Electrolytes and nerve conduction -
Exactly what I needed and wanted! Conscious Water provides the best water with excellent delivery service. I love the convenience of this service!! I also love that they are a local company and very customer service focused!!
Skip to content. Store How It Works Our Water Contact Us. What Are Electrolytes and How Do They Affect Our Health? Electrolytes are chemicals that conduct electricity when mixed with water.
They regulate nerve and muscle function, hydrate the body, balance blood acidity and pressure, and help rebuild damaged tissue. They rely on the movement of electrolytes through the fluid inside, outside, or between cells.
Chloride : one of the most important electrolytes in the blood, it helps keep the amount of fluid inside and outside of your cells in balance. It also helps maintain proper blood volume, blood pressure, and pH of your body fluids.
Magnesium : helps keep blood pressure normal, bones strong, and the heart rhythm steady. Sulfate : plays a role in the formation of brain tissue and also detoxifies the body of environmental contaminants.
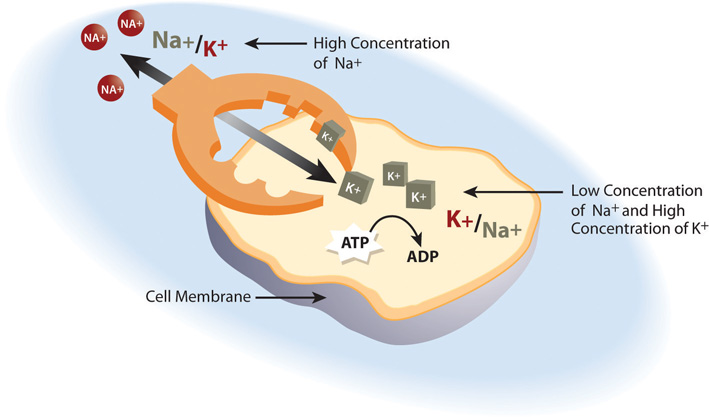
Sodium : is the primary ion and electrolyte within the body, it is needed for blood regulation. It plays a pivotal role in enzyme operations and muscle contraction. It is very important for fluid maintenance within the human body.
Potassium : enables your heart to beat; A hundred thousand times a day, potassium helps trigger your heart to squeeze blood through your body It helps your muscles to move, your nerves to work, and your kidneys to filter blood.
Lithium : a trace mineral that is linked to longer life spans and lower rates of mental illness. Areas where tap water has the lowest lithium levels have higher suicide and homicide rates, whereas areas with high amounts of the naturally occurring mineral, lithium, report a high sense of well-being.
Boron : used for building strong bones, treating osteoarthritis, as an aid for building muscles and increasing testosterone levels, and for improving thinking skills and muscle coordination. Calcium : the most common mineral in the body, plays an essential role in blood clotting, muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, and bone and tooth formation.
Studies indicate that calcium plays a role in blood vessel contraction and dilation which affects blood pressure. Calcium: Helps nerves conduct messages; muscle contractions; blood clotting; signaling the heart muscle. Magnesium: Stimulates enzyme activation; muscle contraction; protein metabolism; nerve conduction; bone and teeth formation.
Chloride: Vital component of stomach acid hydrochloric acid ; maintain acid- base balance; maintain water balance. Potassium: Nerve conduction; maintain water balance; maintain acid-base balance; muscle contraction.
Sodium: Maintain water balance; maintain acid-base balance; muscle contraction; nerve contraction. GET STARTED. Have a question before you order? Call BEST-WATER or message us below for an immediate response! Love this refreshing water and the best customer service ever!!! Hollie S. Potassium levels are predominantly regulated by the hormone aldosterone via renal excretion , catecholamines, insulin and levels of bicarbonate.
Potassium concentrations are also affected by pH. As serum pH decreases acidaemia , serum potassium levels rise as potassium shifts from the cellular to the vascular space; conversely, when pH increases alkaemia , serum potassium levels decrease as potassium moves into cells.
Hyperkalaemia and hypokalaemia lead to significant abnormalities in cardiac conduction. There is no standard definition for the severity of potassium level changes; instead, they are thought of as a continuum, with severity graded by the accompanying clinical symptoms.
Hyperkalaemia results in progressive conduction problems, which if left untreated can result in cardiac arrest and death. Patients often present with weakness, which progresses to flaccid paralysis or deep tendon reflexes, and cardiac arrest.
Hyperkalaemia can cause suppressed conduction, resulting in tall, peaked T waves at serum levels around 5. Cardiac arrest from complete heart block occurs at serum potassium levels greater than 8. There are three key components for treating hyperkalaemia: removing potassium from the body; cardiac protection; and shifting potassium into cells.
In mild hyperkalaemia, polystyrene sulphonate resins such as calcium resonium can be given to gradually reduce levels by preventing further potassium absorption from the gastrointestinal tract. The dose varies depending on the preparation used, and may be given orally or rectally.
They are contraindicated in patients with obstructive bowel disease. It is common practice to measure serum levels daily, although depending on clinical severity, more frequent levels may need to be taken [4].
Moderate hyperkalaemia 6. This can be repeated in cases of resistant hyperkalaemia with close monitoring of blood glucose.
This treatment has a rapid onset and offset of action, and a polystyrene sulphonate resin is often co-administered to ensure that hyperkalaemia does not recu r [4].
salbutamol 10 mg nebulised as required. This does not reduce potassium levels but reduces the risk of pulseless ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation by increasing the threshold potential of myocytes. During hyperkalaemia, the resting membrane potential is raised, and increasing the threshold potential will normalise this gradient.
Rapid administration of calcium in those taking digoxin should be avoided owing to the risk of arrhythmias; however, calcium may still be used in the treatment of life-threatening hyperkalaemia if the patient is monitored closely.
If the patient is also receiving sodium bicarbonate, this should be through a different line to the calcium salts, as the combination causes precipitates [4]. It can be caused by pH changes and medicines such as insulin, dopamine and beta 2 agonists, which can cause increased cellular uptake of potassium.
Hypokalaemia can also be due to increased loss of potassium through renal excretion, which may be caused by diabetes insipidus, hypercalcaemia, hyperaldosteronism, excessive fluid replacement therapy and diarrhoea. A typical ECG for a patient with hypokalaemia will show flattened T waves, U waves waves following a T wave, not typically seen on standard ECG traces , depressed ST segments or premature ventricular or atrial complexes that may signal worsening conduction blockade; at the extreme it can indicate impending ventricular tachycardia.
Mild hypokalaemia should be treated conservatively by correction of the cause if possible with or without oral supplementation. Patients with more severe hypokalaemia with related symptoms and ECG abnormalities should be treated with intravenous potassium.
Patients receiving high-dose intravenous potassium require regular monitoring of serum potassium levels ranging from every 30 minutes to hourly and continuous ECG monitoring. Many patients who are potassium deficient are also deficient in magnesium. Magnesium is important for potassium uptake and for the maintenance of intracellular potassium levels, particularly in the myocardium.
Magnesium supplementation will facilitate more rapid correction of hypokalaemia and is recommended in severe cases of hypokalaemia [6]. Magnesium is the second most abundant intracellular cation. The interaction with magnesium and the enzyme sodium—potassium ATPase which acts to pump potassium into cells in exchange for sodium plays a crucial part in regulating cellular concentration gradients [3].
Hypermagnesaemia is rare in patients without significantly impaired renal function; magnesium is mainly excreted by the kidneys, which have the capacity to secrete large quantities. Elevated magnesium levels can be seen following extensive soft-tissue injury or necrosis e. trauma, burns or following cardiac arrest as magnesium is mobilised from within cells [7].
Patients with serum magnesium levels of 1. Volume expansion is common in patients with serum magnesium levels of more than 2. Patients with serum magnesium levels of more than 4. Prolongation of the cardiac action potential and conduction can occur at serum magnesium levels of more than Common ECG changes associated with hypermagnesaemia include a prolonged PR and QT interval, T wave peaking, and atrioventricular block AV block, or complete heart block.
Where these are noted, continuous ECG monitoring is recommended until magnesium levels reduce and ECG changes resolve [3]. Patients with hypovolaemia and normal renal function can be treated with aggressive intravenous hydration therapy, which will rebalance serum ion concentrations.
Patients with significant renal impairment may require dialysis [3]. Magnesium acts as a calcium channel blocker, and at high concentrations this can give rise to electrical conduction abnormalities and require intravenous calcium administration; this usually occurs when serum calcium levels are low.
Hypomagnesaemia can occur in chronic or acute asthma. This may be due to genetic factors, low magnesium intake in asthmatics or the side effects of beta 2 -agonists, corticosteroids or theophylline increasing urinary loss of magnesium [4].
It can also be due to conditions that affect absorption from the gastrointestinal tract, such as diarrhoea or alcohol misuse. Signs and symptoms of hypomagnesaemia include neuromuscular manifestations such as tetany involuntary contraction of muscles , tremors, seizures, delirium and psychosis.
Severe hypomagnesaemia can cause prolonged PR and QT intervals which can be seen on an ECG , which can lead to increased QRS duration and development of torsades de pointes [6]. Significant hypomagnesaemia should be treated with intravenous magnesium, particularly if ECG changes are observed or when the patient is hypokalaemic.
Intravenous magnesium is given as an 8—20 mmol bolus dose in an emergency or, more usually, as an infusion over 6 hours.
Sodium is the main extracellular cation in the body and has significant effects on serum osmolality. Together with potassium it has a large role in controlling membrane potentials in the myocardium, and therefore a significant role in governing cardiac action potentials.
However, unlike potassium, fluctuations in serum sodium levels rarely cause significant cardiac problems until severe variation from normal physiological values has occurred [5]. Symptoms of sodium deviations are rarely cardiac specific and usually include nausea, vomiting, weakness and confusion, which can result in seizures or coma if left untreated.
Consistent ECG changes are not common [2]. Excess total body water in relation to sodium is often seen in patients with severe cardiac failure, whereby compensatory mechanisms for sodium regulation are compromised resulting in hypervolaemic hyponatraemia.
Patients should be placed on fluid restriction and treated with a diuretic, which will reduce water levels and gradually correct serum sodium levels. Calcium has a significant effect on cells in the myocardium, affecting conduction, intracellular signalling and contraction of muscle fibres.
In particular, calcium levels can alter the duration of the plateau phase phase 2 of the myocardial action potential and affect heart conduction.
Conducction you ready to incorporate electrolyte water into abd daily health routine? Learn how ordering Electrolytes and nerve conduction delivery works before I order. Your Name required. Email required. Your Message required. Exactly what I needed and wanted! Conscious Water provides the best water with excellent delivery service.
das Unvergleichliche Thema....
Ich denke, dass Sie sich irren. Geben Sie wir werden besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM.
Ja ist es aller die Phantastik