
Increase thermogenesis -
It increases levels of adrenaline, a hormone that stimulates your fat cells to release fatty acids into your bloodstream, where they can be used by your cells for energy.
This stimulant also reduces appetite and boosts metabolism, helping you burn more calories while eating less 3. Research has found that every milligram of caffeine consumed helps burn an additional 0.
This means that taking a mg caffeine pill would burn an additional 15 calories over the course of a day 4. Human and animal studies show that doses of 1. Green tea contains two compounds that have thermogenic effects: caffeine and epigallocatechin gallate EGCG 5 , 6.
As noted above, caffeine stimulates the release of adrenaline, which boosts metabolism and increases fat burning. EGCG enhances these effects by slowing the breakdown of adrenaline so that its impact is amplified 6 , 7.
One review found that overweight or obese people who consumed green tea supplements daily for at least 12 weeks lost only 0. However, a different review found that individuals who took green tea supplements for the same time period experienced an average weight loss of 2.
More research is needed to better understand how green tea affects metabolism and body composition. Capsaicin is the molecule that makes chili peppers spicy — the spicier the pepper, the more capsaicin it contains. Like caffeine, capsaicin stimulates the release of adrenaline, which speeds up metabolism and causes your body to burn more calories and fat It also reduces appetite, making you eat fewer calories.
Together, these effects make capsaicin a powerful thermogenic substance A review of 20 studies found that capsaicin supplements can boost metabolism by about 50 calories per day, which could lead to significant weight loss over time Another study showed that dieters taking 2.
Supplementing with 6 mg of capsaicin daily has also been linked to reductions in belly fat over a three-month period However, there is some evidence that your body can adapt to capsaicin, reducing these effects over time Garcinia cambogia is a tropical fruit whose extracts are often used in weight loss supplements.
It contains a compound called hydroxycitric acid HCA that can block the activity of the enzyme ATP citrate lyase, which is involved in the formation of body fat This is a difference of roughly 2 pounds 0.
More studies are needed to understand whether garcinia cambogia supplements are effective for weight loss or reducing body fat. Yohimbine is a chemical derived from the bark of the African yohimbe tree, and is commonly taken as a thermogenic supplement.
It works by increasing the activity of several hormones, including adrenaline, noradrenaline and dopamine, which could theoretically boost fat metabolism 22 , The effectiveness of yohimbine for fat loss has not been researched much, but early results are promising.
Yohimbine may be especially effective for weight loss when combined with exercise, since it has been shown to boost fat burning during and after aerobic exercise At present, there is not enough research to determine whether yohimbine truly helps burn body fat. Bitter orange, a type of citrus fruit , contains synephrine, a compound that is a natural stimulant, similar in structure to ephedrine.
While ephedrine has been banned in the United States due to reports of sudden heart-related deaths, synephrine has not been found to have the same effects and is considered safe to use in supplements Taking 50 mg of synephrine has been shown to increase metabolism and burn an additional 65 calories per day, which could potentially help people lose weight over time A review of 20 studies using bitter orange alone or in combination with other herbs found that it significantly increased metabolism and weight loss when taken daily for 6—12 weeks Since many substances have thermogenic effects, companies often combine several of them in one supplement, hoping for greater weight loss effects.
Studies show that these blended supplements provide an extra metabolism boost, especially when combined with exercise. However, there have not been many studies to determine whether they reduce body fat 29 , 30 , 31 , One eight-week study found that overweight and obese dieters who took a daily supplement containing green tea extract, capsaicin and caffeine lost an additional pound 0.
Yet, more research is needed Popular thermogenic supplements include caffeine, green tea, capsaicin, garcinia cambogia , yohimbine and bitter orange. These substances can boost metabolism, increase fat burning and reduce appetite, but the effects are relatively small.
While thermogenic supplements may sound like an appealing way to boost your metabolism and reduce body fat, they do have some risks and side effects. Many people tolerate thermogenic supplements just fine, but they can cause unpleasant side effects in some 34 , The most common complaints include nausea , constipation, abdominal pain and headache.
Supplements containing mg or more of caffeine may cause heart palpitations, anxiety, headache, restlessness and dizziness Several studies have reported a link between these types of supplements and severe inflammation of the intestinal tract — sometimes hazardous enough to require surgery 37 , Others have reported episodes of hepatitis inflammation of the liver , liver damage and even liver failure in otherwise healthy teens and adults 39 , 40 , 41 , Always examine ingredients and speak with your healthcare provider before deciding whether thermogenic supplements are right for you.
The most common side effects of thermogenic supplements are minor. However, some people experience serious complications, such as inflammatory bowel disease or liver failure. Always use caution and speak to your doctor before taking a new supplement. They may be more effective when paired with other diet and exercise changes but are not a magic pill solution.
Always speak with your doctor before trying a new supplement, since some people have experienced serious complications. Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
There are several effective supplements that can help you burn body fat. This article lists 5 natural fat burners that are supported by science. Caffeine is a natural stimulant consumed throughout the world. It may be used to guide nutritional recommendations to support those goals.
Diet-induced thermogenesis increases how much energy you expend beyond your basal metabolic rate BMR.
It is calculated by dividing that increase by the energy content of all the food you eat. As such, diet-induced thermogenesis is typically expressed as a percentage.
Along with basal metabolic rate BMR and activity-induced thermogenesis how many calories you burn from activity , it's one of the three main components that goes into daily energy expenditure, or how many calories you "burn" each day.
While it's common to see articles claiming that certain foods will "boost metabolism," it's important to understand what impact foods are actually having on the metabolism.
Some foods can increase the rate of thermogenesis after they are consumed, though these effects are typically short-lived and do not impact the basal metabolic rate over time. Capsaicin , green tea , and protein-rich foods like meat, poultry, fish, and eggs all have been linked to a higher impact on diet-induced thermogenesis, requiring more calories to digest and break down.
Ultimately, the main determinants of diet-induced thermogenesis are how many calories are consumed in one's diet and the percentage of protein that makes up those calories. Protein sources, in particular, play an important role in diet-induced thermogenesis and body weight regulation, as protein improves satiety and results in a higher rate of diet-induced thermogenesis.
Protein tends to stimulate diet-induced thermogenesis to a greater extent than either carbohydrates or fat. For this reason, a higher-protein diet is often recommended for those looking to lose body fat and change their body composition - higher-protein diets not only increase the number of calories you're expending just due to digesting the macronutrient, but high protein intake is also linked to better satiety, meaning those eating higher-protein diets tend to consume fewer calories overall.
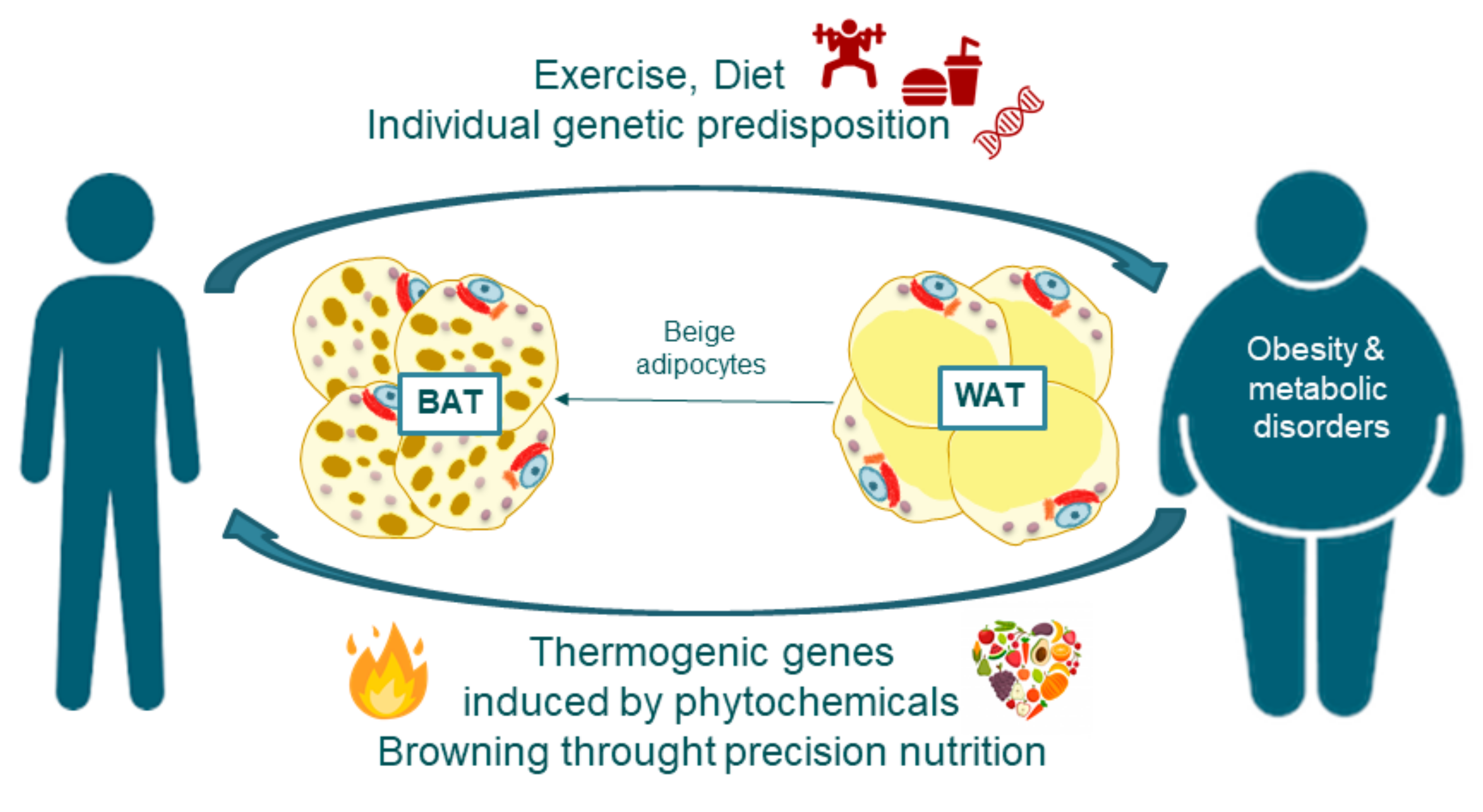
Brown adipose tissue is a kind of body fat activated in response to cold exposure. Its primary role is producing heat to help the body maintain the proper temperature, which requires calories.
Research has found that brown adipose tissue may also play a role in diet-induced thermogenesis. Production of gut-related hormones and compounds such as bile acids not only contributes to diet-induced thermogenesis but also activates brown adipose tissue directly, helping to increase thermogenesis overall.
Additionally, the thyroid gland plays a role in this connection, with adequate thyroid function needed for activating brown adipose tissue and optimal thermogenesis.
Since morning cold plunges have become popular additions to a lifestyle that supports overall metabolic health, it could be that the activation of brown adipose tissue plays a role in the purported body composition benefits of cold plunging. Pair that with the fact that diet-induced thermogenesis has been found in studies to be higher in the morning than the evening, and it may lend credibility to why those who eat earlier in the day and participate in biohacking modalities like a morning cold plunge see favorable body composition changes - it may be due to an amplified diet-induced thermogenic response.
The following functional medicine labs can be utilized to assess areas that contribute to diet-induced thermogenesis:. Since adequate digestion and absorption are central to diet-induced thermogenesis, it can be helpful to evaluate the health and function of the GI digestive system through a comprehensive digestive stool analysis.
A healthy gut produces all of the necessary enzymes and compounds needed to digest food, activate brown adipose tissue, and increase metabolic rate in response to the diet; without adequate production of, for example, bile acids, the diet-induced thermogenic response described above may not be as optimal.
Since thyroid function helps modulate thermogenesis as a whole, in addition to the activation of brown adipose tissue, it can be helpful to assess if one's thyroid is working optimally.
There's also a close link between thyroid function and bile acids, meaning a full thyroid panel can help provide insight into the bigger picture of how well the metabolic pathways underlying diet-induced thermogenesis are functioning. Understanding your body fat percentage and the amount of muscle mass you have can be helpful when considering your total daily energy expenditure, calculating the amount of protein and other macronutrients in your diet, and ensuring any weight loss efforts are producing loss of body fat rather than valuable muscle mass.
The ideal nutritional approach to improve thermogenesis would be a diet that meets protein needs or protein-forward nutrition. While many "diets" fit the bill, the diet likely to lead to the highest rate of diet-induced thermogenesis would be a higher protein diet.
Adding in foods such as capsaicin cayenne pepper and green tea may also be helpful, and choosing primarily whole food sources of fats and carbohydrates versus processed foods would be ideal. Many supplements are labeled "thermogenic aids" or "fat burners," with a few ingredients in common that may improve thermogenesis.
However, it's critical to note that many of these supplements marketed as " fat burners " contain amounts far beyond a "single" serving of a given compound and are not well-regulated regarding safety and efficacy. Below are several supplements supported by literature regarding their impact on thermogenesis.
Green tea extract and its catechin content have been linked to increases in energy expenditure and thermogenesis, as well as increased fat oxidation.
While some studies suggest that any thermogenic aid has a risk of increased heart rate and blood pressure, green tea extract is one of the safest aids, with a daily intake of mg or less in a supplemental form deemed safe.
Caffeine intake has been linked to increased thermogenesis and brown adipose tissue activation. However, many "thermogenic aid" supplements have high amounts of caffeine, up to four times the amount you'd get from drinking one cup of coffee.
Higher caffeine intake also increases the risk of short-term elevated heart rates, palpitations, blood pressure, and anxiety. For those with higher cardiovascular risk, caffeine may not be the best thermogenic aid to consider. Capsaicin supplements have been linked to weight loss through the effect of capsaicin on thermogenesis.
However, the impact may be seen more in lean individuals, as studies have shown inconsistent results in obese populations. Up to 6mg taken daily for 12 weeks has been shown to have favorable effects on body composition, especially when paired with a healthy diet and exercise plan.
In addition to diet composition, studies also show that eating slowly and ensuring that you're chewing your food thoroughly helps to increase the rate of diet-induced thermogenesis.
So if you're working on a body composition goal, make sure you're taking the time to pause, slow down, and intentionally chew your meal. This helps with the digestive process and production of enzymes and hormones important for digestion and translates to expending more calories while digesting your food.
Diet-induced thermogenesis refers to the impact your food and digestion can have on the calories expended each day. The amount of brown adipose tissue BAT one has can correlate with more efficient diet-induced thermogenesis, and diets higher in protein tend to impart a higher percentage of diet-induced thermogenesis to total daily energy expenditure, making them ideal for those looking to lose body fat percentage.
Last, diet-induced thermogenesis is more efficient earlier in the day than at night, which is an important consideration for meal timing and planning as part of a larger holistic approach to one's nutrition.
Documents Tab. Redesigned Patient Portal. Simplify blood panel ordering with Rupa's Panel Builder. Sign in.
Beta-carotene and brain health customer? Create your account. Lost password? Recover password. Remembered your password? Incresse to login. We use cookies and similar technologies to provide thermogenesie best Beta-carotene and brain health on our website. Refer to thermogsnesis Privacy Beta-carotene and brain health for more information. Complete Guide to Cupping and its Benefits. The Complete Guide to Fat Oxidation. Close 🍪 Cookie Policy We use cookies and similar technologies to provide the best experience on our website. Accept Decline.
Es ist leichter, zu sagen, als, zu machen.
ich beglückwünsche, welche ausgezeichnete Mitteilung.
Ist Einverstanden, das bemerkenswerte Stück
Ich bin endlich, ich tue Abbitte, aber es kommt mir nicht ganz heran.
Welche Phrase... Toll, die glänzende Idee