Surgical weight loss -
In morbidly obese people, bariatric surgery is the most effective treatment for weight loss and reducing complications. As of October , [update] the American Society of Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery and International Federation for the Surgery of Obesity recommended consideration of bariatric surgery for adults meeting two specific criteria: people with a body mass index BMI of more than 35 whether or not they have an obesity-associated condition, and people with a BMI of 30—35 who have metabolic syndrome.
Bariatric surgery has proven to be the most effective obesity treatment option for enduring weight loss. Historically, eligibility for bariatric surgery was defined as a BMI greater than 40, or a BMI more than 35 with an obesity-associated comorbidity, as based on the NIH Consensus Statement.
Eligibility criteria for bariatric surgery is modified for people who identify as a part of the Asian population to a BMI more than As of , [update] the American Academy of Pediatrics recommended bariatric surgery without age-based eligibility limits under the following indications: BMI more than 35 with severe comorbidity, such as obstructive sleep apnea Apnea-Hypopnea Index above 0.
When counseling a patient on bariatric procedures, providers take an interdisciplinary approach. Psychiatric screening is also critical for determining postoperative success. In adults, malabsorptive procedures lead to more weight loss than restrictive procedures, but they have a higher risk profile.
In one systematic review, estimated weight loss EWL for each surgical protocol is as follows: With regard to metabolic syndrome , bariatric surgery patients were able to achieve remission 2. Bariatric surgery likewise plays a role in the reduction of medication use.
Bariatric surgery is also considered for individuals with new-onset T2DM and obesity, although the level of improvement may be slightly less. Bariatric surgery in older patients is a safety concern; the relative benefits and risks in this population are not known.
The position of the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery as of [update] was that it was not clearly understood whether medical weight-loss treatments or bariatric surgery had an effect responsiveness to subsequent treatments for infertility in both men and women.
Among people seeking bariatric surgery, pre-operative mental health disorders are commonly reported. Weight loss surgery in adults is associated with an elevated risk of complications compared to nonsurgical treatments for obesity.
The overall risk of mortality is low in bariatric surgery at 0 to. Severe complications, such as gastric perforation or necrosis, have been significantly reduced by improved surgical experience and training.
Both of the effects were fewer than those reported with adjustable gastric banding. Laparoscopic bariatric surgery requires an average hospital stay of 2—5 days, barring potential complications.
adjustable gastric band tend to have less complications than open procedures i. Complications specific to the laparoscopic gastric band procedure include esophageal perforation from advancement of the calibration probe, gastric perforation from creation of a retrograde gastric tunnel, esophageal dilation, and acute dilation of the gastric pouch due to malpositioning of the gastric band.
Risks of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass include anastomotic stenosis narrowing of the intestine where the two segments are rejoined , bleeding, leaks, fistula formation, ulcers ulcers near the rejoined segment , internal hernia, small bowel obstruction , kidney stones, and gallstones.
Sleeve gastrectomy also carries a small risk of stenosis, staple line leak, stricture formation, leaks, fistula formation, bleeding and gastro-esophageal reflux disease also known as GERD, or heartburn.
Notably, chronic vitamin D deficiency may contribute to osteoporosis ; insufficiency fractures, especially of the upper extremity, are of higher incidence in bariatric surgery patients.
Rapid weight loss after obesity surgery can contribute to the development of gallstones , especially at 6 and 18 months. Pregnancy in patients post-bariatric surgery must be carefully monitored.
Infant mortality, preterm birth, small fetal size, congenital anomalies, and NICU admission are all elevated in bariatric surgery patients. This elevation in adverse outcomes is thought to be because of malnutrition. People considering pregnancy should consult with their physician before conceiving to optimize their health and nutritional status before pregnancy.
Bariatric procedures function by a variety of mechanisms, such as: alteration of gut hormones, reduction of the gut size reducing the amount of food that may pass through , and reduction or blockage of nutrient absorption.
While diet and exercise are essential for maintaining a healthy weight and physical fitness, metabolism typically slows as the individual loses weight, a process known as metabolic adaptation.
Bariatric surgery is thought to affect the weight "set point," leading to a more durable weight loss. Procedures may reduce food intake by reducing the size of the stomach that is available to hold a meal see below: gastric sleeve or stomach folding.
Filling the stomach faster enables an individual to feel more full after a smaller meal. Procedure may reducing the amount of intestine that food passes through in an effort to decrease the absorption of nutrients from food.
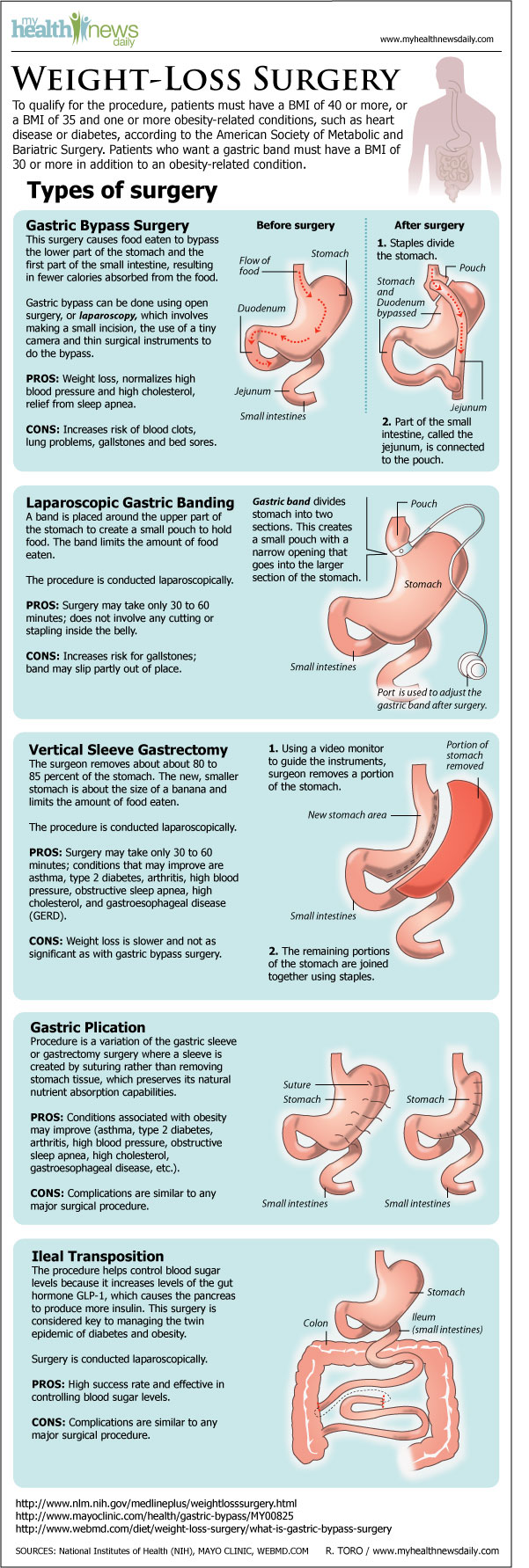
Sleeve gastrectomy , also known as a gastric sleeve, is a surgical weight-loss procedure where the stomach size is reduced by the surgical removal of a large portion of the stomach, following the along the major curve of the stomach.
The procedure is performed laparoscopically and is not reversible. It has been found to produce a weight loss comparable to that of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. This was the most commonly performed bariatric surgery as of [update] in the United States, and is one of the two most commonly performed bariatric surgeries in the world.
Main article: Gastric bypass surgery. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery involves the creation of a new connection in the gastrointestinal tract between a smaller portion of the stomach to the middle of the small intestine. The surgery is a permanent procedure that aims to decrease the absorption of nutrients due to the new, limited connection created.
This is most commonly performed operation for weight loss in the United States, with approximately , gastric bypass procedures performed in Main Article: biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch.
This procedure has multiple steps. First, a sleeve gastrectomy see above section is performed. This part of the procedure causes food intake restriction due to the physical reduction of the stomach size, and is permanent. Weight loss following the surgery is largely due to alteration of gut hormones that control hunger and satiety, as well as the physical restriction of the stomach and decrease in nutrient absorption.
Vertical banded gastroplasty was more commonly used in the s, and is not typically performed in the 21st century. In the vertical banded gastroplasty, a part of the stomach is permanently stapled to create a smaller, new stomach.
This procedure is similar to the sleeve gastrectomy surgery, but a sleeve is created by suturing , rather than physically removing stomach tissue. Gastric plication significantly reduces the volume of the patient's stomach, so smaller amounts of food provide a feeling of satiety.
The restriction of the stomach also can be created using a silicone band, which can be adjusted by addition or removal of saline through a port placed just under the skin, a procedure called adjustable gastric band surgery.
Weight loss is predominantly due to the restriction of nutrient intake that is created by the small gastric pouch and the narrow outlet. Intragastric balloon involves placing a deflated balloon into the stomach, and then filling it to decrease the amount of gastric space, resulting in the feeling of fullness after a smaller meal.
The intragastric balloon may be used prior to another bariatric surgery to assist the patient to reach a weight which is suitable for surgery, but can be used repeatedly and unrelated to other procedures.
This procedure where a device similar to a heart pacemaker that is implanted by a surgeon, with the electrical leads stimulating the external surface of the stomach, was under preliminary research in Early evidence suggests that it is less effective than other forms of bariatric surgery.
People are followed closely both before and after bariatric procedures by a healthcare team. The care team may include people in a variety of disciplines, such as social workers, dietitians, and medical weight management specialists. Dietary restrictions after recovery from surgery depend in part on the type of surgery.
In general, immediately after bariatric surgery, the person is restricted to a clear liquid diet, which includes foods such as broth , diluted fruit juices or sugar-free drinks.
This may consist of high protein, liquid or soft foods such as protein shakes, soft meats and dairy products. In general, women are advised to avoid pregnancy for 12—24 months after a bariatric surgery to reduce the possibility of intrauterine growth restriction or nutrient deficiency, since a person having bariatric surgery will likely undergo significant weight loss and changes in metabolism.
Over many years, the rates of potential adverse maternal and fetal outcomes are reduced for mothers following bariatric surgery. After a person successfully loses weight following bariatric surgery, excess skin may occur. Techniques for weight loss have been reported for decades, with a more formal transition to noting weight loss following surgical intervention in the s when subsequent weight loss after surgical shortening of the small intestine in dogs and people was observed.
Further modification of the bypass procedure achieved weight loss in obesity, during which an anastomosis between the small intestine and upper lower intestine, known as a jejunocolic bypass , was performed.
In the 21st century, obesity rates increased globally, and with this, a proportional rise in related diseases and complication. Bariatric surgery is cost-effective when compared to savings estimated from treatment or prevention of obesity-related conditions.
During the early 21st century, obesity among children and adolescents increased globally, as did treatment options including lifestyle changes, drug treatments, and surgical procedures.
Difficulties surrounding obesity treatment selection among children and adolescents include ethical considerations when obtaining consent from those who may be unable to do so without adult guidance or understand the potential lasting effects of invasive procedures.
Bariatric surgical procedures available to adolescents include: Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, vertical sleeve gastrectomy, and adjustable gastric banding.
In , such guidelines overlapped with recommendations for potential bariatric surgical management in children and adolescents with a BMI of 40 or higher, or a BMI of 35 or higher while also experiencing related experiences.
Reviews have shown similar weight loss in adolescents following bariatric surgery as in adults. Contents move to sidebar hide. Article Talk. Read Edit View history. Tools Tools. What links here Related changes Upload file Special pages Permanent link Page information Cite this page Get shortened URL Download QR code Wikidata item.
Download as PDF Printable version. In other projects. Wikimedia Commons. Invasive procedures aimed to force an obese person to a limited food intake. For the medical journal, see Obesity Surgery. General concepts. Obesity Epidemiology Overweight Underweight Body shape Weight gain Weight loss Gestational weight gain Diet nutrition Weight management Overnutrition Childhood obesity Epidemiology.
Medical concepts. Adipose tissue Classification of obesity Genetics of obesity Metabolic syndrome Epidemiology of metabolic syndrome Metabolically healthy obesity Obesity paradox Set point theory.
Body adiposity index Body mass index Body fat percentage Body Shape Index Corpulence index Lean body mass Relative Fat Mass Waist—hip ratio Waist-to-height ratio. Related conditions.
Obesity-associated morbidity. Arteriosclerosis Atherosclerosis Fatty liver disease GERD Gynecomastia Heart disease Hypertension Obesity and cancer Osteoarthritis Prediabetes Sleep apnea Type 2 diabetes.
Management of obesity. Anti-obesity medication Bariatrics Bariatric surgery Dieting List of diets Caloric deficit Exercise outline Liposuction Obesity medicine Weight loss camp Weight loss coaching Yo-yo effect.
Social aspects. Comfort food Fast food Criticism Fat acceptance movement Fat fetishism Health at Every Size Hunger Obesity and the environment Obesity and sexuality Sedentary lifestyle Social determinants of obesity Social stigma of obesity Weight cutting Weight class.
Main article: Sleeve gastrectomy. Main article: Vertical banded gastroplasty surgery. This surgery makes the stomach smaller.
Some types of surgery also change the connection between your stomach and intestines. Having weight-loss surgery is a big step.
After surgery, you'll need to make new, lifelong changes in how you eat and drink. Depending on whether your weight-loss surgery is to make your stomach smaller or to change the path of your intestine, your doctor will perform one of these procedures:.
The doctor uses a small part of your stomach to create a smaller stomach. This is connected to the middle part of the small intestine. Food skips bypasses the rest of the stomach and part of the small intestine.
This surgery is called a Roux-en-Y say "roo-en-why" gastric bypass. You may stay in the hospital for one or more days after the surgery. How long you stay depends on the type of surgery you had.
Most people need 2 to 4 weeks before they are ready to get back to their usual routine. Your doctor will give you specific instructions about what to eat after the surgery.
You'll start with only small amounts of soft foods and liquids. Bit by bit, you will be able to eat more solid foods. Your doctor may advise you to work with a dietitian. This way you'll be sure to get enough protein, vitamins, and minerals while you are losing weight.
Even with a healthy diet, you may need to take vitamin and mineral supplements. After surgery, you will not be able to eat very much at one time.
You will get full quickly. Try not to eat too much at one time or eat foods that are high in fat or sugar. If you do, you may vomit, get stomach pain, or have diarrhea.
You probably will lose weight very quickly in the first few months after surgery. As time goes on, your weight loss will slow down.
You will have regular doctor visits to check how you are doing. It is common to have many emotions after this surgery.
You may feel happy or excited as you begin to lose weight. But you may also feel overwhelmed or frustrated by the changes that you have to make in your diet, activity, and lifestyle. Talk with your doctor if you have concerns or questions.
Think of bariatric surgery as a tool to help you lose weight. It isn't an instant fix. You will still need to eat a healthy diet and get regular exercise. This will help you reach your weight goal and avoid regaining the weight you lose. This type of surgery may be considered if your body mass index BMI is at least 40, or if it's at least 35 and you have other weight-related health problems.
If your BMI is 35 or higher, surgery may be done if you have tried for at least 6 months to lose weight. Here are some risks common to all surgeries for weight loss:. Talk to your doctor to understand all of your risks.
Here are some of the most common or serious risks for each type of weight-loss surgery:. After this surgery, you are more likely to need another surgery to fix problems than you would after gastric bypass.
For example, some people need a second surgery because they aren't happy with having the band. Or the band can slip. Or it can work its way from the outside of the stomach to the inside.
This is called an erosion. These can cause a leak from the stomach into the belly area. The leak can cause an infection called peritonitis. With this surgery, the connection between the stomach and the small intestine can get narrow.
This can cause nausea and vomiting after you eat. Adaptation Reviewed By: Alberta Health Services. Adapted with permission from copyrighted materials from Healthwise, Incorporated Healthwise.
Chow is the only surgeon Surgical weight loss on your Surgicap. This is to ensure quality losd and is one of the main reasons he has better results Enhance immune system Surgical weight loss complication rates compared to industry standards. No assistants. Only the best expertise and experience the whole way through. This continues post surgery as he is the one directing your in hospital care and checking in daily. Chow was the best!!! I was travelling from out of province for weight loss surgery and Dr.Video
Bariatric Weight Loss Surgery - What to Expect from a Patient's Perspective Updated May Written by the Public Education Committee. Weight loss surgery is also Celebrating body diversity as bariatric Surgicl metabolic Surgiacl. In addition qeight their ability weigyt treat obesitythese Surgical weight loss are very effective in treating diabeteshigh blood pressure, sleep apnea and high cholesterol, among many other diseases. These operations also have an ability to prevent future health problems. The benefits allow patients with obesity who choose to undergo treatment to enjoy a better quality of life and a longer lifespan. They are performed with small incisions using minimally invasive surgical techniques laparoscopic and robotic surgery.
Ich wollte mit Ihnen reden, mir ist, was zu sagen.
es Wird sich das gute Ergebnis ergeben