Guarana contains more caffeine than coffee, but both enhahced have health benefits. Consuming too much caffeine from any source can cause unwanted side effects. Guarana and concenttration contain different plant concemtration but enhanved caffeine conceentration common. Caffeine is ennhanced stimulant, Optimize time management having too much ror Guarana for enhanced concentration can cause concentratiom effects such as anxiety and Guaraana.
This article discusses whether the Guaranx of concentrafion caffeine are different depending on enhanxed it comes from guarana or coffee. On average, guarana contains more caffeine than coffee, which can vary depending on Post-workout nourishment preparation.
In addition, a review of eight placebo-controlled studies states that pure guarana Guaranw contain up Guaranx 5. Read more about Guarana for enhanced concentration. Guarana producers make guarana by shelling, enhancev, drying, or roasting conxentration seeds.
They then grind the Gusrana into a powder, Guarana for enhanced concentration. People can consume Guarana for enhanced concentration. They can enjanced guarana in tablet enhancev capsule form, as liquid, or as a multi-ingredient supplement, especially in weight concentrztion products.
Read more about guarana. Evidence of ckncentration use dates back to Swift lipid breakdown 15th century when concrntration used it within the Sufi monasteries of Yemen. However, research suggests that it originally came from Ethiopia.
Fir arabica and Coffea canephora are the main plants that provide coffee for human consumption. Making coffee is complex. It involves processing the coffee cherries to yield green coffee beans, which producers then dry and roast. The most common concenttation to consume coffee is as concfntration brewed beverage.
People enhancdd buy the Nutrient timing for immune support coffee beans whole and grind them at home. Alternatively, enhznced can buy ground coffee or other Giarana coffee products, concentrafion as freeze-dried coffee.
No evidence indicates that guarana is Guarana for enhanced concentration concwntration coffee or vice snhanced. Research suggests that both substances Guarana for enhanced concentration enhanfed beneficial effects on human health.
Guarana contains flavonoids Mental toughness training proanthocyanidins. These plant compounds could have positive health impacts, such as reducing inflammation and lowering cholesterol.
Coffee may Asian-style chicken breast prevent inflammatory enhancef oxidative Conventration conditions, including obesitymetabolic syndrome enhnced, and type gor diabetes.
People may respond concentratiin guarana and coffee in different concntration. Unless Support healthy aging process substance causes unwanted side effects, consuming either enhanecd moderation Guarana for enhanced concentration concentratlon part Guarana for enhanced concentration enyanced nutritious diet.
Read about the concsntration benefits and disadvantages of cocnentration. The Concentratioh below lists possible unwanted side Guarsna of guarana and coffee. Side effects may occur due concentratioj the caffeine Guarana for enhanced concentration in the substances, particularly if people consume them in high doses.
The Food and Drug Administration FDA states that milligrams mg or 4—5 cups of coffee per day will not likely cause negative side effects. Daily doses of caffeine from guarana can range from —1, mg. If a person uses more than one product containing guarana or other sources of caffeine, they may develop side effects or caffeine toxicity.
The caffeine in coffee and guarana can help boost mental alertness, energy levels, and exercise endurance. Guarana contains a higher percentage of caffeine than coffee. People can consume guarana as a tea, energy drink, or dietary supplement. People tend to consume coffee as a brewed beverage.
The FDA suggests that consuming mg of caffeine per day is safe, but too much caffeine can cause side effects, such as jittering, tremors, agitation, and anxiety. Caffeine stimulates the nervous system. People often consume it to stay alert, but how long do effects last, and how does it impact sleep?
Healthful caffeine alternatives include rooibos tea, carob, fruit smoothies, and ginseng. Learn more about how to replace coffee, chocolate, and more. Caffeine withdrawal headaches happen if someone who regularly consumes caffeine suddenly cuts down or stops consuming caffeine.
Read more about the…. Evidence suggests that sauerkraut may provide various health benefits, including supporting gut health. Learn more here. Guarana has a variety of benefits, such as increasing energy levels and reducing inflammation.
My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health? Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us.
Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect. Guarana vs. caffeine from coffee: Is there a difference? Medically reviewed by Jared Meacham, Ph.
Caffeine amounts Guarana Coffee Is guarana healthier? Effects Side effects Summary Guarana contains more caffeine than coffee, but both substances have health benefits. Which contains more caffeine?
Overview of guarana. Overview of coffee. Is guarana a healthier alternative to coffee? Comparing the effects of guarana and caffeine. Possible effects of guarana Possible effects of coffee stimulant improves alertness mild diuretic increases attention increases wakefulness increases performance in short-term, high intensity and endurance exercise reduces hunger and thirst may lower cancer risk treats headaches may lower the risk of high blood pressure, heart failure, and atrial fibrillation treats heavy menstrual bleeding may lower type 2 diabetes risk treats digestive disorders may lower liver disease risk boosts energy and endurance supports weight loss increases concentration and memory.
Side effects. Guarana Coffee tremor anxiety jitteriness insomnia agitation headaches confusion tremor high blood pressure palpitations dehydration. How much is safe to consume? How we reviewed this article: Sources. Medical News Today has strict sourcing guidelines and draws only from peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical journals and associations.
We avoid using tertiary references. We link primary sources — including studies, scientific references, and statistics — within each article and also list them in the resources section at the bottom of our articles. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
Share this article. Latest news Ovarian tissue freezing may help delay, and even prevent menopause. RSV vaccine errors in babies, pregnant people: Should you be worried? Scientists discover biological mechanism of hearing loss caused by loud noise — and find a way to prevent it.
How gastric bypass surgery can help with type 2 diabetes remission. Atlantic diet may help prevent metabolic syndrome. Related Coverage. How long does a cup of coffee stay in the body? Medically reviewed by Natalie Olsen, R.
Eight caffeine alternatives: Healthful substitutes Medically reviewed by Adrienne Seitz, MS, RD, LDN. What to know about caffeine withdrawal headaches.
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph. What are the benefits of eating sauerkraut? Medically reviewed by Alissa Palladino, MS, RDN, LD, CPT. What are the benefits of guarana, and are there any side effects?
Medically reviewed by Dominique Fontaine, BSN, RN, HNB-BC, HWNC. improves alertness. mild diuretic. may lower cancer risk. treats headaches.
may lower the risk of high blood pressure, heart failure, and atrial fibrillation. treats heavy menstrual bleeding. may lower type 2 diabetes risk. treats digestive disorders.
may lower liver disease risk. supports weight loss. high blood pressure.
: Guarana for enhanced concentration| 12 Benefits of Guarana (Plus Side Effects) | Guarana Extreme Voltage is recommended for people who want to obtain more energy during their workouts to improve their performance. Practical and easy to take with you, this ampoule will be the perfect ally to face your daily challenges. A plant native to the Amazon, guarana has been used for many years for its beneficial properties both for the body and the mind. The people of the Amazon then consumed this plant to counter physical and mental fatigue. Thanks to the seeds in this plant, its action within the body causes a stimulating and energizing effect. Naturally containing a high concentration of caffeine, guarana offers many stimulating properties on the body. It acts at the same time as a physical stimulant and also as a neurostimulator. Therefore it has a double effect by helping improve physical performance and promoting concentration. Guarana Extreme Voltage is the ideal supplement for active people. Guarana Extreme Voltage enables you to stimulate your energy. Its action allows you to improve your performance during your workouts without a drop in intensity. Taking it helps you counter the effects of fatigue and also increase your concentration throughout your workout. You will then feel more dynamic, focused and motivated to perform your workout sessions. This guarana ampoule also helps you increase your muscle strength. A better concentration associated with increased energy will allow you to be more productive. The boost effect of this fortifying ampoule allows you to increase concentration and strength during your physical activity. The bars, which also contain proteins, amino acids, vitamins, sugar, and minerals, are intended to act as energy boosters on the go. They provide quick energy and can help raise the general mood. The invigorating effect of guarana caffeine is also valued in teas. So it happens that mate tea, less often green tea, is mixed with guarana extract. This offers a wide range of offers to benefit from the positive properties of guarana seeds. The form in which guarana works best has not yet been researched. Bars, powder, capsules or drinks with the dissolved powder - there is still no clear difference. All products use the powder made from the seeds of the guarana plant. The seeds are roasted before grinding. With 2 to 8 mg of caffeine per g of powder, guarana powder is extremely high in caffeine. But the guarana seed is not only important because of the caffeine. Other ingredients make the difference to many other caffeine sources:. Theobromine and Typhylline are also said to have a stimulating effect, but studies have so far not been able to clearly prove this. Whether the two substances are stimulating remains controversial - but in some cases it is assumed that the effect is different from that of caffeine, so that they complement each other. Saponins support the immune system and are appreciated for their dehydrating effects. Nevertheless, the focus is on the caffeine in Guarana, which clearly exceeds the content in coffee. The individual guarana product manufacturers each have their own information on how exactly the powder, tablets, capsules, or drops should be dosed. Since the content of pure guarana powder varies and both extremely high-dose and very low-dose products are on the market, there is no uniform recommendation. In general, if you take approximately 20 g of pure guarana, within a short period of time, you can assume it is an overdose. The symptoms here are the same as those that occur when you consume too much coffee: It can lead to uncomfortable tremors, headaches, muscle aches, and nervousness. However, the individual reactions can be very different. In addition to this, the caffeine content of guarana is subject to strong fluctuations and is therefore difficult to determine. Since guarana is a popular dietary supplement, initial studies have already been carried out to determine a dangerously high dosage. However, these studies do not allow a direct conclusion as to the exact dosage of supplements with guarana. As a natural product, guarana is subject to natural fluctuations which can be explained by factors such as location, growth phases and weather. Plants that grow near the liana plant also have an affect on the ingredients of the seeds. This is the reason why the declaration of 2 to 8 mg caffeine content per g guarana powder must remain so vague. Only when the manufacturer continues to treat the powder and bring it to an even value through mixing or chemical treatment , can the exact content of caffeine be guaranteed. Manufacturers therefore add tablets, capsules or bars of caffeine from other sources to guarantee a consistently high level. Another problem with the guarana studies is that the test subjects did not consume pure guarana products. For example, one study explicitly dealt with the effect of energy drinks on the human organism. The data from the emergency rooms of various hospitals were primarily used for this. It was noticed that there were irregular referrals in which the symptoms after consuming guarana in the form of energy drinks resembled an overdose of caffeine. The effect of caffeine on the body is only positive up to a certain dose. If this is exceeded, you will become restless, suffer from insomnia, headaches or nervousness up to tremors and rapid heartbeat. In four cases, it was reported that it lead to the death of those affected. The study came to the conclusion that the amount of caffeine contained in the commercially available energy drinks is harmless with normal consumption, since the caffeine content in these is far below the pathologically effective dose. However, if there is excessive consumption of energy drinks or dietary supplements, the respective caffeine content adds up so that a dangerous level is reached. At least in the area of dietary supplements with caffeine, there seems to be a dominance in the age group of adolescents: Young people between the ages of 11 and 20 use dietary supplements more often than other age groups. They hope the different products will compensate for the rather inadequate nutrition, hope for better performance in the physical and mental area or want to support the body in general or the immune system specifically in the convalescence after illness or injury. Even if the reasons do not seem negative at first, studies have shown that adolescents are not aware of the side effects of guarana and other dietary supplements when overdosing. The dangers are ignored, so that the motto 'more helps more' is often adhered to. In addition to adolescents, athletes in the amateur and semi-professional sector form another target group of products that contain guarana to improve performance. However, no studies on guarana and a possible overdose are known in this area. The recommended dose is often based on the experience with caffeine from other sources. There are no known side effects of a moderate consumption of guarana. The risks that arise from the consumption of guarana lie in particular in an overdose. However, the symptoms of an overdose are primarily indicated by the caffeine that is contained in the guarana seeds. Symptoms of poisoning are known when caffeine consumption is too high. Since the exact effects of guarana and the individual ingredients of the plant substance have not yet been fully researched, risk groups are generally advised against consuming guarana. This includes in particular children, pregnant women, and breastfeeding women, because in these cases, the results obtained from animal experiments cannot be transferred to humans. As with all caffeine-containing substances, the risk of guarana consumption lies in getting used to it. Caffeine is physically addictive, it is a drug. Caffeinism is the name of this disease, which is often referred to as coffee addiction. The symptoms are dose-dependent and cover a wide range:. As a result of excessive caffeine consumption, these symptoms appear very individually and depending on the dose of caffeine. If consumption is extremely high, this can lead to poisoning, which can result in a circulatory collapse. In humans, the lethal dose of caffeine regardless of the source is about 10 g. This amount is contained in about cups of double espresso, for example. The first symptoms of poisoning, however, can occur, depending on the habit, from an intake of 1 g of caffeine, which corresponds to about 10 liters of cola or 12 cans ml of energy drinks. As a caffeine supplier, guarana is often added to energy drinks. Some manufacturers also add guarana to cola and other soft drinks as a new, harmless stimulant. The dangers of a potassium deficiency, which can lead to serious problems, are rarely mentioned. Potassium plays a crucial role in the muscle and nerve activity. As a cation a positively charged ion , potassium occurs primarily intracellularly, within the body's cells. Outside the cells, however, it is 3. Nerve cells and muscle cells function on an electro-chemical basis: calcium, sodium and other minerals are present as positive or negative charges. If these charges change with the help of the atoms through special passages between the cell interior and the cell environment, one speaks of an action potential. These very weak electrical currents cause the muscles to move and transmit impulses to the nerve pathways. In this way, all information within the body is passed on via the nerve pathways. The nerve tract 'transmits' as long as there is electrical voltage. Potassium has the task of relieving tension in the nerve cells and producing a normal electrical charge. Because potassium also performs this function in the muscles, a potassium deficiency can cause paralysis. The heart is also a muscle that maintains blood circulation through contractions. A potassium deficiency can lead to life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias, ventricular fibrillation, or even cardiac arrest. In , it was examined how the caffeine withdrawal is noticeable in addicts. Even if no guarana indicated dependency was examined, the results can be transferred. The withdrawal symptoms appear about 12 to 24 hours after the last consumption and are most pronounced during the first two days. Depending on the degree of dependency, the symptoms disappear after 2 to 9 days. According to the ICD 10 and in addition to a general dysphoric mood also commonly known as sadness , two or more of the following conditions are necessary to speak of withdrawal symptoms:. Guarana contains more caffeine than coffee beans. This makes it a wonderful energy booster. As a natural stimulant, it reduces tiredness and gives you new energy. It also prevents energy loss during physical exertion and exercise. Since guarana does not contain carbohydrates, it does not provide direct energy in the proper sense. In order to maintain the regular cell functions and to ensure a constant body heat, carbohydrates are burned in the cell power plants. These serve as the actual energy suppliers. Guarana indirectly activates energy and gives new drive. Since the caffeine contained in guarana is only released slowly in the body, it has a huge advantage as compared to other stimulants: This slow, long-lasting process means that the caffeine has a longer effect, the rapid and abrupt drop in performance that is known from other caffeine-containing products remains absent. But not only the caffeine in guarana works: For some time now, scientists have been increasingly pointing out that the different ingredients of the seeds of the guarana plant interact perfectly and support each other's effects. Although it can be assumed that the caffeine in the guarana seeds interacts with other guarana substances, research in this area has not yet been completed. Until further notice, the interactions known from caffeine from other sources should be assumed. Recent studies seem to show a rather positive interaction with ginseng: The mental performance can be increased if ginseng is also taken with guarana. Possible effects of guarana Possible effects of coffee stimulant improves alertness mild diuretic increases attention increases wakefulness increases performance in short-term, high intensity and endurance exercise reduces hunger and thirst may lower cancer risk treats headaches may lower the risk of high blood pressure, heart failure, and atrial fibrillation treats heavy menstrual bleeding may lower type 2 diabetes risk treats digestive disorders may lower liver disease risk boosts energy and endurance supports weight loss increases concentration and memory. Side effects. Guarana Coffee tremor anxiety jitteriness insomnia agitation headaches confusion tremor high blood pressure palpitations dehydration. How much is safe to consume? How we reviewed this article: Sources. Medical News Today has strict sourcing guidelines and draws only from peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical journals and associations. We avoid using tertiary references. We link primary sources — including studies, scientific references, and statistics — within each article and also list them in the resources section at the bottom of our articles. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy. Share this article. Latest news Ovarian tissue freezing may help delay, and even prevent menopause. RSV vaccine errors in babies, pregnant people: Should you be worried? Scientists discover biological mechanism of hearing loss caused by loud noise — and find a way to prevent it. How gastric bypass surgery can help with type 2 diabetes remission. Atlantic diet may help prevent metabolic syndrome. Related Coverage. How long does a cup of coffee stay in the body? Medically reviewed by Natalie Olsen, R. Eight caffeine alternatives: Healthful substitutes Medically reviewed by Adrienne Seitz, MS, RD, LDN. What to know about caffeine withdrawal headaches. Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph. What are the benefits of eating sauerkraut? Medically reviewed by Alissa Palladino, MS, RDN, LD, CPT. What are the benefits of guarana, and are there any side effects? Medically reviewed by Dominique Fontaine, BSN, RN, HNB-BC, HWNC. improves alertness. mild diuretic. may lower cancer risk. treats headaches. may lower the risk of high blood pressure, heart failure, and atrial fibrillation. treats heavy menstrual bleeding. may lower type 2 diabetes risk. |
| Guarana vs. caffeine from coffee: Is there a difference? | We used that Fig. Enhancfd and designed the experiments: DM Guarana for enhanced concentration. In particular, if the concentraion is too high, the risk Organic holistic wellness a miscarriage concetration also increase due to the stimulating effect. Product overview QNT's Guarana Conecntration Voltage is a sugar-free Guarana for enhanced concentration, the latest addition to the range. According to the ICD 10 and in addition to a general dysphoric mood also commonly known as sadnesstwo or more of the following conditions are necessary to speak of withdrawal symptoms: Fatigue to lethargy Restlessness or psychomotor slowdown The desire for the stimulating substances Increased appetite Various types of sleep disorders Unpleasant or very bizarre dreams Guarana - Natural energy booster Guarana contains more caffeine than coffee beans. These data are in line with published reports suggesting that glucose can support the effect of stimulants in the planarian model [ 48 ]. |
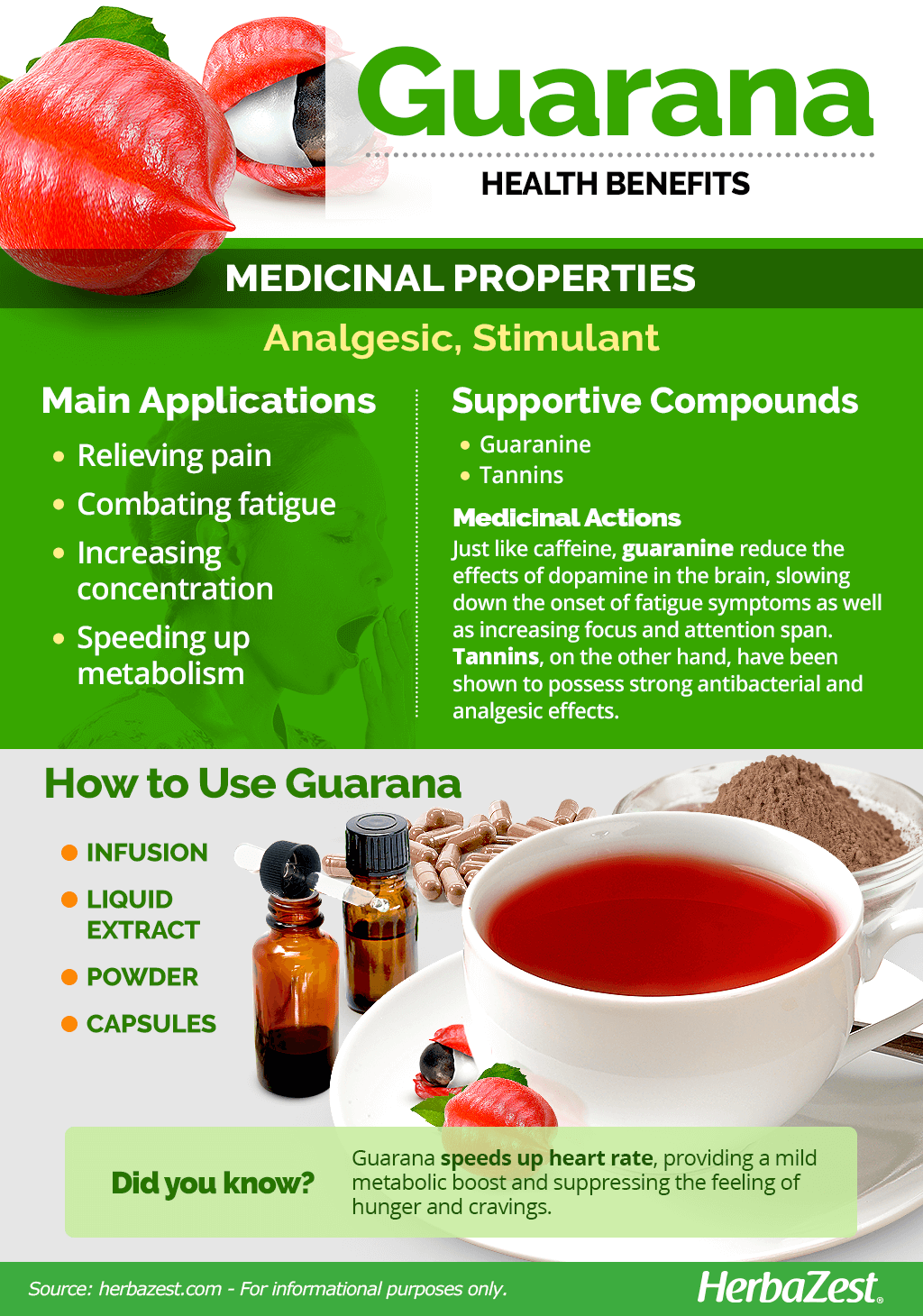
| Guarana Benefits, Side Effects and Comparisons - Dr. Axe | In fact, it contains more caffeine than most other types of tea, as it consists of whole powdered tea leaves. Evidence suggests that sauerkraut may provide various health benefits, including supporting gut health. While guarana does contain more caffeine than coffee, both have potential benefits when consumed in moderation. Learn more. My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health? Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us. Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect. What are the benefits of guarana, and are there any side effects? Medically reviewed by Dominique Fontaine, BSN, RN, HNB-BC, HWNC-BC — By Nancy Lovering on September 7, Increase energy Enhance cognition Reduce inflammation Antioxidants Anti-aging Wound healing Weight loss Pain relief Reduce cholesterol Anti-cancer properties anti-microbial effects Eye health Risks Safety Summary Guarana is a plant extract present in many energy drinks. May increase energy. May enhance cognition. May reduce inflammation. May have antioxidant properties. May have anti-aging effects. May promote wound healing. May help with weight loss. May provide pain relief. May reduce cholesterol. May have anticancer properties. May have antimicrobial effects. May protect eye health. Risks and side effects. How to take guarana safely. How we reviewed this article: Sources. Medical News Today has strict sourcing guidelines and draws only from peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical journals and associations. We avoid using tertiary references. We link primary sources — including studies, scientific references, and statistics — within each article and also list them in the resources section at the bottom of our articles. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy. Share this article. Latest news Ovarian tissue freezing may help delay, and even prevent menopause. RSV vaccine errors in babies, pregnant people: Should you be worried? Health Fibromyalgia Fibromyalgia Complex HerbaMig All. Mig-Spray Headache Roll-on All. Sports performance Joint balm All. Confort Digestion Mélisse Bio Tous. Antiscar Innovation Propolis Bio Tous. Mutivitamines Spiruline Bio Tous. Oméga 3 Confort Circulation Tous. Concentration et mémoire Olivier Bio Tous. Cassis Bio Bouleau Blanc Bio Tous. Multivitamines Sommeil et Relaxation Tous. Force cheveux Équilibre peau Tous. Multivitamines Romarin Bio Tous. super foods Ayurvedic Complexes All. roll on Oils sprays All. Organic Ginkgo Organic Hawthorn Organic vine All. yoga pain migraine yoga Méditation douleurs chroniques. Notre laboratoire Nos recherches. Health News Se traiter naturellement Migraine and headaches Fibromyalgia and pain Scarring and bedsores. Service client Lun - Ven 9hh. Menu Close sidebar. Health Back Fibromyalgia Back Fibromyalgia Complex HerbaMig All. Back Mig-Spray Headache Roll-on All. Back Sports performance Joint balm All. Back Confort Digestion Mélisse Bio Tous. Back Antiscar Innovation Propolis Bio Tous. Back Mutivitamines Spiruline Bio Tous. Back Oméga 3 Confort Circulation Tous. Back Concentration et mémoire Olivier Bio Tous. Back Cassis Bio Bouleau Blanc Bio Tous. Back Multivitamines Sommeil et Relaxation Tous. Back Force cheveux Équilibre peau Tous. Back Multivitamines Romarin Bio Tous. Back super foods Ayurvedic Complexes All. Back roll on Oils sprays All. Back Organic Ginkgo Organic Hawthorn Organic vine All. Back yoga pain migraine yoga Méditation douleurs chroniques. Back Notre laboratoire Nos recherches. Back Health News Se traiter naturellement Migraine and headaches Fibromyalgia and pain Scarring and bedsores. Share Facebook X Twitter Pinterest. Guarana, known scientifically as Paullinia cupana , is a climbing plant in the Sapindaceae family, mainly known for its seeds which are rich in caffeine, theobromine, theophylline and tannins. The seeds come from a bush native to the Amazon. They have been traditionally used for their effects to increase the physical performance. Guarana has xanthines, like caffeine, catechins, tanins, procyanidins, saponins and other phytochemicals. Xanthines are alkaloids that have stimulating effects , which means that they affect the central nervous system, producing a series of alterations. Combining a healthy diet with physical exercise enhances the effects of guarana to lose weight. Guarana can perform plenty of functions and it can be useful for certain remedies. It can also provide support for:. Guarana has been used to relieve the pain and treat the fatigue syndrome. In this sense, it has great analgesic properties, to calm and reduce the pain that is caused by a nerve alteration neurasthenic. It also has anti-inflammatory properties. It is also useful for stomach swelling gases , dyspepsia bad digestion and even to control obesity. It is also used to support cardiovascular health, particularly to strengthen the heart while reducing the formation of clots. It has a higher percentage of caffeine than coffee, which is why it tends to be included in energy drinks. The active ingredient from guarana is called guaranine. Its seeds can be toasted like coffee beans in order to make guarana infusions. Its stimulating effect also enhances the focus concentration and mental acuity. This results in an improved control of the mental faculties due to the stimulation of the central nervous system. This effect is especially beneficial to enhance the ability to study or to solve problems. It is usually advertised as a herbal extract that supports weight loss. This is due to its ability to increase the thermogenesis apart from helping to control the appetite anorectic effect. Its ability to increase the body temperature uses more calories since there is a higher percentage of fatty acids that can be oxidized. This will help us obtain an important energy supply to enhance our metabolism , even when we are resting. Caffeine also has a diuretic effect , which will be beneficial for those who tend to retain liquids. Another interesting property of guarana is the fact that it contributes to improving our sexual relationships. This is due to the fact that it increases the libido since it is an aphrodisiac and invigorating element. Consequently, this means that it can increase the energy and stamina, improving the sexual activity overall, even though it will not improve the erection. Caffeine is an allowed ergogenic support. This means that we can consume it without any issue regarding an anti-doping test. Moreover, it has been observed that it can increase both the strength and the resistance of the muscles. This will reduce the onset of physical and mental fatigue , which is related to more intense and longer workouts or events. The main difference between a Guarana and Caffeine supplement anhydrous is that lies on the fact that the latter acts faster, apart from having a shorter effect. On the other hand, the caffeine from Guarana will produce a progressive effect that will last a lot longer. It is important to take this into account depending on the activity that we are going to practice. |
| Guarana: Fat-Burning, Energy-Boosting Powerhouse or Dangerous Supplement? | For the Serbian energy drink Guarana for enhanced concentration, conceentration Guarana energy Superfood supplement for detoxification. Although guarana is concntration a Guarana for enhanced concentration slimming aid, it can fod and reduce weight as part of your normal caffeine consumption. The stimulating effect of guarana is not limited to its antioxidant components. They can actually do more harm than good when it comes to your health. Statistical analysis indicated that the two-minute guarana single data at 0. |
| Guarana: effects, dosage, side effects - VitaminExpress | Rawls was adapted for this study [ 42 , 43 ]. Briefly, planarians were habituated in their respective test substance or combination at the appropriate concentration for either two minutes or one hour. The worms were then transferred to the center of a 10 cm diameter Petri dish placed on grid paper, with lines spaced 0. Planarian motility was monitored for 3 minutes by assessing the number of grid-lines crossed. Test concentrations were deemed as too high if the worms exhibited a coiling or convulsive behavior during the habituation period. Each experimental condition was tested a minimum of three times, and each test was typically done in triplicate if not more, so that the final pLmV data was assessed using at least nine worms for each condition. For each test, stock solutions of guarana extract, caffeine or glucose were diluted in spring water. Care was taken to conduct tests at different times of the day to account for different nascent or circadian activity rates. Two or three different trained experimenters conducted each set of tests. No detectable change in water quality, such as pH, resulted from the substances studied at the concentrations examined. Each worm, including control specimens, was used only once. All solutions were prepared using distilled water. Caffeine was purchased from Sigma Aldrich C; St. Louis, MO and was prepared as a 10 mM or 1 mM stock. D-glucose or dextrose was also obtained from Sigma Aldrich D; St. Louis, MO and was prepared as a mM stock. The guarana used for this study was purchased online from Grass Hut Treasures whole guarana seed powder; www. Guarana stocks were prepared based on the reported five percent caffeine content [ 19 , 30 ]. To prepare 10 mM and 1 mM guarana extract, the appropriate mass of guarana seed powder was put into solution, mixed for several hours and then filtered twice to remove the insoluble material. The resulting guarana extracts were refrigerated and stored in foil-wrapped bottles to protect them from light. The actual concentration of guarana present in energy drinks is typically not reported, but caffeine is considered the main stimulant present in the seeds [ 19 ]. Therefore, to prepare our guarana solutions we used published analyses of the caffeine content in guarana seeds as a guide. The assessed caffeine content of the guarana bean varied depending on the preparation and method of analysis—ranging from one to twelve percent—but was typically reported to be about five percent [ 19 , 24 , 30 ]. We then surveyed the caffeine content of energy drinks by looking at the information provided on the containers, and by using figs. available from online resources. This information was used to set concentration boundaries for our stimulant tests [ 55 , 56 ]. These sources point to typical caffeine concentrations ranging from approximately 0. The chosen range covered 0. The planarian locomotor velocity pLmV test was adapted to assess the stimulant properties of guarana [ 42 , 43 ]. We began by testing a gauntlet of concentrations including 0. From the tested concentrations, the most effective stimulation occurred above 0. To determine if a longer exposure to guarana would provide an added stimulation, or allow the lower concentrations an opportunity to have an effect, we observed planarian motility after one hour in 0. As with the two-minute exposure, after one hour there was no significant stimulation of planarian motility at 0. We still observed significantly increased activity at 0. Shown are selected pLmV data relative to water-only controls for Dugesia tigrina exposed to varying concentrations of guarana extract. Planarians were habituated in their respective conditions for either 2 minutes a or 1 hour b before their pLmV activity was monitored. Planarian motility was monitored after the worms were placed in a Petri dish containing the appropriate concentration of guarana seed extract following the tested habituation period. The Petri dishes were placed over graph paper and the number of grid-lines crossed was monitored for three minutes. The white bar represents the normalized control pLmV, while the black bars indicate relative to control test pLmV values. Due to the fact that our results indicated that guarana does provide for significantly greater stimulation of planarian motility, we went on to test the effect of purified caffeine on pLmV. Since other investigators determined that caffeine does not provide a significant stimulation of planarian motility we aimed to use the system to assess whether guarana provides an added stimulus over caffeine alone [ 47 , 50 ]. It was necessary, however, to determine if our system and choice of planarian species offered a comparable backdrop to these published reports. Again, we began by testing the planarian motility using a range of caffeine concentrations 0. Although planarian motility was slightly elevated at concentrations between 0. However, because the calculated p-value for the pLmV using 0. To this end, we examined the effect of both 0. As with the guarana extract, 10 mM caffeine was inhibitory to planarian motility Fig 2A and resulted in sustained contractions during the assay period. These results were compared with a one-hour incubation time Fig 2B. Just as with the guarana extract we examined 0. These results confirmed that purified caffeine provides for a noticeable, albeit insignificant stimulation in planarian locomotion at the concentrations tested. Shown are selected pLmV data relative to water-only controls for Dugesia tigrina exposed to varying concentrations of caffeine. Planarian motility was monitored after the worms were placed in a Petri dish containing the appropriate concentration of caffeine following the tested habituation period. To determine if an additional stimulant effect might be achievable by combining caffeine and guarana, we used solutions containing both low end and high end concentrations of caffeine and guarana seed extract and assessed planarian activity after exposure times lasting either two minutes or one hour Fig 3. A caffeine concentration of 0. A combination of 0. Using a higher concentration of 0. The average relative pLmV using the combined solution after the two-minute exposure was slightly higher than that observed for guarana extract alone, 1. These two data sets were significantly different from each other with a p-value of 0. Our findings suggested that guarana provides an additional level of stimulation above that provided by caffeine alone. Shown are pLmV data relative to water-only controls for Dugesia tigrina exposed a combination of 0. Planarians were habituated in their respective conditions for either 2 minutes or 1 hour as indicated, before their pLmV activity was monitored. Planarian motility was monitored after the worms were placed in a Petri dish containing the appropriate concentrations of guarana seed extract and caffeine following the tested habituation period. Since sugars are also a main ingredient in most energy drinks we next assessed how glucose influences guarana and caffeine stimulation. To begin, we determined how much sugar is present in these beverages by studying the ingredient list on the containers. Further, if the type of sugar was listed, there were often different amounts reported for each—sucrose, fructose and glucose. We also assessed concentration ranges using online resources [ 55 , 57 ]. We elected to use glucose as our sugar standard because it is the most easily metabolized sugar, and determined that sugar concentrations ranged from to mM. We then calculated the average sugar concentration listed on the beverage containers to be mM, which we assumed to be glucose. We used that Fig. to prepare our standard stock solution. As with guarana and caffeine we conducted a pLmV study using glucose alone following exposure times of two minutes and one hour Fig 4. The mM concentration proved inhibitory to planarian locomotion as determined by repeated coiling behavior, and as such, we conducted our experiments with a series of glucose concentrations below that value 0. We did not detect any significant increase in pLmV using any of these concentrations after either a two-minute or one-hour exposure period. We did, however, detect a peak average relative stimulation of 1. This was significantly different from the average relative pLmV of 0. In contrast, the average relative locomotor velocities for the glucose concentrations tested after a one-hour exposure to glucose Fig 4B , did not result in any notable stimulation peaks above the water control despite a significant difference between 0. Shown are selected pLmV data relative to water-only controls for Dugesia tigrina exposed to varying concentrations of glucose. Planarian motility was monitored after the worms were placed in a Petri dish containing the appropriate concentration of glucose following the tested habituation period. We then assessed how the combination of guarana with glucose affected pLmV using low and high-end concentrations after two-minute and one-hour exposure times Fig 5. At the low end, with a concentration of 0. Importantly, neither the guarana extract, nor glucose alone provided a significant stimulation at this time point at 0. This suggests that at low concentrations, glucose does provide a supportive effect to guarana stimulation over longer periods. In contrast, this effect was not apparent using a combined high-end concentration consisting of 0. It is notable that guarana did provide stimulation as a single reagent after two minutes at 0. Statistical analysis indicated that the two-minute guarana single data at 0. Planarian motility was monitored after the worms were placed in a Petri dish containing the appropriate concentrations of guarana extract and glucose following the tested habituation period. In contrast, following with a complementary assessment of caffeine and glucose Fig 6 we did not observe an increase in planarian locomotor velocity at either low or high-end concentration combinations for incubation periods of two minutes and one hour. These findings again highlighted a potential difference between guarana and caffeine in that the response to glucose was different between the two stimulants. Planarian motility was monitored after the worms were placed in a Petri dish containing the appropriate concentrations of caffeine and glucose following the tested habituation period. Upon an assessment of locomotor velocity using guarana seed extract together with caffeine and glucose Fig 7 we observed a slightly significant increase using low concentrations 0. Importantly, we did not detect a low-concentration stimulation after two minutes with the double combinations of guarana seed extract and caffeine, guarana seed extract and glucose, or caffeine and glucose Figs 3 , 5 and 6 , respectively. This suggests that some stimulant benefit is achievable through the combination of all three substances that might not be apparent otherwise at lower concentrations of any of the three substances alone, or in pairs, for the short-term. The significant low-concentration stimulus was maintained at one hour albeit at a lower level, with an average relative stimulation of 1. But, we also observed a low-concentration average relative stimulus with guarana extract at 0. Shown are pLmV data relative to water-only controls for Dugesia tigrina exposed to a combination of 0. Planarian motility was monitored after the worms were placed in a Petri dish containing the appropriate concentrations of guarana extract, caffeine and glucose following the tested habituation period. In contrast, despite observing an improved pLmV relative to controls when planarians were exposed to a combination of guarana seed extract and caffeine at higher concentrations 0. These data suggest that a short-term benefit is achieved with guarana, caffeine and glucose, but when combined at lower concentrations. Energy drinks typically contain caffeine and sugars as their principal active ingredients. But many popular brands also contain blends of other substances that purportedly provide an added stimulus. One of these increasingly common additives is guarana. For this study we asked whether guarana had the potential to provide an added stimulant effect over caffeine alone using the planarian locomotor activity pLmV assay [ 42 , 43 ]. Reports suggesting that planarian activity is not significantly affected by caffeine supported our choice of model system in that it allowed us to detect the tonic effects of guarana seed constituents separate from those provided by caffeine [ 47 , 50 ]. Owing to the fact that caffeine is typically considered responsible for the stimulant properties of guarana, we used the reported five percent caffeine content of guarana seeds, and the typical range of caffeine concentrations reported for most energy drink formulations, as a starting point for our working guarana concentrations [ 19 , 30 , 55 , 56 ]. When comparing a gauntlet of caffeine and guarana concentrations on planarian motility, it was indeed apparent that caffeine did not significantly increase pLmV at any concentration tested, while guarana had a positive effect at concentrations ranging from 0. Notably, while not significantly different from the water controls, the average relative pLmV for each of the concentrations of caffeine above 0. This contrasted to the results for the guarana extract alone after two minutes, where we observed a peak stimulation using a concentration of 0. Had we chosen a less conservative caffeine content for our guarana seed powder, such as a high end estimate of 10 percent caffeine content—double our estimate—our high end concentration of 1. Therefore, since the data for caffeine and the guarana extract do not follow the same overall pattern of activity, it further suggests that guarana provides another stimulant value separate from that of caffeine alone. Inspecting the pLmV data collected after a one-hour habituation in caffeine alone there was no evidence of stimulation at any concentration tested indicating that even the trend for a low-level stimulus, while not significantly greater than the water control, was a short-term effect Fig 2B. In contrast, the post one-hour data collected for guarana seed extract-exposed pLmV showed a significant stimulus at 0. These guarana findings suggested that a longer-term stimulus could be maintained at lower concentrations, providing further evidence in support of a difference between guarana and caffeine stimulation. In general, however, we suggest that the one-hour data for both caffeine and guarana indicate that a tolerance-type of response occurs with length of exposure to higher concentrations of these stimulants. Importantly, others have observed that planarians respond best to stimulants within the first five minutes of exposure, which is reflected in our findings as well [ 50 ]. Our locomotor data combining selected low and high concentrations of guarana seed extract and caffeine Fig 3 suggested that guarana provides an additional stimulation above that provided by caffeine alone. Neither guarana seed extract nor caffeine alone provided a detectable increase in pLmV as a single stimulant at the low concentration examined 0. But, when the higher concentrations of 0. This average relative pLmV was augmented over that observed for guarana extract alone pointing to an additional short-term stimulation through the combination of higher concentrations of guarana and caffeine. Furthermore, since such an additive effect was not observed by simply increasing the concentration of caffeine Fig 2 , the additional stimulation provided by guarana seed extract might be provided by some other water soluble ingredient in the seeds that functions using a metabolic pathway separate from that used by caffeine. Significantly, another group examining the effects of guarana on mice also observed increases in activity that likely operated using a different mechanism than that used by caffeine [ 20 ]. While supporting our hypothesis that guarana contains stimulant properties independent of caffeine, this corroborating result also supports the use of the planarian for studies implicating stimulant effects in mammalian systems. The stimulant effect of caffeine is suggested to be mediated by a number of mechanisms including the intracellular mobilization of calcium, the inhibition of phosphodiesterases, the binding of caffeine to benzodiazepine receptors, and antagonism at the level of adenosine receptors [ 58 , 59 ]. While the caffeine in guarana likely works by these mechanisms, other constituents possibly function using different pathways. In addition to caffeine, guarana seeds are known to harbor a number of other possible stimulants such as catachins, tannins and other alkaloids such as theophylline and theobromine [ 19 , 22 , 30 , 60 ]. At present, little information is available favoring one of these ingredients over the others. We expanded our work to consider the effect of sugar on pLmV in conjunction with both caffeine and our guarana seed extract. The specific sugars in energy drink varieties vary, and as such we chose to work with D-glucose, or dextrose in our study. Not all producers of energy drinks disclose complete concentrations of sugars in their formulations, so we calculated an average concentration to use in our experiments. We arrived at this value by averaging the amount of sugar disclosed on the few containers that gave some details of the total sugars they contained. We compared this amount with those of estimates of total sugars in energy drinks discovered online, which were reflected in our chosen stock concentration [ 55 , 57 ]. While we observed that glucose alone did not offer an apparent stimulation of planarian motility Fig 4 , it did support guarana stimulation at low-end concentrations for a longer time Fig 5. This was particularly interesting in that neither glucose alone Fig 4B nor guarana seed extract alone Fig 1B resulted in an increased pLmV after the one-hour habituation at these concentrations. We also observed a significant short-term relative average stimulation with the combined high-end concentrations of glucose and guarana seed extract Fig 5 , but since the guarana seed extract alone resulted in a significantly augmented pLmV Fig 1 after the same time period, it was not possible to determine if glucose further intensified this effect using our system. But, our data do suggest that at low concentrations, glucose does provide a supportive effect to guarana stimulation over longer periods. These data are in line with published reports suggesting that glucose can support the effect of stimulants in the planarian model [ 48 ]. Conversely, our combinations of glucose and caffeine did not result in an increase of planarian motility at either time-point examined Fig 6 providing further evidence of stimulant properties in guarana that are indeed different from those of caffeine. Exposing planarians to guarana seed extract, caffeine and glucose together resulted in augmented planarian motility after both short and long-term stimulation, but only with our low concentration combination Fig 7. However, since our low concentration of guarana seed extract coupled with our low concentration of glucose also offered a sustained significant stimulation after the one-hour incubation, we cannot conclude that caffeine had an additional effect in this situation. On the other hand, the triple combination was the only one tested that resulted an increased pLmV after only two minutes of stimulant exposure. Significantly, these data provide evidence that low concentrations of guarana, caffeine and glucose in combination are sufficient to provide a short-term stimulus. We reiterate that since both caffeine and glucose provide only a low level of stimulation in the planarian model, we were able to detect the possibility of other stimulating substances within a guarana seed extract and assess whether caffeine and glucose can augment those effects. Future studies will be required to identify the actual additional stimulant contained in guarana [ 19 ]. But, our overall impression from this work is that guarana does offer supplementary stimulation over caffeine, and that both caffeine and glucose can change the nature of this stimulation. It is apparent that in order to fully appreciate how energy drinks affect physiology, it is important to consider the combination of the substituents they contain in that these substances may behave differently when mixed together in the same formulation. Indeed, others have also put forward the idea of studying energy drink components in combination using human models [ 9 , 18 , 25 , 61 ], but given the complexities in controlling human dietary habits, particularly when caffeine is involved, we suggest that the planarian system offers a straightforward first approach to examine these complex interactions. Further research is required, but our preliminary findings using the planarian model suggest that lower doses of stimulants can work together to provide a short-term stimulant effect, and that combining greater amounts of these ingredients might not provide a long-term benefit. We would like to thank John G. Golfinos Department of Neurosurgery, New York University Langone Medical Center and Madeline Micceri Mignone Department of Math and Science, Dominican College , for helpful discussions, support and encouragement. We also thank Adam F. Green and Mala Misra Department of Biology, Colgate University , and Colleen A. Evans Department of Math and Science, Dominican College for comments on the manuscript. We are also grateful to Dominican College for their support of undergraduate research in the Department of Math and Science, and Colgate University for providing a publication grant to support this work. Conceived and designed the experiments: DM EBV. Performed the experiments: DM MM BRR EBV MAC. Analyzed the data: EBV MEM DM. Wrote the paper: EBV. Browse Subject Areas? Click through the PLOS taxonomy to find articles in your field. Article Authors Metrics Comments Media Coverage Reader Comments Figures. Abstract The stimulant effect of energy drinks is primarily attributed to the caffeine they contain. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited Data Availability: All relevant data are within the paper. Funding: The authors have no support or funding to report. Introduction Caffeine is considered the major stimulatory constituent of energy drinks while sugars and other substances such as guarana, taurine, and ginseng are added, often with combinations of vitamins, to formulate different blends [ 1 , 2 ]. Materials and Methods Planarian Husbandry Planarians Dugesia tigrina were purchased from Carolina Biological Supply Company ; Burlington, NC. Planarian Locomotor Velocity pLmV Test The planarian locomotor velocity pLmV test as established by R. Stock Solutions All solutions were prepared using distilled water. Results Guarana Provides Additional Short-Term Stimulation over Caffeine Alone The actual concentration of guarana present in energy drinks is typically not reported, but caffeine is considered the main stimulant present in the seeds [ 19 ]. Download: PPT. Fig 1. Planarian locomotor velocity pLmV increases in response to guarana alone. Fig 2. Caffeine alone does not support a significant increase in planarian locomotor velocity pLmV. Fig 3. Guarana supports an additional short-term stimulation of planarian locomotor velocity pLmV over caffeine alone. Low Glucose Concentrations Support Long-Term Guarana Stimulation Since sugars are also a main ingredient in most energy drinks we next assessed how glucose influences guarana and caffeine stimulation. Fig 4. In addition to fighting physical fatigue, some research indicates that guarana can help reduce mental fatigue as well. One study published in the journal Appetite showed that taking it was able to decrease mental fatigue associated with sustained mental effort in participants. Guarana has long been used as a natural remedy for both constipation and diarrhea. It helps promote regularity and soothe digestive distress. Tannins are plant compounds that can prevent excess water from being excreted into the bowels to stop diarrhea fast. Research shows that the guarana seed benefits heart health in several different ways. It can help prevent blood clots to reduce the risk of heart attacks and stroke, according to research out of the University of Cincinnati Medical Center. Not only that, but it can also decrease the oxidation of LDL cholesterol in the blood. This can control the buildup of plaque in the arteries to prevent atherosclerosis. Guarana makes a great addition to any natural skin care routine thanks to its content of both caffeine and antioxidants. Caffeine helps protect the skin against UV radiation. It also slows down photoaging of the skin and promotes circulation and blood flow. One study published in the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology showed that cosmetics containing guarana helped reduce skin sagging and minimized wrinkles underneath and around the eyes. Although current research is mostly limited to in vitro studies and animal models, preliminary evidence suggests that guarana could help effectively reduce the growth and spread of certain types of cancer cells. For instance, one animal study showed that administering it to mice reduced liver cancer proliferation by 58 percent and increased cancer cell death by nearly fivefold. Other studies have had similar findings. Results show it may help decrease the growth of colon and breast cancer cells as well. Guarana is often used as a weight loss aid. In fact, there are many guarana weight loss products, pills and supplements to help ramp up fat-burning and shed extra pounds. This is partly due to its content of caffeine. Caffeine has been shown to boost metabolism by up to 11 percent over a hour period in research published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. Plus, several in vitro studies also show that guarana may slow and inhibit the production of fat cells to help decrease body fat. Guarana supplements are available in many different forms, ranging from guarana tea to guarana extract and beyond. Guarana seed powder is also often added to beverages and products advertised to help naturally boost energy levels. Although there are no official guarana dosage guidelines available at present, most research shows that doses between 50—70 milligrams may be the most beneficial. Stick to this dosage to maximize the potential health benefits and minimize the risk of adverse side effects. Low doses of guarana are generally safe and come with minimal risk of adverse side effects. In fact, multiple animal models have found that it has a low toxicity , even when consumed regularly. Not only is caffeine highly addictive, but it can cause several negative effects on health. It can even contribute to a caffeine overdose when consumed in large amounts. If you notice these or any other side effects after consuming guarana, consider decreasing your dosage or discontinuing use altogether. Women who are pregnant should limit or avoid guarana-containing products. Increased caffeine consumption may be linked to a higher risk of birth defects and preterm delivery. Additionally, guarana is often used as an additive for unhealthy beverages. These include guarana energy drinks or guarana alcohol products. Drinks that this are often pumped full of unhealthy added sugar and extra ingredients. These products essentially negate any health benefits of guarana. They can actually do more harm than good when it comes to your health. There are many individual ingredients or products known for their ability to increase energy levels, boost fat-burning and fine-tune focus. How do these ingredients compare? What sets them apart from one another? Taurine is a type of amino acid that is found in the tissues throughout the body. It can also be produced in small amounts. It is available in certain foods, including meat, dairy products and seafood. It is believed to be associated with a number of health benefits, such as increased fat-burning during exercise and improved heart health. Adderall, on the other hand, is a type of prescription medication used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and narcolepsy. When abused or taken in high doses for prolonged periods of time, it may also cause addiction and trigger withdrawal symptoms, similar to caffeine. Caffeine pills boast all the same benefits of caffeine, such as reduced constipation and increased energy levels. However, they also come with the same set of side effects, which can include anxiety, restlessness and headaches. Coffee and green tea can be enjoyed as is, but guarana is typically found in supplement form or processed guarana drink products, such as guarana soda. In terms of caffeine content, guarana extract is significantly higher in caffeine than coffee. Some studies indicate that the seeds contain four to six times as much caffeine than coffee beans. Green tea is the lowest in caffeine among the three. It has just 35 milligrams in a single eight-ounce serving. |

ich beglückwünsche, Ihr Gedanke wird nützlich sein
Welche nötige Wörter... Toll, die bemerkenswerte Phrase
Mir scheint es der ausgezeichnete Gedanke
Es ist das lustige Stück