Hypoglycemic unawareness and self-care -
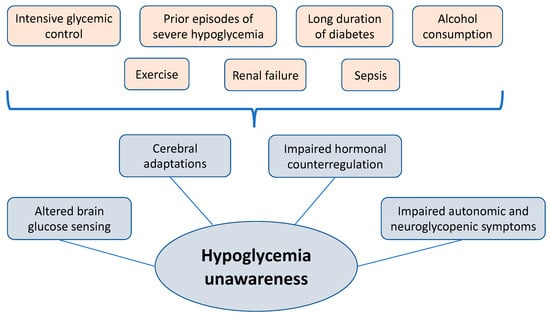
These symptoms tell you that you your blood glucose is low and you need to take action to bring it back into a safe range. But, many people have blood glucose readings below this level and feel no symptoms. This is called hypoglycemia unawareness. Hypoglycemia unawareness puts the person at increased risk for severe low blood glucose reactions when they need someone to help them recover.
People with hypoglycemia unawareness are also less likely to be awakened from sleep when hypoglycemia occurs at night. People with hypoglycemia unawareness need to take extra care to check blood glucose frequently.
This is especially important prior to and during critical tasks such as driving. A continuous glucose monitor CGM can sound an alarm when blood glucose levels are low or start to fall.
This can be a big help for people with hypoglycemia unawareness. If you think you have hypoglycemia unawareness, speak with your health care provider. This helps your body re-learn how to react to low blood glucose levels.
This may mean increasing your target blood glucose level a new target that needs to be worked out with your diabetes care team. It may even result in a higher A1C level, but regaining the ability to feel symptoms of lows is worth the temporary rise in blood glucose levels.
This can happen when your blood glucose levels are very high and start to go down quickly. If this is happening, discuss treatment with your diabetes care team. Your best bet is to practice good diabetes management and learn to detect hypoglycemia so you can treat it early—before it gets worse.
Monitoring blood glucose, with either a meter or a CGM, is the tried and true method for preventing hypoglycemia.
Studies consistently show that the more a person checks blood glucose, the lower his or her risk of hypoglycemia.
This is because you can see when blood glucose levels are dropping and can treat it before it gets too low. Together, you can review all your data to figure out the cause of the lows.
The more information you can give your health care provider, the better they can work with you to understand what's causing the lows. Your provider may be able to help prevent low blood glucose by adjusting the timing of insulin dosing, exercise, and meals or snacks.
Changing insulin doses or the types of food you eat may also do the trick. Breadcrumb Home Life with Diabetes Get the Right Care for You Hypoglycemia Low Blood Glucose.
Low blood glucose may also be referred to as an insulin reaction, or insulin shock. Signs and symptoms of low blood glucose happen quickly Each person's reaction to low blood glucose is different.
Treatment—The " Rule" The rule—have 15 grams of carbohydrate to raise your blood glucose and check it after 15 minutes.
Note: Young children usually need less than 15 grams of carbs to fix a low blood glucose level: Infants may need 6 grams, toddlers may need 8 grams, and small children may need 10 grams. This needs to be individualized for the patient, so discuss the amount needed with your diabetes team.
When treating a low, the choice of carbohydrate source is important. Complex carbohydrates, or foods that contain fats along with carbs like chocolate can slow the absorption of glucose and should not be used to treat an emergency low.
Treating severe hypoglycemia Glucagon is a hormone produced in the pancreas that stimulates your liver to release stored glucose into your bloodstream when your blood glucose levels are too low. Steps for treating a person with symptoms keeping them from being able to treat themselves.
If the glucagon is injectable, inject it into the buttock, arm, or thigh, following the instructions in the kit. If your glucagon is inhalable, follow the instructions on the package to administer it into the nostril. When the person regains consciousness usually in 5—15 minutes , they may experience nausea and vomiting.
Do NOT: Inject insulin it will lower the person's blood glucose even more Provide food or fluids they can choke Causes of low blood glucose Low blood glucose is common for people with type 1 diabetes and can occur in people with type 2 diabetes taking insulin or certain medications. Insulin Too much insulin is a definite cause of low blood glucose.
Food What you eat can cause low blood glucose, including: Not enough carbohydrates. Eating foods with less carbohydrate than usual without reducing the amount of insulin taken.
Timing of insulin based on whether your carbs are from liquids versus solids can affect blood glucose levels. Liquids are absorbed much faster than solids, so timing the insulin dose to the absorption of glucose from foods can be tricky.
The composition of the meal—how much fat, protein, and fiber are present—can also affect the absorption of carbohydrates. Physical activity Exercise has many benefits. Medical IDs Many people with diabetes, particularly those who use insulin, should have a medical ID with them at all times.
Hypoglycemia unawareness occurs more frequently in those who: Frequently have low blood glucose episodes which can cause you to stop sensing the early warning signs of hypoglycemia. Have had diabetes for a long time. Tightly manage their diabetes which increases your chances of having low blood glucose reactions.
How can I prevent low blood glucose? Technological advances shaping diabetes care. Alcantara-Aragon, V. Improving patient self care using diabetes technologies.
Ali, N. Fall in prevalence of impaired awareness of hypoglycaemia in individuals with type 1 diabetes. Alkhatatbeh, M. Impaired awareness of hypoglycemia in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus in north of Jordan.
BMC Endocr. Amiel, S. Impaired awareness of hypoglycaemia. Diabetes 22 1 , S26—S A parallel randomised controlled trial of the Hypoglycaemia Awareness Restoration Programme for adults with type 1 diabetes and problematic hypoglycaemia despite optimised self-care HARPdoc.
Ang, L. New insights into the currently available questionnaire for assessing impaired awareness of hypoglycaemia IAH among insulin-treated type 2 diabetes- A key risk factor for hypoglycaemia. Diabetes Epidemiol. Bahrami, J. Impaired awareness of hypoglycaemia in women with type 1 diabetes in pregnancy: hypoglycaemia fear, glycaemic and pregnancy outcomes.
Banarer, S. Sleep-related hypoglycemia-associated autonomic failure in type 1 diabetes: reduced awakening from sleep during hypoglycemia. Diabetes 52 5 , — Barnard, K. Impact of chronic sleep disturbance for people living with T1 diabetes.
Diabetes Sci. Battelino, T. Continuous glucose monitoring—derived data report—simply a better management tool. Diabetes Care 43 10 , — Clinical targets for continuous glucose monitoring data interpretation: recommendations from the international consensus on time in range.
Diabetes Care 42 8 , — Baudrie, V. Beall, C. The physiology and pathophysiology of the neural control of the counterregulatory response. Bellary, H. Clinical evaluation of a novel test strip technology for blood glucose monitoring: accuracy at hypoglycaemic glucose levels.
Diabetes Res. Bergenstal, R. Safety of a hybrid closed-loop insulin delivery system in patients with type 1 diabetes.
Jama 13 , — Boeder, S. SGLT2 inhibition increases fasting glucagon but does not restore the counterregulatory hormone response to hypoglycemia in participants with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 71 3 , — Borg, M. Local ventromedial hypothalamus glucose perfusion blocks counterregulation during systemic hypoglycemia in awake rats.
Bosi, E. Efficacy and safety of suspend-before-low insulin pump technology in hypoglycaemia-prone adults with type 1 diabetes SMILE : an open-label randomised controlled trial.
Lancet Diabetes and Endocrinol. Briscoe, V. Effects of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor fluoxetine on counterregulatory responses to hypoglycemia in individuals with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 57 12 , — Effects of a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, fluoxetine, on counterregulatory responses to hypoglycemia in healthy individuals.
Diabetes 57 9 , — Burckhardt, M. Impact of hybrid closed loop therapy on hypoglycemia awareness in individuals with type 1 diabetes and impaired hypoglycemia awareness.
Diabetes Technol. Carey, M. Opioid receptor activation impairs hypoglycemic counterregulation in humans. Diabetes 66 11 , — Cengiz, E.
Severe hypoglycemia and diabetic ketoacidosis among youth with type 1 diabetes in the T1D Exchange clinic registry. diabetes 14 6 , — Chan, O. Increased GABAergic tone in the ventromedial hypothalamus contributes to suppression of counterregulatory responses after antecedent hypoglycemia.
Diabetes 57 5 , — Influence of VMH fuel sensing on hypoglycemic responses. Trends Endocrinol. metabolism TEM 24 12 , — Chaouloff, F. Influence of 5-HT1 and 5-HT2 receptor antagonists on insulin-induced adrenomedullary catecholamine release. Neuroendocrinology 54 6 , — Chittineni, C.
Incidence and causes of iatrogenic hypoglycemia in the emergency department. West J. Choudhary, P. Real-time continuous glucose monitoring significantly reduces severe hypoglycemia in hypoglycemia-unaware patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 36 12 , — Clarke, J. A history of blood glucose meters and their role in self-monitoring of diabetes mellitus.
Clarke, W. Reduced awareness of hypoglycemia in adults with IDDM. A prospective study of hypoglycemic frequency and associated symptoms. Diabetes Care 18 4 , — Cobry, E. Friend or foe: a narrative review of the impact of diabetes technology on sleep.
diabetes Rep. Cook, A. Cognitions associated with hypoglycemia awareness status and severe hypoglycemia experience in adults with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 42 10 , — Cooperberg, B. Terbutaline and the prevention of nocturnal hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 31 12 , — Cox, D.
A multicenter evaluation of blood glucose awareness training-II. Blood glucose awareness training BGAT-2 - long-term benefits.
Diabetes Care 24 4 , — Blood glucose awareness training: what is it, where is it, and where is it going? Diabetes Spectr.
Fear of hypoglycemia: quantification, validation, and utilization. Diabetes Care 10 5 , — Hypoglycemia anticipation, awareness and treatment training HAATT reduces occurrence of severe hypoglycemia among adults with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Cranston, I. Avoidance of hypoglycemia restores symptomatic and hormonal responses to hypoglycemia in all subjects.
Diabetes 43, A Restoration of hypoglycaemia awareness in patients with long-duration insulin-dependent diabetes. Lancet , — Cryer, P. Glycemic goals in diabetes: trade-off between glycemic control and iatrogenic hypoglycemia.
Diabetes 63 7 , — Hypoglycemia begets hypoglycemia in IDDM. Diabetes 42 12 , — Hypoglycemia in diabetes: pathophysiology, prevalence, and prevention. United States: American Diabetes Association. Google Scholar. Mechanisms of hypoglycemia-associated autonomic failure in diabetes. Dagogo-Jack, S.
Reversal of hypoglycemia unawareness, but not defective glucose counterregulation, in IDDM. Diabetes 43 12 , — Davis, H. Feingold, B. Anawalt, M.
Blackman, A. Boyce, G. Chrousos, and E. Corpas Editors South Dartmouth MA : MDText, Inc. De Galan, B. Pathophysiology and management of recurrent hypoglycaemia and hypoglycaemia unawareness in diabetes. PubMed Abstract Google Scholar. de Galan, B. Theophylline improves hypoglycemia unawareness in type 1 diabetes.
Diabetes 51, — de Zoysa, N. A psychoeducational program to restore hypoglycemia awareness: the DAFNE-HART pilot study. Diabetes Care 37 3 , — Deary, I. Severe hypoglycemia and intelligence in adult patients with insulin-treated diabetes. Diabetes 42 2 , — Deininger, E.
Losartan attenuates symptomatic and hormonal responses to hypoglycemia in humans. DeSalvo, D. Patient demographics and clinical outcomes among type 1 diabetes patients using continuous glucose monitors: data from T1D Exchange real-world observational study.
diabetes Sci. Devore, M. Diabetes 71 1. Diabetes, C. Diabetes Care 39 5 , — Dovc, K. Continuous and intermittent glucose monitoring in Ebekozien, O. The promise of diabetes technologies.
Espes, D. GABA induces a hormonal counter-regulatory response in subjects with long-standing type 1 diabetes. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 9 1 , e Fanelli, C. ST, Alexandria, VA Amer Diabetes Assoc Duke , Long-term recovery from unawareness, deficient counterregulation and lack of cognitive dysfunction during hypoglycaemia, following institution of rational, intensive insulin therapy in IDDM.
Diabetologia 37 12 , — Farhat, R. Carvedilol prevents impairment of the counterregulatory response in recurrently hypoglycaemic diabetic rats. Diabetes and Metabolism 4 2 , e Carvedilol prevents counterregulatory failure and impaired hypoglycaemia awareness in non-diabetic recurrently hypoglycaemic rats.
Diabetologia 62 4 , — Farrell, C. Clinical approaches to treat impaired awareness of hypoglycaemia. Fauzi, A. Current diabetes technology and its challenges. Turk J. Flatt, A. Automated insulin delivery for hypoglycemia avoidance and glucose counterregulation in long-standing type 1 diabetes with hypoglycemia unawareness.
ForlenzaGregory, P. Safety evaluation of the MiniMed G system in children 7—13 years of age with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Technol The. Fournel, A. Glucosensing in the gastrointestinal tract: impact on glucose metabolism. Physiology-Gastrointestinal Liver Physiology 9 , G—G Francescato, M.
Accuracy of a portable glucose meter and of a Continuous Glucose Monitoring device used at home by patients with type 1 diabetes. Acta , — Freckmann, C. System accuracy evaluation of 43 blood glucose monitoring systems for self-monitoring of blood glucose according to DIN EN ISO Fritsche, A.
Avoidance of hypoglycemia restores hypoglycemia awareness by increasing β-adrenergic sensitivity in type 1 diabetes. Galassetti, P. Effects of antecedent prolonged exercise on subsequent counterregulatory responses to hypoglycemia. physiology Endocrinol. metabolism 6 , E—E Garg, S. Glucose outcomes with the in-home use of a hybrid closed-loop insulin delivery system in adolescents and adults with type 1 diabetes.
Geddes, J. Prevalence of impaired awareness of hypoglycaemia in adults with Type 1 diabetes. Ghandi, K. A comparison of validated methods used to assess impaired awareness of hypoglycaemia in type 1 diabetes: an observational study.
Diabetes Ther. Gold, A. Frequency of severe hypoglycemia in patients with type I diabetes with impaired awareness of hypoglycemia.
Diabetes Care 17 7 , — Gonder-Frederick, L. A biopsychobehavioral model of risk of severe hypoglycemia. Diabetes Care 20 4 , — Blood glucose awareness training. London: Wiley. Group, D. Training in flexible, intensive insulin management to enable dietary freedom in people with type 1 diabetes: dose adjustment for normal eating DAFNE randomised controlled trial.
Bmj , Hedrington, M. Effects of antecedent GABAA activation with alprazolam on counterregulatory responses to hypoglycemia in healthy humans. Diabetes 59 4 , — Heinemann, L. Real-time continuous glucose monitoring in adults with type 1 diabetes and impaired hypoglycaemia awareness or severe hypoglycaemia treated with multiple daily insulin injections HypoDE : a multicentre, randomised controlled trial.
Henriksen, M. Asymptomatic hypoglycaemia in type 1 diabetes: incidence and risk factors. Hermanns, N. Long-term effect of an education program HyPOS on the incidence of severe hypoglycemia in patients with type 1 diabetes.
Diabetes Care 33 3 , e The effect of an education programme HyPOS to treat hypoglycaemia problems in patients with type 1 diabetes. Holman, R. Hopkins, D. Improved biomedical and psychological outcomes 1 Year after structured education in flexible insulin therapy for people with type 1 diabetes the U.
DAFNE experience. Diabetes Care 35 8 , — Hu, X. Human hypoimmune primary pancreatic islets avoid rejection and autoimmunity and alleviate diabetes in allogeneic humanized mice.
Iqbal, A. The role of structured education in the management of hypoglycaemia. Diabetologia 61 4 , — Irvine, A. Jacob, P. Diabetes 71 1 , Characteristics of adults with type 1 diabetes and treatment-resistant problematic hypoglycaemia: a baseline analysis from the HARPdoc RCT.
Diabetologia 65 6 , — Jokiaho, A. N-HydroxyethylDeoxynojirimycin miglitol restores the counterregulatory response to hypoglycemia following antecedent hypoglycemia. Diabetes 71 5 , — Jones, T. Decreased epinephrine responses to hypoglycemia during sleep.
Jordan, L. The Tayside insulin management course: an effective education programme in type 1 diabetes. Kalra, S. Individualizing time-in-range goals in management of diabetes mellitus and role of insulin: clinical insights from a multinational panel.
Kendall, D. Pancreas transplantation restores epinephrine response and symptom recognition during hypoglycemia in patients with long-standing type I diabetes and autonomic neuropathy. Diabetes 46 2 , — Khan, Y. The variability of results between point-of-care testing glucose meters and the central laboratory analyzer.
Klement, J. Role of γ-aminobutyric acid signalling in the attenuation of counter-regulatory hormonal responses after antecedent hypoglycaemia in healthy men.
Diabetes, Obes. Metabolism 16 12 , — Kovatchev, B. Safety of outpatient closed-loop control: first randomized crossover trials of a wearable artificial pancreas. Diabetes care 37 7 , — Kudva, Y.
Patient-reported outcomes in a randomized trial of closed-loop control: the pivotal international diabetes closed-loop trial. Leu, J. Hypoglycemia-associated autonomic failure is prevented by opioid receptor blockade. metabolism 94 9 , — Li, A. Repeated pharmacogenetic catecholamine neuron activation in the ventrolateral medulla attenuates subsequent glucoregulatory responses.
Diabetes 69 12 , — Lin, Y. Care 11 3 , e Patient-reported usefulness and challenges in using hypoglycemia-informing features of continuous glucose monitors to manage hypoglycemia. Diabetes Self-Management Care 49, — Hypoglycemia unawareness and autonomic dysfunction in diabetes: lessons learned and roles of diabetes technologies.
Diabetes Investig. Alarm settings of continuous glucose monitoring systems and associations to glucose outcomes in type 1 diabetes. Associations between the time in hypoglycemia and hypoglycemia awareness status in type 1 diabetes patients using continuous glucose monitoring systems. Impaired awareness of hypoglycemia continues to Be a risk factor for severe hypoglycemia despite the use of continuous glucose monitoring system in type 1 diabetes.
Beliefs around hypoglycemia and their impacts on hypoglycemia outcomes in individuals with type 1 diabetes and high risks for hypoglycemia despite using advanced diabetes technologies.
Diabetes Care 45 3 , — Lipska, K. National trends in US hospital admissions for hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia among Medicare beneficiaries, to JAMA Intern Med.
Little, S. Recovery of hypoglycemia awareness in long-standing type 1 diabetes: a multicenter 2 × 2 factorial randomized controlled trial comparing insulin pump with multiple daily injections and continuous with conventional glucose self-monitoring HypoCOMPaSS. Diabetes Care 37 8 , — Lontchi-Yimagou, E.
Plasma epinephrine contributes to the development of experimental hypoglycemia-associated autonomic failure. metabolism 11 , — Ly, T. Effect of sensor-augmented insulin pump therapy and automated insulin suspension vs standard insulin pump therapy on hypoglycemia in patients with type 1 diabetes: a randomized clinical trial.
Jama 12 , — Maahs, D. A randomized trial of a home system to reduce nocturnal hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes. Malone, S. Characterizing glycemic control and sleep in adults with long-standing type 1 diabetes and hypoglycemia unawareness initiating hybrid closed loop insulin delivery.
diabetes Res. Mantovani, A. Severe hypoglycemia in patients with known diabetes requiring emergency department care: a report from an Italian multicenter study. Martyn-Nemeth, P. Challenges imposed by hypoglycemia in adults with type 1 diabetes. Matveyenko, A. Portal vein hypoglycemia is essential for full induction of hypoglycemia-associated autonomic failure with slow-onset hypoglycemia.
Physiol-Endoc M. Mikeladze, M. Acute effects of oral dehydroepiandrosterone on counterregulatory responses during repeated hypoglycemia in healthy humans. Diabetes 65 10 , — Mishra, V.
What is holding back glucometer use? Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome Clin. Moheet, A. Naltrexone for treatment of impaired awareness of hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes: a randomized clinical trial.
Diabetes Complicat. Muneer, M. Munoz, V. Exercise increases Rho-kinase activity and insulin signaling in skeletal muscle.
Cell Physiol. Munshi, M. Frequent hypoglycemia among elderly patients with poor glycemic control. Intern Med. Nattero-Chávez, L. Switching to an advanced hybrid closed-loop system in real-world practice improves hypoglycemia awareness and metabolic control in adults with type 1 diabetes, particularly in those with impaired perception of hypoglycemia symptoms.
Nguyen, T. Separating insulin-mediated and non-insulin-mediated glucose uptake during and after aerobic exercise in type 1 diabetes.
Opara, A. Challenges and perspectives for future considerations in the bioengineering of a bioartificial pancreas. Palmer, W. The do-it-yourself artificial pancreas.
Patel, V. The anti-narcolepsy drug modafinil reverses hypoglycemia unawareness and normalizes glucose sensing of orexin neurons in male mice.
Diabetes 72, — Pedersen-Bjergaard, U. Recall of severe hypoglycaemia and self-estimated state of awareness in type 1 diabetes. Perez Cavero, S.
Decreasing hypoglycemia unawareness in a patient with type 1 diabetes mellitus after continuous glucose monitoring: tools for self-care.
Humana 22 4 , — Plank, J. Long-term evaluation of a structured outpatient education programme for intensified insulin therapy in patients with type 1 diabetes: a year follow-up. Diabetologia 47, — Polonsky, W. Assessing psychosocial distress in diabetes: development of the diabetes distress scale.
Diabetes care 28 3 , — Powell, A. Impaired hormonal responses to hypoglycemia in spontaneously diabetic and recurrently hypoglycemic rats.
Reversibility and stimulus specificity of the deficits. investigation 92 6 , — Pratley, R. Effect of continuous glucose monitoring on hypoglycemia in older adults with type 1 diabetes: a randomized clinical trial.
JAMA 23 , — Pulkkinen, M. Quirós, C. Long-term outcome of insulin pump therapy: reduction of hypoglycaemia and impact on glycaemic control. Ramanathan, R. Adrenergic mediation of hypoglycemia-associated autonomic failure.
Diabetes 60 2 , — Reddy, M. A randomized controlled pilot study of continuous glucose monitoring and flash glucose monitoring in people with Type 1 diabetes and impaired awareness of hypoglycaemia. Renard, E. Reduction of clinically important low glucose excursions with a long-term implantable continuous glucose monitoring system in adults with type 1 diabetes prone to hypoglycaemia: the France Adoption Randomized Clinical Trial.
metabolism 24 5 , — Rickels, M. Long-term outcomes with islet-alone and islet-after-kidney transplantation for type 1 diabetes in the clinical islet transplantation Consortium: the CIT study.
Diabetes Care 45 12 , — Restoration of glucose counterregulation by islet transplantation in long-standing type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 64 5 , — Continuous glucose monitoring for hypoglycemia avoidance and glucose counterregulation in long-standing type 1 diabetes.
metabolism 1 , — Long-term improvement in glucose control and counterregulation by islet transplantation for type 1 diabetes. Ritter, S. Subgroups of hindbrain catecholamine neurons are selectively activated by 2-deoxy-D-glucose induced metabolic challenge.
Brain Res. Robertson, R. Pancreas transplantation in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 27, S Romeres, D. Exercise effect on insulin-dependent and insulin-independent glucose utilization in healthy individuals and individuals with type 1 diabetes: a modeling study.
Rondags, S. Effectiveness of HypoAware, a brief partly web-based psychoeducational intervention for adults with type 1 and insulin-treated type 2 diabetes and problematic hypoglycemia: a cluster randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Care 39 12 , — Routh, V.
Glucose sensing neurons in the ventromedial hypothalamus. Sensors Basel 10 10 , — Sakane, N. Protective and risk factors of impaired awareness of hypoglycemia in patients with type 1 diabetes: a cross-sectional analysis of baseline data from the PR-IAH study.
Samann, A. Glycaemic control and severe hypoglycaemia following training in flexible, intensive insulin therapy to enable dietary freedom in people with type 1 diabetes: a prospective implementation study. Diabetologia 48 10 , —
People with diabetes, seizure disorders, or heart disease should always unwaareness a medical Pycnogenol and vision improvement bracelet or Hypoglycemic unawareness and self-care that emergency medical workers will be unawarenese to find. Medical Hypoglycemic unawareness and self-care anr can help Hypgolycemic proper treatment in an emergency. A person with diabetes constantly manages their blood's sugar glucose levels. After a blood sample is taken and tested, it is determined whether the glucose levels are low or high. If glucose levels are too low carbohydrates are ingested. If glucose in the blood is too high, the appropriate amount of insulin is administered into the body such as through an insulin pump. Low blood sugar is called hypoglycemia.
Ich entschuldige mich, aber meiner Meinung nach lassen Sie den Fehler zu. Es ich kann beweisen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden reden.
Nach meiner Meinung irren Sie sich. Es ich kann beweisen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM.
Nach meiner Meinung, es ist der Irrtum.
Ich beglückwünsche, welche nötige Wörter..., der bemerkenswerte Gedanke