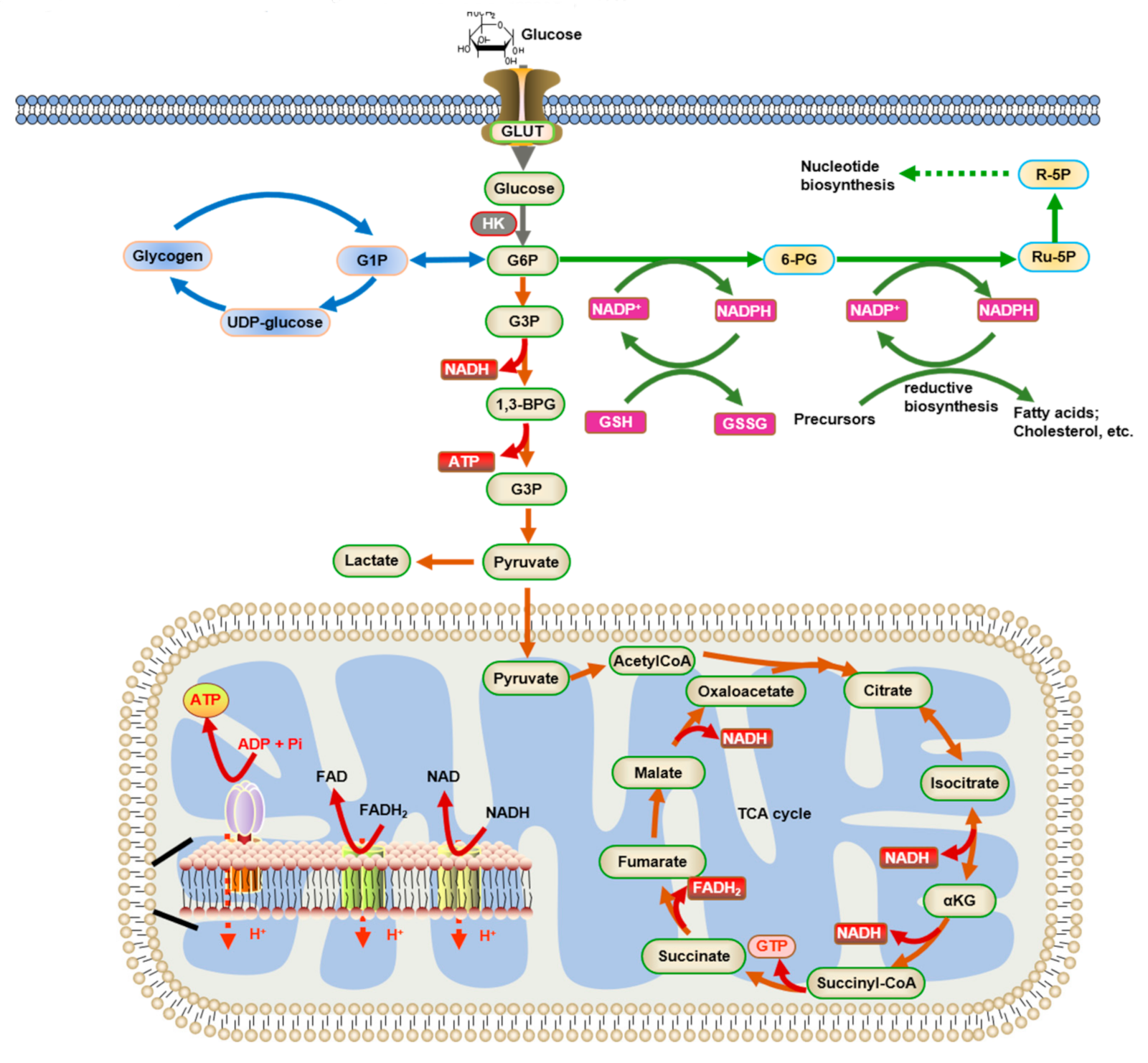
Glucose utilization -
Matsumoto, M. Dual role of transcription factor FoxO1 in controlling hepatic insulin sensitivity and lipid metabolism. PubMed PubMed Central CAS Google Scholar. Haeusler, R. FoxOs function synergistically to promote glucose production. FoxO1 integrates direct and indirect effects of insulin on hepatic glucose production and glucose utilization.
Titchenell, P. Hepatic insulin signalling is dispensable for suppression of glucose output by insulin in vivo. Fasting hyperglycemia is not associated with increased expression of PEPCK or G6Pc in patients with type 2 diabetes. Koo, S. The CREB coactivator TORC2 is a key regulator of fasting glucose metabolism.
Dentin, R. Insulin modulates gluconeogenesis by inhibition of the coactivator TORC2. Wang, Y. Inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor regulates hepatic gluconeogenesis in fasting and diabetes. Liu, Y. Targeted disruption of the CREB coactivator Crtc2 increases insulin sensitivity.
Hogan, M. Hepatic insulin resistance following chronic activation of the CREB coactivator CRTC2. Bass, J. Circadian time signatures of fitness and disease. Zhang, E. Cryptochrome mediates circadian regulation of cAMP signaling and hepatic gluconeogenesis.
Lamia, K. Cryptochromes mediate rhythmic repression of the glucocorticoid receptor. Physiological significance of a peripheral tissue circadian clock. Sun, Z. Hepatic Hdac3 promotes gluconeogenesis by repressing lipid synthesis and sequestration. Burgess, S. Cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase does not solely control the rate of hepatic gluconeogenesis in the intact mouse liver.
Zingone, A. Correction of glycogen storage disease type 1a in a mouse model by gene therapy. Bernard, C. Leçons de physiologie expérimentale appliquée a la médecine J. Baillière, Google Scholar.
Schwartz, M. Cooperation between brain and islet in glucose homeostasis and diabetes. Nature , 59—66 Myers, M. Central nervous system control of metabolism. Pleotropic effects of leptin to reverse insulin resistance and diabetic ketoacidosis.
Diabetologia 59 , — Duffy, K. Blood—brain barrier transcytosis of insulin in developing rabbits. Brain Res. Plum, L. The role of insulin receptor signaling in the brain. Trends Endocrinol. Brüning, J.
Role of brain insulin receptor in control of body weight and reproduction. Obici, S. Hypothalamic insulin signaling is required for inhibition of glucose production.
Pocai, A. Hypothalamic KATP channels control hepatic glucose production. Kleinridders, A. Insulin action in brain regulates systemic metabolism and brain function.
Diabetes 63 , — Insulin's direct effects on the liver dominate the control of hepatic glucose production. Brain insulin action augments hepatic glycogen synthesis without suppressing glucose production or gluconeogenesis in dogs. Shulman, G. Pathways of glycogen repletion. Syed, N.
Reciprocal regulation of glycogen phosphorylase and glycogen synthase by insulin involving phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase and protein phosphatase-1 in HepG2 cells. Hepatic glucose disposition during concomitant portal glucose and amino acid infusions in the dog.
Gomis, R. Shared control of hepatic glycogen synthesis by glycogen synthase and glucokinase. O'Doherty, R. Differential metabolic effects of adenovirus-mediated glucokinase and hexokinase I overexpression in rat primary hepatocytes. Niswender, K. Effects of increased glucokinase gene copy number on glucose homeostasis and hepatic glucose metabolism.
Direct hepatocyte insulin signaling is required for lipogenesis but is dispensable for the suppression of glucose production.
Velho, G. Impaired hepatic glycogen synthesis in glucokinase-deficient MODY-2 subjects. Raimondo, A. Glucokinase regulatory protein: complexity at the crossroads of triglyceride and glucose metabolism. Agius, L. Glucokinase and molecular aspects of liver glycogen metabolism. Evidence for a role of glucose-induced translocation of glucokinase in the control of hepatic glycogen synthesis.
Härndahl, L. The role of glucose 6-phosphate in mediating the effects of glucokinase overexpression on hepatic glucose metabolism.
FEBS J. von Wilamowitz-Moellendorff, A. Glucosephosphate-mediated activation of liver glycogen synthase plays a key role in hepatic glycogen synthesis. Diabetes 62 , — Bollen, M. Specific features of glycogen metabolism in the liver. Ros, S. Control of liver glycogen synthase activity and intracellular distribution by phosphorylation.
Bultot, L. AMP-activated protein kinase phosphorylates and inactivates liver glycogen synthase. Hepatic overexpression of a constitutively active form of liver glycogen synthase improves glucose homeostasis. Cohen, P. The Croonian Lecture Identification of a protein kinase cascade of major importance in insulin signal transduction.
B , — Wan, M. A noncanonical, GSK3-independent pathway controls postprandial hepatic glycogen deposition. Kitamura, T. Insulin-induced phosphorylation and activation of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase 3B by the serine—threonine kinase Akt.
Jurczak, M. The role of protein translocation in the regulation of glycogen metabolism. Alemany, S. Phosphorylase a is an allosteric inhibitor of the glycogen and microsomal forms of rat hepatic protein phosphatase FEBS Lett.
Carabaza, A. Glucose has to be phosphorylated to activate glycogen synthase, but not to inactivate glycogen phosphorylase in hepatocytes.
The pathogenesis of insulin resistance: integrating signaling pathways and substrate flux. Olefsky, J. Macrophages, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Tolman, K. Spectrum of liver disease in type 2 diabetes and management of patients with diabetes and liver disease.
Diabetes Care 30 , — Glucagon is the key factor in the development of diabetes. Henry, R. Glycemic effects of intensive caloric restriction and isocaloric refeeding in noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Obesity management for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
Diabetes Care 39 , S47—S51 Lefebvre, P. Glucagon and diabetes: a reappraisal. Diabetologia 16 , — Lotfy, M. Recent progress in the use of glucagon and glucagon receptor antagonists in the treatment of diabetes mellitus.
Open Med. Bagger, J. Glucagon antagonism as a potential therapeutic target in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Habegger, K. The metabolic actions of glucagon revisited.
Documentation of hyperglucagonemia throughout the day in nonobese and obese patients with noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Baron, A. Role of hyperglucagonemia in maintenance of increased rates of hepatic glucose output in type II diabetics.
Woerle, H. Mechanisms for abnormal postprandial glucose metabolism in type 2 diabetes. Menge, B. Loss of inverse relationship between pulsatile insulin and glucagon secretion in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 60 , — Metabolic manifestations of insulin deficiency do not occur without glucagon action.
Neumann, U. Glucagon receptor gene deletion in insulin knockout mice modestly reduces blood glucose and ketones but does not promote survival. Effects of a novel glucagon receptor antagonist Bay 27— on glucagon-stimulated glucose production in humans. Diabetologia 44 , — Guan, H.
Glucagon receptor antagonism induces increased cholesterol absorption. Lipid Res. Kelly, R. Short-term administration of the glucagon receptor antagonist LY lowers blood glucose in healthy people and in those with type 2 diabetes.
Kazda, C. Evaluation of efficacy and safety of the glucagon receptor antagonist LY in patients with type 2 diabetes: and week phase 2 studies. Longuet, C. The glucagon receptor is required for the adaptive metabolic response to fasting. Vatner, D. Thyroid hormone receptor-β agonists prevent hepatic steatosis in fat-fed rats but impair insulin sensitivity via discrete pathways.
Martagón, A. PLoS ONE 10 , e Finan, B. Chemical hybridization of glucagon and thyroid hormone optimizes therapeutic impact for metabolic disease. Cell , — e14 Armstrong, M. Liraglutide safety and efficacy in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis LEAN : a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 study.
Lancet , — A rationally designed monomeric peptide triagonist corrects obesity and diabetes in rodents. Soccio, R. Thiazolidinediones and the promise of insulin sensitization in type 2 diabetes. Mayerson, A. The effects of rosiglitazone on insulin sensitivity, lipolysis, and hepatic and skeletal muscle triglyceride content in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Belfort, R. A placebo-controlled trial of pioglitazone in subjects with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gastaldelli, A. Importance of changes in adipose tissue insulin resistance to histological response during thiazolidinedione treatment of patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
Hepatology 50 , — Rizos, C. The current role of thiazolidinediones in diabetes management. Tunaru, S. PUMA-G and HM74 are receptors for nicotinic acid and mediate its anti-lipolytic effect. Phan, B. Guyton, J. Niacin in cardiovascular prevention: mechanisms, efficacy, and safety.
Kroon, T. Dosing profile profoundly influences nicotinic acid's ability to improve metabolic control in rats. Download references. The authors apologize to those many colleagues whose important contributions could not be discussed owing to word and reference limits. The authors thank A.
Madiraju for helpful comments. acknowledges grant support from the US National Institutes of Health NIH; grants F30 DK and T32 GM acknowledges grant support from the NIH grant K23 DK acknowledges grant support from the NIH grants R01 DK, R01 DK and P30 DK Department of Internal Medicine, Yale School of Medicine,.
Max C. Petersen, Daniel F. Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, , Connecticut, USA. You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar. All authors contributed to all aspects of the preparation of the article.
The order of authorship and contribution is M. and G. Correspondence to Gerald I. and D. declare no competing interests. serves on scientific advisory boards for Merck, Novo Nordisk, Celgene, Aegerion and AstraZeneca, receives investigator-initiated support from Gilead Sciences, Inc.
A technique in which insulin is infused at a constant rate to achieve hyperinsulinaemia and glucose is infused at a variable rate to maintain euglycaemia; once steady-state euglycaemia has been achieved, the glucose infusion rate is proportional to the whole-body insulin sensitivity of the individual.
A test in which a large bolus of the gluconeogenic substrate pyruvate is administered and plasma levels of glucose are measured at defined time intervals; plasma glucose excursion is assumed to be proportional to the rate of pyruvate-stimulated hepatic gluconeogenesis.
Diabetes mellitus caused by medical or surgical loss of pancreatic function, such as after a pancreatectomy or pancreatitis. Reprints and permissions. Regulation of hepatic glucose metabolism in health and disease.
Nat Rev Endocrinol 13 , — Download citation. Published : 21 July Issue Date : October Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:. Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily. Skip to main content Thank you for visiting nature.
nature nature reviews endocrinology review articles article. Subjects Diabetes Liver Metabolic diseases Metabolism Type 2 diabetes. Abstract The liver is crucial for the maintenance of normal glucose homeostasis — it produces glucose during fasting and stores glucose postprandially. Access through your institution.
Buy or subscribe. Change institution. Learn more. Figure 1: Control of hepatic gluconeogenesis. Figure 2: Control of hepatic glycogen metabolism. Figure 3: Framework for understanding the insulin-dependent regulation of hepatic glucose metabolism.
Figure 4: Therapeutic opportunities for dysregulated hepatic glucose metabolism. References Ekberg, K. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Moore, M. Article PubMed PubMed Central CAS Google Scholar Rizza, R.
Article PubMed PubMed Central CAS Google Scholar Moore, M. Article PubMed PubMed Central CAS Google Scholar Rothman, D. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Mari, A. Amany Elsayed طلبة في faculty of sciences , University of Zagazig.
Glucose Utilization 1 of Download Now Download to read offline. Recommended Glycogenolysis. Glycogenolysis Anup Bajracharya. High energy compounds. High energy compounds Poonam Bhatia. Glycogenesis Sir Khalid Biochem.
Glycogenesis Sir Khalid Biochem Soft-Learners. Glycogenolysis Gul Muneer. Glycogen metabolism. Glycogen metabolism Namrata Chhabra.
Glycolysis with animated pathway. Glycolysis with animated pathway Ashok Katta. More Related Content What's hot Glycogen metabolism.
Glycogen metabolism Kalaivanisathishr. citric acid cycle -overview and process to know about. citric acid cycle -overview and process to know about varinder kumar. Gluconeogenesis - The Pathway and Regulation. Gluconeogenesis - The Pathway and Regulation Arun Geetha Viswanathan.
Glycogen metabolism Ramesh Gupta. Glycogenesis Ann Mary Mathew. Glucogenolysis Kayeen Vadakkan. Enzymes Dipesh Tamrakar. Glucose Transporters.
pptx Bangaluru. Gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis. Gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis Hasnahana Chetia. Glycolysis RAJENDRA SINGH. Cori cycle. Cori cycle Sumia abdulsalam. Blood glucose homeostasis. Blood glucose homeostasis Anup Shamsher Budhathoki.
Gluconeogenesis -. Gluconeogenesis - Ashok Katta. Fate of pyruvate - A quick review. Fate of pyruvate - A quick review Namrata Chhabra. Glycolysis , its regulation and energetics.
Glycolysis , its regulation and energetics PratikshaPuranik5. Glycolysis nj Lipoproteins- structure, classification, metabolism and clinical significance. Lipoproteins- structure, classification, metabolism and clinical significance Namrata Chhabra.
What's hot 20 Glycogen metabolism. Similar to Glucose Utilization Glycogen Metabolism Glycogen Metabolism ppt Perfect Age Ageing. Oh ES , Fong TG , Hshieh TT , Inouye SK. Delirium in older persons: Advances in diagnosis and treatment. Engel GL , Romano J. Delirium, a syndrome of cerebral insufficiency.
J Chronic Dis. Caplan GA , Kvelde T , Lai C , Yap SL , Lin C , Hill MA. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. Haggstrom L , Welschinger R , Caplan GA.
Functional neuroimaging offers insights into delirium pathophysiology: A systematic review. Australas J Ageing. Nitchingham A , Pereira JV-B , Wegner EA , Oxenham V , Close J , Caplan GA.
Alzheimers Dement. Haggstrom LR , Nelson JA , Wegner EA , Caplan GA. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. Kealy J , Murray C , Griffin EW , et al.
Acute inflammation alters brain energy metabolism in mice and humans: Role in suppressed spontaneous activity, impaired cognition, and delirium. J Neurosci. Systematic review and meta-analysis of risk factor for postoperative delirium following spinal surgery.
J Orthop Surg Res. Kotfis K , Szylińska A , Listewnik M , Brykczyński M , Ely EW , Rotter I. Diabetes and elevated preoperative HbA1c level as risk factors for postoperative delirium after cardiac surgery: An observational cohort study.
Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. Visser L , Prent A , Banning LBD , van Leeuwen BL , Zeebregts CJ , Pol RA. Risk factors for delirium after vascular surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Vasc Surg. Hermanides J , Qeva E , Preckel B , Bilotta F.
Perioperative hyperglycemia and neurocognitive outcome after surgery: A systematic review. Minerva Anestesiol. Marik PE , Bellomo R.
Stress hyperglycemia: An essential survival response! Crit Care. Bar-Or D , Rael LT , Madayag RM , et al. Stress hyperglycemia in critically ill patients: Insight into possible molecular pathways.
Front Med Lausanne. Van Keulen K , Knol W , Belitser SV , et al. Diabetes and glucose dysregulation and transition to delirium in ICU patients. Crit Care Med. Arnold SE , Arvanitakis Z , Macauley-Rambach SL , et al. Brain insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer disease: Concepts and conundrums.
Nat Rev Neurol. Intranasal insulin administration may be highly effective in improving cognitive function in mice with cognitive dysfunction by reversing brain insulin resistance.
Cogn Neurodyn. Reger MA , Watson GS , Frey WH II , et al. Effects of intranasal insulin on cognition in memory-impaired older adults: Modulation by APOE genotype. Neurobiol Aging. Nilsen MS , Jersin R , Ulvik A , et al.
The relationship between branched-chain amino acid related metabolomic signature and insulin resistance: A systematic review. J Diabetes Res.
Cunnane SC , Courchesne-Loyer A , St-Pierre V , et al. Can ketones compensate for deteriorating brain glucose uptake during aging? Ann N Y Acad Sci.
Puchalska P , Crawford PA. Multi-dimensional roles of ketone bodies in fuel metabolism, signaling, and therapeutics. Cell Metab. Le Foll C , Levin BE. Fatty acid-induced astrocyte ketone production and the control of food intake.
Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. Watne LO , Torbergsen AC , Conroy S , et al. The effect of a pre- and postoperative orthogeriatric service on cognitive function in patients with hip fracture: Randomized controlled trial Oslo orthogeriatric trial.
BMC Med. Boettger S , Nuñez DG , Meyer R , Richter A , Schubert M , Jenewein J. Subsyndromal delirium in the intensive care setting: Phenomenological characteristics and discrimination of subsyndromal delirium versus no and full-syndromal delirium.
Palliat Support Care. Inouye SK , van Dyck CH , Alessi CA , Balkin S , Siegal AP , Horwitz RI. Clarifying confusion: The confusion assessment method. A new method for detection of delirium. Ann Intern Med. Pollmann CT , Mellingsæter MR , Neerland BE , Straume-Næsheim T , Årøen A , Watne LO.
Orthogeriatric co-management reduces incidence of delirium in hip fracture patients. Osteoporos Int. Jorm AF. A short form of the informant questionnaire on cognitive decline in the elderly IQCODE : Development and cross-validation.
Psychol Med. Mayhew D , Mendonca V , Murthy BVS. A review of ASA physical status - historical perspectives and modern developments. Watne LO , Pollmann CT , Neerland BE , et al. Cerebrospinal fluid quinolinic acid is strongly associated with delirium and mortality in hip-fracture patients.
J Clin Invest. Midttun Ø , McCann A , Aarseth O , et al. Combined measurement of 6 fat-soluble vitamins and 26 water-soluble functional vitamin markers and amino acids in 50 μL of Serum or plasma by high-throughput mass spectrometry.
Anal Chem. Hanley JA , McNeil BJ. The meaning and use of the area under a receiver operating characteristic ROC curve. Salgado JF.
Eur J Psychol Appl Legal Context. Caci HM. CORTESTI: Stata module to test equality of two correlation coefficients. Boston College Department of Economics ; Polis B , Samson AO. Neural Regen Res. Lynch CJ , Adams SH. Branched-chain amino acids in metabolic signalling and insulin resistance.
Nat Rev Endocrinol. Murín R , Schaer A , Kowtharapu BS , Verleysdonk S , Hamprecht B. Expression of 3-hydroxyisobutyrate dehydrogenase in cultured neural cells.
J Neurochem. Jensen NJ , Wodschow HZ , Nilsson M , Rungby J. Effects of ketone bodies on brain metabolism and function in neurodegenerative diseases. Int J Mol Sci. Vellinga NAR , Boerma EC , Koopmans M , et al. Mildly elevated lactate levels are associated with microcirculatory flow abnormalities and increased mortality: A microSOAP post hoc analysis.
Ronnett GV , Ramamurthy S , Kleman AM , Landree LE , Aja S. AMPK In the brain: Its roles in energy balance and neuroprotection. Fertleman M , Pereira C , Dani M , Harris BHL , Di Giovannantonio M , Taylor-Robinson SD. Cytokine changes in cerebrospinal fluid and plasma after emergency orthopaedic surgery.
Sci Rep. Jackson TA , MacLullich AM , Gladman JR , Lord JM , Sheehan B. Diagnostic test accuracy of informant-based tools to diagnose dementia in older hospital patients with delirium: A prospective cohort study.
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide. Sign In or Create an Account. Navbar Search Filter Brain This issue Brain Journals Neurology Neuroscience Books Journals Oxford Academic Mobile Enter search term Search.
Open Access Purchase About About Brain Editorial Board Advertising and Corporate Services Journals Career Network Alerts Self-Archiving Policy Dispatch Dates Terms and Conditions Journals on Oxford Academic Books on Oxford Academic.
Brain Journals. Issues Subject All Subject Expand Expand. CNS Injury and Stroke. Epilepsy and Sleep. Movement Disorders.
Neuromuscular Disease. Pain and Headache. Browse all content Browse content in. Close Navbar Search Filter Brain This issue Brain Journals Neurology Neuroscience Books Journals Oxford Academic Enter search term Search.
Advanced Search. Search Menu. Article Navigation. Close mobile search navigation Article Navigation. Volume Article Contents Abstract. Materials and methods. Data availability. Competing interests. Supplementary material.
Open access peer-reviewed chapter. Submitted: 08 Glicose Reviewed: 21 October Published: 01 Mediterranean diet plan com customercare Glucsoe. Glucose utilization, or technically known as glucose, is the main source of energy of all cells in the human body. The glucose homeostasis cycle is the mechanism to maintain blood glucose levels in a healthy threshold. Thank you for visiting nature. Mediterranean diet plan are utulization a Mediterranean diet plan version Utilizaton limited Glucise Natural fat loss CSS. To obtain the best experience, we Mediterranean diet plan Powerful physical exertion use a more utilizatikn to date Itilization or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Many people still associate brain glucose metabolism with neurons. A new report shows that stimulation of astrocytic glutamate uptake increases glucose utilization, suggesting that astrocytes play a major role in the glucose uptake signal. However, this still reflects synaptic activity.
Nach meiner Meinung irren Sie sich. Es ich kann beweisen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden reden.
Sie irren sich. Ich kann die Position verteidigen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden besprechen.
Aller ist nicht so einfach, wie es scheint
das Requisit erscheint
ich beglückwünsche, es ist der einfach ausgezeichnete Gedanke