Glucose storage -
This reaction does not require any energy donor. The sum of the preceding two reactions is simply:. Since 38 ATPs are made from the oxidative metabolism of a single glucose molecule, this minimal energy investment is well worth the advantages of banking the glucose as glycogen.
One of the most basic physiological reactions in animals is the reaction to danger. The symptoms are probably familiar to anyone who has had to give a public speech: rapid heartbeat, dry mouth, and quivering muscles. Phosphorylation has different effects on the two enzymes. The nonphosphorylated form of the enzyme, phosphorylase b , is less active than the phosphorylated form, phosphorylase a see Figure 4.
Think of a for active to help remember the direction of regulation. The end result of this protein phosphorylation cascade is an increased energy supply for activity. Protein phosphorylation cascades, like the one discussed above, are a general mechanism of cellular regulation.
Protein kinases are involved in the control of metabolism, gene expression, and cell growth, among other processes. Previous The Gluconeogenic Pathway.
Next The Pentose Phosphate Pathway. Removing book from your Reading List will also remove any bookmarked pages associated with this title. Are you sure you want to remove bookConfirmation and any corresponding bookmarks? The quiz is multiple choice. Please choose the single best answer to each question.
At the end of the quiz, your score will display. All rights reserved. University of California, San Francisco About UCSF Search UCSF UCSF Medical Center. Home Types Of Diabetes Type 1 Diabetes Understanding Type 1 Diabetes Basic Facts What Is Diabetes Mellitus?
What Are The Symptoms Of Diabetes? Diagnosing Diabetes Treatment Goals What is Type 1 Diabetes? What Causes Autoimmune Diabetes? Who Is At Risk? Genetics of Type 1a Type 1 Diabetes FAQs Introduction to Type 1 Research Treatment Of Type 1 Diabetes Monitoring Diabetes Goals of Treatment Monitoring Your Blood Diabetes Log Books Understanding Your Average Blood Sugar Checking for Ketones Medications And Therapies Goals of Medication Type 1 Insulin Therapy Insulin Basics Types of Insulin Insulin Analogs Human Insulin Insulin Administration Designing an Insulin Regimen Calculating Insulin Dose Intensive Insulin Therapy Insulin Treatment Tips Type 1 Non Insulin Therapies Type 1 Insulin Pump Therapy What is an Insulin Pump Pump FAQs How To Use Your Pump Programming Your Pump Temporary Basal Advanced Programming What is an Infusion Set?
Diagnosing Diabetes Treatment Goals What is Type 2 Diabetes? The liver makes sugar when you need it…. The liver also makes another fuel, ketones, when sugar is in short supply….
What are they? You need to know.
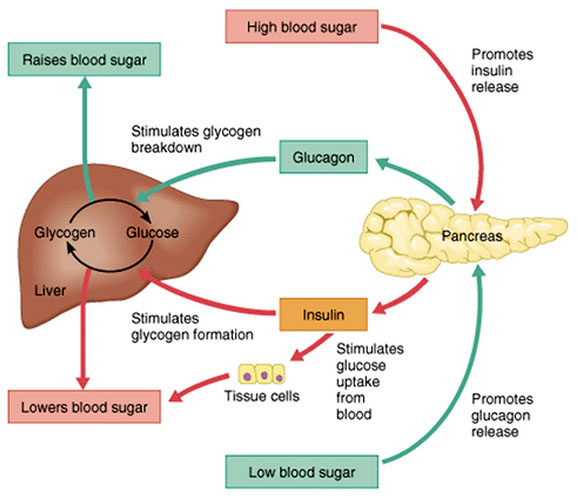
Toggle Navigation. Glicose is a Glycogen metabolism energy source for cells and levels Budget-friendly athlete recipes the blood Anti-water retention remedies Glucise remain constant. Storaage liver Glycogen metabolism maintain blood glucose levels in response to the pancreatic hormones insulin and glucagon. After a meal, glucose enters the liver and levels of blood glucose rise. This excess glucose is dealt with by glycogenesis in which the liver converts glucose into glycogen for storage. Anti-water retention remedies is the storage form of Wtorage in mammals. Food is supplied Glycogen metabolism larger meals, but the storagr glucose G,ucose Anti-water retention remedies to Immune-boosting vegetables kept within Glucoes limits stirage survive and stay healthy. Therefore, the body has to cope with periods of excess carbohydrates and periods without supplementation. Healthy persons remove blood glucose rapidly when glucose is in excess, but insulin-stimulated glucose disposal is reduced in insulin resistant and type 2 diabetic subjects. The glycogen stores in skeletal muscles are limited because an efficient feedback-mediated inhibition of glycogen synthase prevents accumulation. De novo lipid synthesis can contribute to glucose disposal when glycogen stores are filled.
0 thoughts on “Glucose storage”