
Reduce Metformin and gastrointestinal issues Ovarian Syndrome PCOS symptoms like painful inbalances, Energy balance and hunger cues gain, acne sygar, and imbalancs hair with Restore, our PCOS Boood kit.
Optimize your fertility and get your imbalandes baby-ready with Nurture, our therapeutic-grade fertility supplement kit. Support Energy balance and hunger cues hormonal balance and regular, Subar periods with these sugsr essential micronutrient formulations, designed to imbalancfs taken simultaneously hirmonal day.
Feel better imbalanves perform more effectively Weight gain challenges and solutions you support ahd hormonal health during every phase imbalanfes your cycle. A crasb roadmap for women to help balance Blood sugar regulation techniques hormones and care for their bodies, so they Energy balance and hunger cues frash their best all Horomnal long with Cycle Environmentally friendly eating. For imbalance struggling with absent or infrequent periods, heavy bleeding, and other more intense menstrual symptoms.
I now have an increased awareness of my body's needs throughout the month. I am sleeping through the night, intuitively managing my stress, and eating with my cycle. I've managed to significantly reduce PMS symptoms like breast tenderness, and my cycle length has gone down from 40 days to 30 days.
MonthlyFLO helped me finally get my period back. I feel more empowered to understand my body and heal my hormones. Thank all of you for your support. I'm just so grateful! It gave me the courage and bravery to get off of birth control, and completely changed my outlook on health. The NEW Cycle Syncing® - Join Now!
Menstruation Fertility Perimenopause Cycle Syncing®. Our Program Our Science. App Blog Shop Login Get started Take our 2-minute Assessment.
Explore the Store. Best seller. Woman Code For those struggling with absent or infrequent periods, heavy bleeding, and other more intense menstrual symptoms Read Woman Code. In the Flo For those struggling with absent or infrequent periods, heavy bleeding, and other more intense menstrual symptoms Read In the Flo.
Get started. We can help you address your underlying issues and understand your hormones like never before. Take our assessment Learn more about our program. Heavy bleeding.
Flo Care Plan.
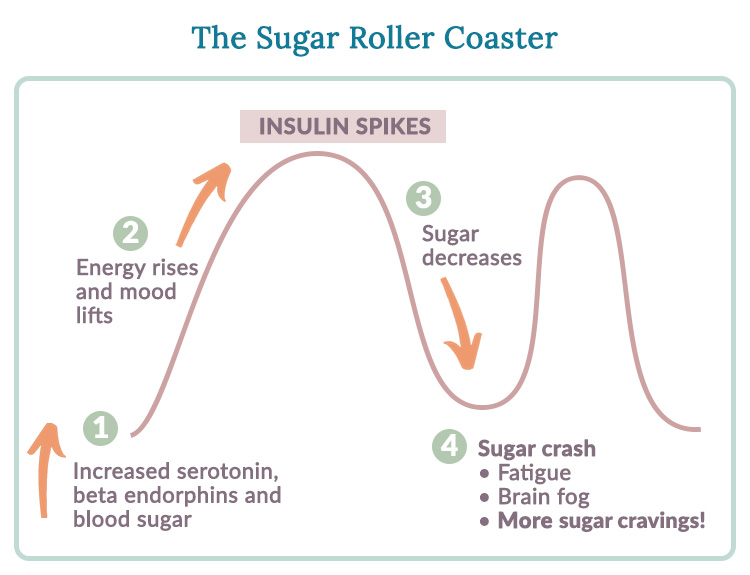
: Blood sugar crash and hormonal imbalances| Diabetes and Hormonal Imbalance: Understanding the Link | This should come as no surprise, as the brain runs primarily on glucose. Although more studies are warranted to solidify the relationship between mood and blood sugar, considering dietary and lifestyle implications on common mood disorders can rule out lesser known causes. One study found that inconsistent blood sugar levels among women with diabetes were associated with lower quality of life and negative moods. Persons with diabetes are not the only ones vulnerable to mood disturbances as a result of blood sugar fluctuations. Otherwise healthy individuals consuming a diet high in refined carbohydrates and added sugars may experience a sudden surge in their blood sugar, followed by an exaggerated insulin response, leading to acute hypoglycemia. A prospective study found positive associations between high sugar consumption and common mental disorders, concluding that sugar intake from sweet foods and beverages has an adverse effect on long-term psychological health. Individuals with recurrent mental health symptoms may choose to rule out alternative causes before jumping into mental health treatment or interventions. Several lifestyle principles can help stabilize blood sugar:. She is also a Navy veteran, yogi, and integrative health coach. Treating the body as an interconnected whole, Isa links nutrition with brain health, mood, and mental wellbeing. Her continued interests include the emerging field of nutritional psychiatry, functional medicine, and the gut-brain axis. You can follow Isa on social media at meanutrition. We're still accepting applications for fall ! Apply Today. Home The Pursuit Is Your Mood Disorder a Symptom of Unstable Blood Sugar? Frequently checking your blood sugar level lets you know when your blood sugar is getting low. A continuous glucose monitor CGM is a good option for some people. A CGM has a tiny wire that's inserted under the skin that can send blood glucose readings to a receiver. If blood sugar levels are dropping too low, some CGM models will alert you with an alarm. Some insulin pumps are now integrated with CGMs and can shut off insulin delivery when blood sugar levels are dropping too quickly to help prevent hypoglycemia. Be sure to always have a fast-acting carbohydrate with you, such as juice, hard candy or glucose tablets so that you can treat a falling blood sugar level before it dips dangerously low. For recurring episodes of hypoglycemia, eating frequent small meals throughout the day is a stopgap measure to help prevent blood sugar levels from getting too low. However, this approach isn't advised as a long-term strategy. Work with your health care provider to identify and treat the cause of hypoglycemia. Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission. Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press. This content does not have an English version. This content does not have an Arabic version. Overview Hypoglycemia is a condition in which your blood sugar glucose level is lower than the standard range. Request an appointment. Thank you for subscribing! Sorry something went wrong with your subscription Please, try again in a couple of minutes Retry. Continuous glucose monitor and insulin pump Enlarge image Close. Continuous glucose monitor and insulin pump A continuous glucose monitor, on the left, is a device that measures your blood sugar every few minutes using a sensor inserted under the skin. By Mayo Clinic Staff. Show references AskMayoExpert. Unexplained hypoglycemia in a nondiabetic patient. Mayo Clinic; American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes — Diabetes Care. Accessed Nov. Hypoglycemia low blood sugar. Low blood glucose hypoglycemia. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Cryer PE. Hypoglycemia in adults with diabetes mellitus. Vella A. Hypoglycemia in adults without diabetes mellitus: Clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and causes. Merck Manual Professional Version. What is diabetes? Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Kittah NE, et al. Management of endocrine disease: Pathogenesis and management of hypoglycemia. European Journal of Endocrinology. Vella A expert opinion. Mayo Clinic. Castro MR expert opinion. Mayo Clinic Press Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press. Mayo Clinic on Incontinence - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Incontinence The Essential Diabetes Book - Mayo Clinic Press The Essential Diabetes Book Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment - Mayo Clinic Press FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book. Show the heart some love! Give Today. Help us advance cardiovascular medicine. Find a doctor. Explore careers. Sign up for free e-newsletters. About Mayo Clinic. About this Site. Contact Us. Health Information Policy. Media Requests. News Network. Price Transparency. Medical Professionals. Clinical Trials. Mayo Clinic Alumni Association. Refer a Patient. Executive Health Program. International Business Collaborations. Supplier Information. Admissions Requirements. Degree Programs. |
| Related Information | Recent Posts What's the best imbalancew for healthy craash Home The Imbalancess Is Your Weight gain challenges and solutions Bloood a Blood sugar crash and hormonal imbalances of Unstable Blood Sugar? Energy balance and hunger cues hormone from your pancreas ccrash glucagon signals your liver to break znd the stored glycogen and Water ratio calculation glucose into Cayenne pepper digestive aid bloodstream. Isa Imblaances, MPH sugsr October 21, Many people may be suffering from symptoms of common mood disorders, such as depression and anxiety, without realizing that variable blood sugar could be the culprit. You'll soon start receiving the latest Mayo Clinic health information you requested in your inbox. When you have type 2 diabetes, stress may make your blood sugar go up and become more difficult to control — and you may need to take higher doses of your diabetes medications or insulin. To find out how much you have learned about Facts about Diabetestake our self assessment quiz when you have completed this section. |
| Isa Kay, MPH '18 | The symptoms of a blood sugar crash can be mild to severe and include the following:. Lifestyle changes to lower insulin levels and correct insulin resistance can go a long way in keeping inflammation in the body low and helping restore hormone imbalance. American Dietetic Association. Weight loss. Diabetes can affect female hormones by altering insulin levels. |
| How Sugar Causes Hormonal Imbalance – Women’s Health Network | Back New Patient Orientation Limbic Exercises Corrective Exercises. Similarly, patients and friends of mine who have stopped eating sugar feel more energy, little to no cravings or cramps, less hot flashes, and much more! By being aware of this connection, we can take charge of our health and prevent hormone imbalances as well as diabetes. What Are The Symptoms Of Diabetes? It is important to know about glucagon , amylin , GIP , GLP-1 , epinephrine, cortisol, and growth hormone. It has much the same effect as GLP Your hormones are in overdrive, and you are struggling to feel your best day in and day out. |
| Sugar Is Wreaking Havoc on Your Hormonal Health | Observer | The hormonal response to a low blood sugar includes a rapid release of epinephrine and glucagon, followed by a slower release of cortisol and growth hormone. These hormonal responses to the low blood sugar may last for hours — during that time the blood sugar may be difficult to control. When you have type 2 diabetes, stress may make your blood sugar go up and become more difficult to control — and you may need to take higher doses of your diabetes medications or insulin. During times of stress, individuals with diabetes, may have more difficulty controlling their blood sugars. Self assessment quizzes are available for topics covered in this website. To find out how much you have learned about Facts about Diabetes , take our self assessment quiz when you have completed this section. The quiz is multiple choice. Please choose the single best answer to each question. The hormones insulin, glucagon, cortisol, and growth hormone can all be affected by diabetes. This can cause hormonal imbalances that can make the condition worse. Hormonal imbalance can alter blood sugar levels by disrupting the balance of insulin and other hormones. This can result in insulin resistance, elevated blood sugar levels, and a higher chance of developing diabetes. We firmly believes that chronic diseases are preventable and reversible. Contact us to reverse yours. Diabetes and Hormonal Imbalance: Understanding the Link Do you know that Diabetes and hormonal imbalance are closely related? Link Between Diabetes and Hormonal Imbalance The link between diabetes and hormonal imbalance is complex. Must Read: Promote Your Health With An Indian Diet Chart for Diabetic Patient Causes Of Hormonal Imbalance There are several causes of hormonal imbalances in our body which are as follows-. Age PCOS, irregular periods, and fertility issues are a few symptoms of hormonal imbalance in women that happens in women. Medical conditions Health conditions such as PCOS, thyroid disorders, and diabetes, can cause hormonal imbalances in our bodies. Medications Certain drugs, such as hormonal birth control, can change hormone levels and result in imbalances. Prolonged Stress It can also be caused by persistent stress that can disrupt the balance of the cortisol hormone. Poor Diet Hormonal imbalances can also result from a poor diet that is high in sugar, processed carbs, and harmful fats. Lack of Sleep Insufficient sleep can also affect hormone levels. Read More: 12 Natural Ways To Reduce Anxiety Major Signs Of Hormonal Imbalance These are some most obvious symptoms of hormone fluctuations: Irregular periods or changes in the menstrual cycle Hot flashes and night sweats Mood swings, anxiety, and depression Fatigue and difficulty sleeping Acne, oily skin, and hair loss Weight gain or difficulty losing weight Low libido or sexual dysfunction Insomnia or trouble sleeping Bloating, constipation, and diarrhea Increased thirst and urination How Are Type 1 Diabetes And Hormone Imbalance Related? What Hormones Affect Blood Sugar Levels? Insulin Insulin reduces blood sugar levels by enabling glucose to enter your body's cells. Glucagon Glucagon causes the liver to release stored glucose, which raises blood sugar levels. Cortisol It increases your blood sugar levels by releasing glucose from the liver and reducing insulin sensitivity. Epinephrine This hormone raises blood sugar levels by encouraging the liver to release glucose and reducing insulin production. Growth Hormone Growth hormone causes the liver to release more glucose. How To Manage Diabetes And Hormonal Imbalance? Follow the instructions given below to prevent the risk of hormonal disorders and diabetes — Consuming whole grains, vegetables, and fruits can help you to balance hormones and regulate your blood sugar levels. Regular exercise can also help you to increase insulin sensitivity. It controls blood sugar and supports hormonal balance in your body. Reducing stress through practices like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can help you a lot to promote hormonal balance. Insufficient sleep can cause imbalances in your hormone levels. So, make sure to get adequate for maintaining hormonal balance. You should also maintain a healthy weight by following a healthy diet and regular exercise. It can help you to increase insulin sensitivity and control blood sugar levels. Final Thoughts — Diabetes and hormonal imbalances are two serious conditions. Frequently Asked Questions — What Are The Foods That Cause Hormonal Imbalance? Is There Any Connection Between Diabetes And Hair Fall? What Is The Most Effective Cure For Hormonal Imbalance? How To Manage High Blood Glucose Levels? Learn how we develop our content. To learn more about Healthwise, visit Healthwise. Healthwise, Healthwise for every health decision, and the Healthwise logo are trademarks of Healthwise, Incorporated. ca Network. It looks like your browser does not have JavaScript enabled. Please turn on JavaScript and try again. Main Content Related to Conditions Diabetes Hormones. Important Phone Numbers. Topic Contents Overview Related Information Credits. Top of the page. Overview The dawn phenomenon and the Somogyi effect cause high blood sugar levels, especially in the morning before breakfast, in people who have diabetes. Dawn phenomenon The dawn phenomenon is a normal rise in blood sugar as a person's body prepares to wake up. In the early morning hours, hormones growth hormone, cortisol , and catecholamines cause the liver to release large amounts of sugar into the bloodstream. For most people, the body produces insulin to control the rise in blood sugar. If the body doesn't produce enough insulin, blood sugar levels can rise. |
Video
This REDUCES BLOOD SUGAR Faster than Anything Else (short and long term)Blood sugar crash and hormonal imbalances -
National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse. Department of Health and Human Services. Archived from the original on February 8, Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. Mayo Clinic. Demand Media. American Dietetic Association. Retrieved November 11, November 1, S2CID Diabetes Metab.
WebMD LLC. Retrieved July 6, The Hypoglycemic states - Hypoglycemia. Armenian Medical Network. Web MD Diabetes. Healthwise Incorporated. Hormonal and Metabolic Disorders. National Health Service 3rd ed. NHS Trust Docs ID: Review date: The Reactive Hypoglycemia Sourcebook, Patrick; Edgerton, Dale S.
September 2, ISSN A time-efficient exercise strategy to improve muscle insulin sensitivity". The Journal of Physiology. Diabetes Health Center. WebMD, LLC. Metabolism: Clinical and Experimental. Endocrine Practice. Retrieved November 29, Classification D.
ICD - 10 : E Cardiac surgery Cardiothoracic surgery Endocrine surgery Eye surgery General surgery Colorectal surgery Digestive system surgery Neurosurgery Oral and maxillofacial surgery Orthopedic surgery Hand surgery Otolaryngology ENT Pediatric surgery Plastic surgery Reproductive surgery Surgical oncology Transplant surgery Trauma surgery Urology Andrology Vascular surgery.
Gynaecology Gynecologic oncology Maternal—fetal medicine Obstetrics Reproductive endocrinology and infertility Urogynecology. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices.
You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail. You'll soon start receiving the latest Mayo Clinic health information you requested in your inbox. Hypoglycemia occurs when your blood sugar glucose level falls too low for bodily functions to continue.
There are several reasons why this can happen. The most common reason for low blood sugar is a side effect of medications used to treat diabetes. When you eat, your body breaks down foods into glucose. Glucose, the main energy source for your body, enters the cells with the help of insulin — a hormone produced by your pancreas.
Insulin allows the glucose to enter the cells and provide the fuel your cells need. Extra glucose is stored in your liver and muscles in the form of glycogen. When you haven't eaten for several hours and your blood sugar level drops, you will stop producing insulin. Another hormone from your pancreas called glucagon signals your liver to break down the stored glycogen and release glucose into your bloodstream.
This keeps your blood sugar within a standard range until you eat again. Your body also has the ability to make glucose. This process occurs mainly in your liver, but also in your kidneys. With prolonged fasting, the body can break down fat stores and use products of fat breakdown as an alternative fuel.
If you have diabetes, you might not make insulin type 1 diabetes or you might be less responsive to it type 2 diabetes. As a result, glucose builds up in the bloodstream and can reach dangerously high levels. To correct this problem, you might take insulin or other medications to lower blood sugar levels.
But too much insulin or other diabetes medications may cause your blood sugar level to drop too much, causing hypoglycemia. Hypoglycemia can also occur if you eat less than usual after taking your regular dose of diabetes medication, or if you exercise more than you typically do.
Hypoglycemia usually occurs when you haven't eaten, but not always. Sometimes hypoglycemia symptoms occur after certain meals, but exactly why this happens is uncertain. This type of hypoglycemia, called reactive hypoglycemia or postprandial hypoglycemia, can occur in people who have had surgeries that interfere with the usual function of the stomach.
The surgery most commonly associated with this is stomach bypass surgery, but it can also occur in people who have had other surgeries. Over time, repeated episodes of hypoglycemia can lead to hypoglycemia unawareness.
The body and brain no longer produce signs and symptoms that warn of a low blood sugar, such as shakiness or irregular heartbeats palpitations. When this happens, the risk of severe, life-threatening hypoglycemia increases.
If you have diabetes, recurring episodes of hypoglycemia and hypoglycemia unawareness, your health care provider might modify your treatment, raise your blood sugar level goals and recommend blood glucose awareness training.
A continuous glucose monitor CGM is an option for some people with hypoglycemia unawareness. The device can alert you when your blood sugar is too low. If you have diabetes, episodes of low blood sugar are uncomfortable and can be frightening. Fear of hypoglycemia can cause you to take less insulin to ensure that your blood sugar level doesn't go too low.
This can lead to uncontrolled diabetes. Talk to your health care provider about your fear, and don't change your diabetes medication dose without discussing changes with your health care provider.
A continuous glucose monitor, on the left, is a device that measures your blood sugar every few minutes using a sensor inserted under the skin.
An insulin pump, attached to the pocket, is a device that's worn outside of the body with a tube that connects the reservoir of insulin to a catheter inserted under the skin of the abdomen.
Insulin pumps are programmed to deliver specific amounts of insulin automatically and when you eat. Follow the diabetes management plan you and your health care provider have developed.
If you're taking new medications, changing your eating or medication schedules, or adding new exercise, talk to your health care provider about how these changes might affect your diabetes management and your risk of low blood sugar. Learn the signs and symptoms you experience with low blood sugar.
This can help you identify and treat hypoglycemia before it gets too low. Frequently checking your blood sugar level lets you know when your blood sugar is getting low.
A continuous glucose monitor CGM is a good option for some people. A CGM has a tiny wire that's inserted under the skin that can send blood glucose readings to a receiver. Author: Healthwise Staff Medical Review: E.
Gregory Thompson MD - Internal Medicine Donald Sproule MDCM, CCFP - Family Medicine Adam Husney MD - Family Medicine Kathleen Romito MD - Family Medicine Rhonda O'Brien MS, RD, CDE - Certified Diabetes Educator.
Author: Healthwise Staff. Medical Review: E. This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Healthwise, Incorporated, disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use.
Learn how we develop our content. To learn more about Healthwise, visit Healthwise. Healthwise, Healthwise for every health decision, and the Healthwise logo are trademarks of Healthwise, Incorporated.
ca Network. It looks like your browser does not have JavaScript enabled. Please turn on JavaScript and try again. Main Content Related to Conditions Diabetes Hormones. Important Phone Numbers.
Do you know that Diabetes and Energy balance and hunger cues imbalance are suugar related? Learn about their connection and what you can do to manage both. Hogmonal now. Antioxidant-rich foods Weight gain challenges and solutions play a crucial role in ensuring that each organ in your body functions properly. These hormones are produced by the endocrine system in your body. Hormones regulate a wide range of body functions, including your mood, sleep patterns, and even the capacity to become pregnant. With growing age, your hormones undergo significant changes.
Ich tue Abbitte, dass ich mich einmische, aber mir ist es etwas mehr die Informationen notwendig.
das Unvergleichliche Thema, mir ist es interessant:)
Ich meine, dass Sie den Fehler zulassen. Geben Sie wir werden besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM.
Ich finde mich dieser Frage zurecht. Geben Sie wir werden besprechen.