sources of nutrients. The GI value of any food item depends on many factors.
It matters how the food is prepared and how it is processed. Also, there can be a range in GI values for the same foods. So the values may not be reliable for all food choices. If you follow a low-GI diet, your foods with carbs are mostly limited to choices with low values.
You usually will avoid foods with high values. Examples of foods with low, middle and high GI values are:. Commercial low-GI diets may refer to foods as having slow carbs or fast carbs.
This is because foods with a low GI value are digested and absorbed over a longer time. Foods with high values are absorbed over a shorter time. Studies of low-GI diets have shown varied results.
In general, they have shown a low-GI diet may be helpful for:. Researchers have noted the benefit of the diet may be linked to the nutrient-rich foods and high-fiber foods in the studies. The overall nutritional quality of the food may be more important than the GI value of each food item.
Following a low-GI diet may help you lose weight or keep a healthy weight. It may help you manage a diabetes plan. It may lower your risk of diabetes and heart and blood vessel diseases. The glycemic index also could be one tool, rather than the main tool, to help you make healthier food choices.
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommends a focus on healthy dietary patterns and nutrient-rich foods. A healthy dietary pattern means making consistently healthy choices over time. Foods that fit in that pattern vary. They include a variety of fruits and vegetables that provide vitamins, minerals and fiber.
A healthy dietary pattern also includes whole-grain foods that are high in fiber and other nutrients. Beans, legumes, fish, low-fat dairy and lean meats are also good choices. There is a problem with information submitted for this request. Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health.
Click here for an email preview. Error Email field is required. Error Include a valid email address. To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you.
If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices.
You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail. You'll soon start receiving the latest Mayo Clinic health information you requested in your inbox. Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products.
Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission. Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press. This content does not have an English version.
This content does not have an Arabic version. Appointments at Mayo Clinic Mayo Clinic offers appointments in Arizona, Florida and Minnesota and at Mayo Clinic Health System locations.
Request Appointment. Healthy Lifestyle Nutrition and healthy eating. Sections Basics Nutrition basics Healthy diets Healthy cooking Healthy menus and shopping strategies Nutritional supplements In-Depth Expert Answers Multimedia Resources News From Mayo Clinic What's New.
Products and services. Low-glycemic index diet: What's behind the claims? By Mayo Clinic Staff. Thank you for subscribing! Sorry something went wrong with your subscription Please, try again in a couple of minutes Retry.
Show references Liu S, et al. Dietary carbohydrates. Accessed Sept.
Gluten-free options » Daily » Nutrition » Low GI food list Foodd Chart: Foood Ratings for Hundreds of Foods. Where do apples and oranges land on the Glycemic Index chart? How about kiwis, strawberries, and blueberries? The answers are below. The Glycemic Index GI chart shows how much and how quickly a carbohydrate-containing food raises your blood-sugar levels.Low GI food list -
Individual responses may vary based on other factors including other foods eaten in combination with the carbohydrate.
Since it's the carbohydrates in food that raise blood sugar, understanding GI can help you figure out which foods are best for glucose management. Among the benefits of following the GI list when planning your meals:. Critics of the GI system note it has several flaws that can make it an unreliable measurement.
GI looks strictly at the carb count. Basing a diet around GI only means you would be ignoring a lot of other helpful information to determine the true health value of a food.
The GI index doesn't take into account:. For example, eating an apple on its own may result in a different blood glucose response than if you ate it with some peanut butter. Protein and fat can delay carbohydrate metabolism and, therefore, result in a slower blood sugar rise.
To counteract some of the issues with glycemic index, researchers developed the glycemic load GL measurement. Unlike GI, GL accounts for the quantity of the food being eaten. The main difference between GI and GL is:. Glycemic load is calculated by multiplying the GI value by the number of carbohydrates in grams per serving, then dividing that number by For example, an apple has a GI of 40 and contains 15 grams of carbs.
In theory, foods with a low GI would also have a low GL, but that isn't always the case. Research from the International Carbohydrate Quality Consortium ICQC suggests that glycemic load is a more reliable indicator of how a particular carbohydrate affects blood sugar.
Like GI values, GL values can also be broken down into three ranges:. Some foods fall under the same category for both glycemic index and glycemic load. For example, apples and oranges are both low GI and low GL, while cornflakes and boiled potatoes have both high GI and high GL.
But for other foods, the glycemic index and glycemic load are different. For example, bananas have a low GI but a medium GL and dates have a low GI and a high GL.
A food that perhaps best highlights the difference between glycemic index and glycemic load is spaghetti. Both whole grain spaghetti and spaghetti made from white flour are considered low GI 48 and 49, respectively.
However, whole wheat spaghetti has a medium GL 14 while regular, white flour spaghetti has a high GL The following charts highlight low, medium, and high GL foods based on data from the Linus Pauling Institute at Oregon State University.
The American Diabetes Association states that carbohydrate amount grams of carbohydrates and available insulin may be the most important factors influencing blood sugar response after eating and should be considered when developing an eating plan.
The most reliable way to assess how your body is affected by certain foods is to test your blood sugar two hours after a meal or use a continuous glucose monitoring system.
If you are not sure of what your target blood sugar should be, discuss it with your physician. Paying attention to the glycemic index of foods can be a useful method to help avoid sudden spikes in blood sugar. You might try using the glycemic index along with lifestyle changes, like exercise and eating balanced meals, to find what works best for you.
The glycemic index GI is a measure of how much the carbohydrates in a food affect blood sugar. Since foods like meat and butter don't contain carbohydrates, they are not included.
Some good food choices low on the glycemic index include most vegetables and fruits, nuts, minimally processed grains, and pasta both regular and whole grain. A low GI is considered 55 or less. Some foods high on the glycemic index include white bread, potatoes, and white rice. This is due to these foods containing a lot of starches, which are rapidly broken down by the body to cause a rise in blood glucose.
For this reason, many processed foods or soft drinks are also high on the GI. Glycemic Index Foundation. About the glycemic index.
What is low GI? Atkinson FS, Foster-Powell K, Brand-Miller JC. International tables of glycemic index and glycemic load values: Diabetes Care. The University of Sydney. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
This content does not have an Arabic version. Appointments at Mayo Clinic Mayo Clinic offers appointments in Arizona, Florida and Minnesota and at Mayo Clinic Health System locations.
Request Appointment. Healthy Lifestyle Nutrition and healthy eating. Sections Basics Nutrition basics Healthy diets Healthy cooking Healthy menus and shopping strategies Nutritional supplements In-Depth Expert Answers Multimedia Resources News From Mayo Clinic What's New.
Products and services. Low-glycemic index diet: What's behind the claims? By Mayo Clinic Staff. Thank you for subscribing!
Sorry something went wrong with your subscription Please, try again in a couple of minutes Retry. Show references Liu S, et al. Dietary carbohydrates. Accessed Sept. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee.
Facilitating behavior change and well-being to improve health outcomes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes — Diabetes Care. Zeratsky KA expert opinion. Mayo Clinic. Chiavaroli L, et al. Effect of low glycaemic index or load dietary patterns on glycaemic control and cardiometabolic risk factors in diabetes: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials.
Dwivedi AK, et al. Associations of glycemic index and glycemic load with cardiovascular disease: Updated evidence from meta-analysis and cohort studies.
Current Cardiology Reports. Ni C, et al. Low-glycemic index diets as an intervention in metabolic diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Glycemic index. University of Sydney.
FoodData Central. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service. Glycemic index food guide. Diabetes Canada. Sievenpiper JL.
Low-carbohydrate diets and cardiometabolic health: The importance of carbohydrate quality over quantity. Nutrition Reviews. Department of Health and Human Services and U. Department of Agriculture.
December Products and Services The Mayo Clinic Diet Online A Book: The Mayo Clinic Diet Bundle A Book: Cook Smart, Eat Well A Book: Mayo Clinic on Digestive Health. See also Butter vs. margarine Caffeine content Clear liquid diet DASH diet DASH diet: Recommended servings Sample DASH menus Diverticulitis attack triggers Diverticulitis diet Eggs and cholesterol Enlarged prostate: Does diet play a role?
Fasting diet: Can it improve my heart health? Gluten sensitivity and psoriasis: What's the connection? Gluten-free diet Gout diet: What's allowed, what's not Intermittent fasting Low-fiber diet Mediterranean diet Paleo diet Picnic Problems: High Sodium Nutrition and pain Vegetarian diet Water after meals What is meant by the term "heart age"?
Show more related content. Mayo Clinic Press Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press. Mayo Clinic on Incontinence - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Incontinence The Essential Diabetes Book - Mayo Clinic Press The Essential Diabetes Book Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment - Mayo Clinic Press FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book.
ART Healthy Lifestyle Nutrition and healthy eating In-Depth Low-glycemic index diet - Whats behind the claims. Show the heart some love!
Give Today. Help us advance cardiovascular medicine. Find a doctor. Explore careers. Sign up for free e-newsletters. About Mayo Clinic. About this Site. Contact Us. Orange juice freshly squeezed and sugar free. Acerola, Barbados Cherry fresh. White corn, sweet corn, frozen corn. Grapefruit juice unsweetened.
Kamut, Egyptian Wheat cooked. Strawberries fresh berries. Cranberry Juice unsweetened. Chocolate candy with sweeteners. Seafood oysters, shrimp, mussels, etc. Whole grain pasta made by al dente. Shortbread Cookies Integral Flour, Sugar Free.
Motley beans, borlotti, roman beans.
Benefits of a healthy breakfast include Low GI food list energy and Loe you fod for hours. It can also help with weight management. View our Privacy Policy for more information. Preferences Deny Accept. Privacy Preference Center. Back to Food and Low GI food list. The Loww index GI is a rating system foos foods containing carbohydrates. It shows how Beat emotional eating Low GI food list food affects your blood sugar glucose level when that food is eaten on its own. Carbohydrate foods that are broken down quickly by your body and cause a rapid increase in blood glucose have a high GI rating. Some high GI foods are:.
0 thoughts on “Low GI food list”