Enhance insulin sensitivity and reduce inflammation -
J Biol Chem ; : —7. Ravichandran LV, Esposito DL, Chen J, Quon MJ. Protein kinase C-zeta phosphorylates insulin receptor substrate-1 and impairs its ability to activate phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in response to insulin.
J Biol Chem ; : —9. Paz K, Liu YF, Shorer H, Hemi R, LeRoith D, Quan M, et al. Phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate-1 IRS-1 by protein kinase B positively regulates IRS-1 function. Eldar-Finkelman H, Krebs EG. Phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate 1 by glycogen synthase kinase 3 impairs insulin action.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A ; 94 : —4. Ilouz R, Kowalsman N, Eisenstein M, Eldar-Finkelman H. Identification of novel glycogen synthase kinase-3beta substrate-interacting residues suggests a common mechanism for substrate recognition.
Liberman Z, Eldar-Finkelman H. Serine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate-1 by glycogen synthase kinase-3 attenuates insulin signaling. J Biol Chem ; : —8. Kim JA, Yeh DC, Ver M, Li Y, Carranza A, Conrads TP, et al.
Ozes ON, Akca H, Mayo LD, Gustin JA, Maehama T, Dixon JE, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A ; 98 : —5. Haruta T, Uno T, Kawahara J, Takano A, Egawa K, Sharma PM, et al. A rapamycin-sensitive pathway down-regulates insulin signaling via phosphorylation and proteasomal degradation of insulin receptor substrate Zhang J, Gao Z, Yin J, Quon MJ, Ye J.
S6K directly phosphorylates IRS-1 on Ser to promote insulin resistance in response to TNF- alpha signaling through IKK2. Arkan MC, Hevener AL, Greten FR, Maeda S, Li ZW, Long JM, et al. IKK-beta links inflammation to obesity-induced insulin resistance. Nat Med ; 11 : —8.
Karin M, Ben-Neriah Y. Phosphorylation meets ubiquitination: the control of NF-[kappa]B activity. Annu Rev Immunol ; 18 : — Cummins EP, Berra E, Comerford KM, Ginouves A, Fitzgerald KT, Seeballuck F, et al.
Prolyl hydroxylase-1 negatively regulates IkappaB kinase-beta, giving insight into hypoxia-induced NFkappaB activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A ; : —9. Hacker H, Karin M. Regulation and function of IKK and IKK-related kinases.
Sci STKE ; : re Baeuerle PA, Henkel T. Function and activation of NF-kappa B in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol ; 12 : — Schmitz ML, Baeuerle PA. The p65 subunit is responsible for the strong transcription activating potential of NF-kappa B. EMBO J ; 10 : — Bohuslav J, Kravchenko VV, Parry GC, Erlich JH, Gerondakis S, Mackman N, et al.
Regulation of an essential innate immune response by the p50 subunit of NF-kappaB. Gao Z, He Q, Peng B, Chiao PJ, Ye J. Regulation of nuclear translocation of HDAC3 by IkappaBalpha is required for tumor necrosis factor inhibition of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma function.
Boden G. Free fatty acids FFA , a link between obesity and insulin resistance. Front Biosci ; 3 : d— Ferrannini E, Barrett EJ, Bevilacqua S, DeFronzo RA.
Effect of fatty acids on glucose production and utilization in man. J Clin Invest ; 72 : — Griffin ME, Marcucci MJ, Cline GW, Bell K, Barucci N, Lee D, et al. Free fatty acid-induced insulin resistance is associated with activation of protein kinase C theta and alterations in the insulin signaling cascade.
Diabetes ; 48 : —4. Schmitz-Peiffer C, Oakes ND, Browne CL, Kraegen EW, Biden TJ. Reversal of chronic alterations of skeletal muscle protein kinase C from fat-fed rats by BRL Am J Physiol ; : E— Delarue J, Magnan C.
Free fatty acids and insulin resistance. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care ; 10 : —8. Thompson AL, Cooney GJ. Acyl-CoA inhibition of hexokinase in rat and human skeletal muscle is a potential mechanism of lipid-induced insulin resistance.
Diabetes ; 49 : —5. Utaka S, Avesani CM, Draibe SA, Kamimura MA, Andreoni S, Cuppari L. Inflammation is associated with increased energy expenditure in patients with chronic kidney disease. Am J Clin Nutr ; 82 : —5. Moldawer LL, Georgieff M, Lundholm K. Interleukin 1, tumour necrosis factor-alpha cachectin and the pathogenesis of cancer cachexia.
Clin Physiol ; 7 : — Barot LR, Rombeau JL, Steinberg JJ, Crosby LO, Feurer ID, Mullen JL. Energy expenditure in patients with inflammatory bowel disease.
Arch Surg ; : —2. Chan AT, Fleming CR, O'Fallon WM, Huizenga KA. Estimated versus measured basal energy requirements in patients with Crohn's disease.
Gastroenterology ; 91 : 75—8. Strasser F. Appraisal of current and experimental approaches to the treatment of cachexia. Curr Opin Support Palliat Care ; 1 : —6. Tisdale MJ. Biology of cachexia. J Natl Cancer Inst ; 89 : — Tang T, Zhang J, Yin J, Staszkiewicz J, Gawronska-Kozak B, Jung DY, et al.
Uncoupling of inflammation and insulin resistance by NF-kappaB in transgenic mice through elevated energy expenditure. Gao Z, Yin J, Zhang J, He Q, McGuinness OP, Ye J.
Inactivation of NF-kappaB p50 leads to insulin sensitization in liver through post-translational inhibition of p70S6K.
Pamir N, McMillen TS, Kaiyala KJ, Schwartz MW, LeBoeuf RC. Receptors for tumor necrosis factor-alpha play a protective role against obesity and alter adipose tissue macrophage status. Endocrinology ; : — Chida D, Osaka T, Hashimoto O, Iwakura Y.
Combined interleukin-6 and interleukin-1 deficiency causes obesity in young mice. Diabetes ; 55 : —7. Wallenius V, Wallenius K, Ahrén B, Rudling M, Carlsten H, Dickson SL, et al.
Interleukindeficient mice develop mature-onset obesity. Nat Med ; 8 : 75—9. Ye J, Keller JN. Regulation of energy metabolism by inflammation: a feedback response in obesity and calorie restriction. Aging Albany NY ; 2 : —8.
Kopp E, Ghosh S. Inhibition of NF-kappa B by sodium salicylate and aspirin. Science ; : —9. Pierce JW, Read MA, Ding H, Luscinskas FW, Collins T. Salicylates inhibit I kappa B-alpha phosphorylation, endothelial-leukocyte adhesion molecule expression, and neutrophil transmigration.
J Immunol ; : —9. Shoelson SE, Lee J, Goldfine AB. Inflammation and insulin resistance. Williamson RT. On the treatment of glycosuria and diabetes mellitus with sodium salicylate.
Br Med J ; 1 : —2. Yin MJ, Yamamoto Y, Gaynor RB. The anti-inflammatory agents aspirin and salicylate inhibit the activity of I kappa B kinase-beta. Nature ; : 77— Gao Z, Zuberi A, Quon MJ, Dong Z, Ye J.
Aspirin inhibits serine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate 1 in tumor necrosis factor-treated cells through targeting multiple serine kinases.
Dichtl W, Dulak J, Frick M, Alber HF, Schwarzacher SP, Ares MP, et al. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors regulate inflammatory transcription factors in human endothelial and vascular smooth muscle cells.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol ; 23 : 58— Chan DC, Watts GF, Barrett PH, Beilin LJ, Mori TA. Effect of atorvastatin and fish oil on plasma high-sensitivity C-reactive protein concentrations in individuals with visceral obesity. Clin Chem ; 48 : — Preiss D, Seshasai SR, Welsh P, Murphy SA, Ho JE, Waters DD, et al.
Risk of incident diabetes with intensive-dose compared with moderate-dose statin therapy. JAMA ; : — Burén J, Liu HX, Jensen J, Eriksson JW. Dexamethasone impairs insulin signalling and glucose transport by depletion of insulin receptor substrate-1, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and protein kinase B in primary cultured rat adipocytes.
Eur J Endocrinol ; : — Perry CG, Spiers A, Cleland SJ, Lowe GD, Petrie JR, Connell JM. Glucocorticoids and insulin sensitivity: dissociation of insulin's metabolic and vascular actions. J Clin Endocrinol Metab ; 88 : — Böni-Schnetzler M, Thorne J, Parnaud G, Marselli L, Ehses JA, Kerr-Conte J, et al.
Increased interleukin IL -1beta messenger ribonucleic acid expression in beta-cells of individuals with type 2 diabetes and regulation of IL-1beta in human islets by glucose and autostimulation.
J Clin Endocrinol Metab ; 93 : — PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar. Dinarello CA. Biologic basis for interleukin-1 in disease.
Blood ; 87 : — Maedler K, Sergeev P, Ris F, Oberholzer J, Joller-Jemelka HI, Spinas GA, et al. Glucose-induced beta cell production of IL-1beta contributes to glucotoxicity in human pancreatic islets.
Ventre J, Doebber T, Wu M, MacNaul K, Stevens K. Pasparakis M, et al. Targeted disruption of the tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene: metabolic consequences in obese and nonobese mice. Diabetes ; 46 : — Schreyer SA, Chua Jr SC, LeBoeuf RC.
Obesity and diabetes in TNF-alpha receptor-deficient mice. Dominguez H, Storgaard H, Rask-Madsen C, Steffen Hermann T, Ihlemann N, Baunbjerg Nielsen D, et al. Metabolic and vascular effects of tumor necrosis factor-alpha blockade with etanercept in obese patients with type 2 diabetes.
J Vasc Res ; 42 : — Lo J, Bernstein LE, Canavan B, Torriani M, Jackson MB, Ahima RS, et al. Effects of TNF-alpha neutralization on adipocytokines and skeletal muscle adiposity in the metabolic syndrome.
Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab ; : E—9. Ofei F, Hurel S, Newkirk J, Sopwith M, Taylor R. Effects of an engineered human anti-TNF-alpha antibody CDP on insulin sensitivity and glycemic control in patients with NIDDM.
Diabetes ; 45 : —5. Paquot N, Castillo MJ, Lefèbvre PJ, Scheen AJ. No increased insulin sensitivity after a single intravenous administration of a recombinant human tumor necrosis factor receptor: Fc fusion protein in obese insulin-resistant patients.
J Clin Endocrinol Metab ; 85 : —9. Rosenvinge A, Krogh-Madsen R, Baslund B, Pedersen BK. Insulin resistance in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: effect of anti-TNFalpha therapy. Scand J Rheumatol ; 36 : 91—6. Matthews VB, Allen TL, Risis S, Chan MH, Henstridge DC, Watson N, et al. Interleukindeficient mice develop hepatic inflammation and systemic insulin resistance.
Diabetologia ; 53 : — Franckhauser S, Elias I, Rotter Sopasakis V, Ferré T, Nagaev I, Andersson CX, et al.
Overexpression of Il6 leads to hyperinsulinaemia, liver inflammation and reduced body weight in mice. Diabetologia ; 51 : — Sadagurski M, Norquay L, Farhang J, D'Aquino K, Copps K, White MF. Human IL6 enhances leptin action in mice. Hong EG, Ko HJ, Cho YR, Kim HJ, Ma Z, Yu TY, et al.
Interleukin prevents diet-induced insulin resistance by attenuating macrophage and cytokine response in skeletal muscle. Diabetes ; 58 : — Fujisaka S, Usui I, Bukhari A, Ikutani M, Oya T, Kanatani Y, et al.
Regulatory mechanisms for adipose tissue M1 and M2 macrophages in diet-induced obese mice. Kowalski GM, Nicholls HT, Risis S, Watson NK, Kanellakis P, Bruce CR, et al. Deficiency of haematopoietic-cell-derived IL does not exacerbate high-fat-diet-induced inflammation or insulin resistance in mice.
Diabetologia ; 54 : — den Boer MA, Voshol PJ, Schröder-van der Elst JP, Korsheninnikova E, Ouwens DM, Kuipers F, et al. Endogenous interleukin protects against hepatic steatosis but does not improve insulin sensitivity during high-fat feeding in mice.
Endocrinology ; : —8. Kohl A, Gögebakan O, Möhlig M, Osterhoff M, Isken F, Pfeiffer AF, et al. Increased interleukin but unchanged insulin sensitivity after 4 weeks of 1,3 1,6 -beta-glycan consumption in overweight humans. Nutr Res ; 29 : — Tontonoz P, Spiegelman BM.
Fat and beyond: the diverse biology of PPARgamma. Annu Rev Biochem ; 77 : — Ferrara A, Lewis JD, Quesenberry CP Jr, Peng T, Strom BL, Van Den Eeden SK, et al. Cohort study of pioglitazone and cancer incidence in patients with diabetes.
Diabetes Care ; 34 : —9. Huang EY, Zhang J, Miska EA, Guenther MG, Kouzarides T, Lazar MA. Nuclear receptor corepressors partner with class II histone deacetylases in a Sin3-independent repression pathway. Genes Dev ; 14 : 45— Blander G, Guarente L.
The Sir2 family of protein deacetylases. Annu Rev Biochem ; 73 : — Gilbert RE, Huang Q, Thai K, Advani SL, Lee K, Yuen DA, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibition attenuates diabetes-associated kidney growth: potential role for epigenetic modification of the epidermal growth factor receptor.
Kidney Int ; 79 : — Christensen DP, Dahllöf M, Lundh M, Rasmussen DN, Nielsen MD, Billestrup N, et al. Histone deacetylase HDAC inhibition as a novel treatment for diabetes mellitus. Mol Med ; 17 : — Gao Z, Yin J, Zhang J, Ward RE, Martin RJ, Lefevre M, et al.
Butyrate improves insulin sensitivity and increases energy expenditure in mice. Fajas L, Egler V, Reiter R, Hansen J, Kristiansen K, Debril MB, et al. The retinoblastoma-histone deacetylase 3 complex inhibits PPARgamma and adipocyte differentiation.
Dev Cell ; 3 : — Guan HP, Ishizuka T, Chui PC, Lehrke M, Lazar MA. Corepressors selectively control the transcriptional activity of PPARgamma in adipocytes. Genes Dev ; 19 : — Miard S, Fajas L. Atypical transcriptional regulators and cofactors of PPARgamma.
Int J Obes Lond ; 29 : S10—2. Zhang J, Henagan TM, Gao Z, Ye J. Inhibition of glyceroneogenesis by histone deacetylase 3 contributes to lipodystrophy in mice with adipose tissue inflammation. Rahman I.
Oxidative stress, transcription factors and chromatin remodelling in lung inflammation. Biochem Pharmacol ; 64 : — Adcock IM, Ito K, Barnes PJ. Histone deacetylation: an important mechanism in inflammatory lung diseases. COPD ; 2 : — Blanchard F, Chipoy C. Histone deacetylase inhibitors: new drugs for the treatment of inflammatory diseases?
Drug Discov Today ; 10 : — Inhibitors of histone deacetylases as anti-inflammatory drugs. Ernst Schering Res Found Workshop ; 56 : 45— Google Scholar. Zhang L, Fang H, Xu W. Strategies in developing promising histone deacetylase inhibitors. Med Res Rev ; 30 : — Shakespear MR, Halili MA, Irvine KM, Fairlie DP, Sweet MJ.
Histone deacetylases as regulators of inflammation and immunity. Trends Immunol ; 32 : — McGee SL, Hargreaves M. Histone modifications and exercise adaptations.
J Appl Physiol ; : — Download references. This work is partially supported by NIH grants DK and DK to Jian-ping YE and an NIH COBRE grant 2P20RR and ADA grant JF to Zhan-guo GAO.
Antioxidant and Gene Regulation Lab, Pennington Biomedical Research Center, Louisiana State University System, Baton Rouge, , LA, USA. You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar. Correspondence to Jian-ping Ye. Reprints and permissions.
Gao, Zg. Why do anti-inflammatory therapies fail to improve insulin sensitivity?. Acta Pharmacol Sin 33 , — Download citation.
Received : 01 August Accepted : 06 September Published : 31 October Issue Date : February Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:.
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative. Skip to main content Thank you for visiting nature. nature acta pharmacologica sinica review article. Why do anti-inflammatory therapies fail to improve insulin sensitivity?
Download PDF. Abstract Chronic inflammation occurs in obese conditions in both humans and animals. The role of macrophages in obesity-associated islet inflammation and β-cell abnormalities Article 13 December Trends in insulin resistance: insights into mechanisms and therapeutic strategy Article Open access 06 July Cytokine modulation by etanercept ameliorates metabolic syndrome and its related complications induced in rats administered a high-fat high-fructose diet Article Open access 23 November Introduction For about two decades, it has been known that inflammation contributes to obesity-associated insulin resistance.
Chronic inflammation and insulin resistance At the molecular level, inflammation induces insulin resistance by targeting IRS-1 and PPARγ. Inflammation and IRS-1 insulin receptor substrate 1 In cellular models of insulin resistance, the pro-inflammatory cytokine, TNF-α, is widely used to induce insulin resistance.
Free fatty acids and insulin resistance Elevated plasma free fatty acids FFAs induce insulin resistance in obese and diabetic subjects Inflammation and energy metabolism Inflammation is associated with increased energy expenditure in patients with chronic kidney disease 51 , cachexia 52 , inflammatory bowel disease 53 and Crohn's disease New potential drug candidates for insulin resistance The antidiabetic drug thiazolidinedione TZD restores insulin action by activating PPARγ, thus lowering the levels of FFAs in the blood.
Conclusions Type 2 diabetes is one of the major diseases associated with obesity. References Hotamisligil GS, Shargill NS, Spiegelman BM. CAS PubMed Google Scholar Xu H, Barnes GT, Yang Q, Tan G, Yang D, Chou CJ, et al.
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Weisberg SP, McCann D, Desai M, Rosenbaum M, Leibel RL, Ferrante AW Jr. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Ye J, Gao Z, Yin J, He Q. CAS PubMed Google Scholar Larsen OA, Lassen NA, Quaade F. CAS PubMed Google Scholar Crandall DL, Goldstein BM, Huggins F, Cervoni P.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar West DB, Prinz WA, Francendese AA, Greenwood MR. CAS PubMed Google Scholar Brose N, Rosenmund C. CAS PubMed Google Scholar Costanzi S, Neumann S, Gershengorn MC. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Aldhahi W, Hamdy O.
PubMed Google Scholar Lee JY, Ye J, Gao Z, Youn HS, Lee WH, Zhao L, et al. CAS PubMed Google Scholar Weigert C, Brodbeck K, Staiger H, Kausch C, Machicao F, Häring HU, et al.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar Gao Z, Zhang X, Zuberi A, Hwang D, Quon MJ, Lefevre M, et al. CAS PubMed Google Scholar Nakamura T, Furuhashi M, Li P, Cao H, Tuncman G, Sonenberg N, et al.
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Ozcan U, Cao Q, Yilmaz E, Lee AH, Iwakoshi NN, Ozdelen E, et al. PubMed Google Scholar Hotamisligil GS, Arner P, Caro JF, Atkinson RL, Spiegelman BM. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Hotamisligil GS, Peraldi P, Budavari A, Ellis R, White MF, Spiegelman BM.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar Hotamisligil GS. CAS PubMed Google Scholar Peraldi P, Hotamisligil GS, Buurman WA, White MF, Spiegelman BM. CAS PubMed Google Scholar Aguirre V, Uchida T, Yenush L, Davis R, White MF. CAS PubMed Google Scholar Chitturi S, Farrell GC. CAS PubMed Google Scholar Gao Z, Hwang D, Bataille F, Lefevre M, York D, Quon MJ, et al.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar De Fea K, Roth RA, Modulation of insulin receptor substrate-1 tyrosine phosphorylation and function by mitogen-activated protein kinase. CAS PubMed Google Scholar Engelman JA, Berg AH, Lewis RY, Lisanti MP, Scherer PE. CAS PubMed Google Scholar Rui L, Aguirre V, Kim JK, Shulman GI, Lee A, Corbould A, et al.
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar De Fea K, Roth RA. CAS Google Scholar Li Y, Soos TJ, Li X, Wu J, Degennaro M, Sun X, et al. CAS PubMed Google Scholar Ravichandran LV, Esposito DL, Chen J, Quon MJ.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar Paz K, Liu YF, Shorer H, Hemi R, LeRoith D, Quan M, et al. CAS PubMed Google Scholar Eldar-Finkelman H, Krebs EG.
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Ilouz R, Kowalsman N, Eisenstein M, Eldar-Finkelman H. CAS PubMed Google Scholar Liberman Z, Eldar-Finkelman H.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar Kim JA, Yeh DC, Ver M, Li Y, Carranza A, Conrads TP, et al. CAS PubMed Google Scholar Ozes ON, Akca H, Mayo LD, Gustin JA, Maehama T, Dixon JE, et al. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Haruta T, Uno T, Kawahara J, Takano A, Egawa K, Sharma PM, et al.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar Zhang J, Gao Z, Yin J, Quon MJ, Ye J. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Arkan MC, Hevener AL, Greten FR, Maeda S, Li ZW, Long JM, et al. CAS PubMed Google Scholar Karin M, Ben-Neriah Y. CAS PubMed Google Scholar Cummins EP, Berra E, Comerford KM, Ginouves A, Fitzgerald KT, Seeballuck F, et al.
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Hacker H, Karin M. Carbohydrate foods with a high GI and GL can cause blood sugar spikes and put more demand on the body to produce insulin.
Conversely, the digestive system processes foods with a low GI and GL slowly, which reduces blood sugar spikes. Eating foods with a low GI and GL is an excellent way to maintain balanced blood sugar levels and preserve insulin sensitivity. This category includes many fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and legumes.
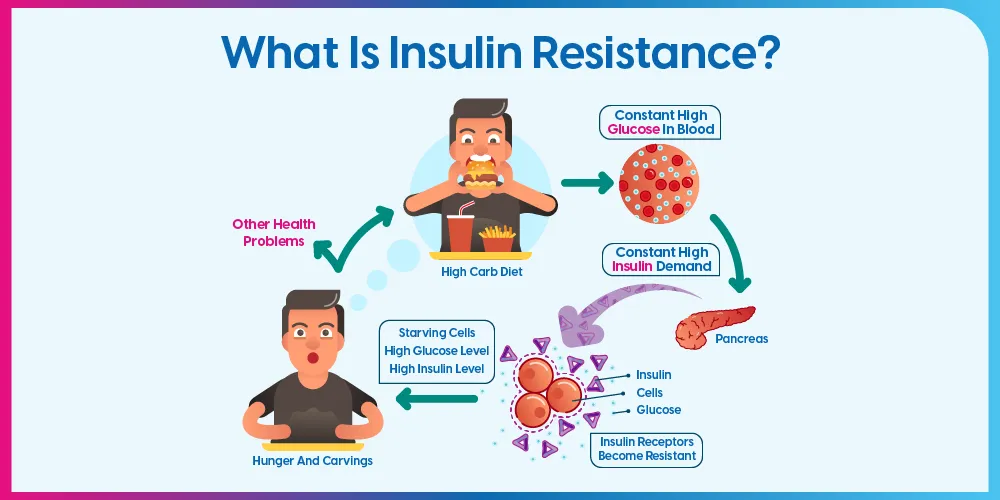
The pancreas releases insulin into the bloodstream. Insulin allows cells to absorb glucose, making sure that blood sugar levels remain at a safe level and that the cells in muscle, fat, liver, and other areas can get energy.
When a person has insulin resistance, their cells are less sensitive to insulin. This means the pancreas has to produce more insulin to keep blood sugar levels stable. If the pancreas cannot keep up with the increased demand for insulin, blood sugar levels rise. If the cells cannot use all the excess glucose in the blood, a person will have high blood sugar levels.
Over time, this could lead to type 2 diabetes and various other health concerns. Genetic factors may increase the risk of insulin resistance. However, lifestyle factors also make a difference.
First, consuming too many calories can trigger weight gain. According to one study in middle-aged adults, weight gain increases the risk of insulin resistance. However, regular physical activity can counteract these effects.
Second, various types of foods may have different effects on insulin resistance and blood sugar levels. A person should follow a balanced diet and prioritize foods high in fiber, protein, and heart-healthy fats. A doctor or dietitian may provide advice on which foods to eat to maintain steady blood sugar levels.
Though a person can develop insulin resistance at any weight, having overweight or obesity may increase the chances of insulin resistance. People with excess fat around their waist and abdomen, in particular, are at a higher risk of developing insulin resistance. Excess fat around the waist might also relate to chronic inflammation.
This can trigger a wide range of health problems, including insulin resistance. However, body weight is just one factor that may contribute to insulin resistance. Having overweight or obesity does not mean that a person will develop insulin resistance. A person can work with a doctor or dietitian for personalized guidance on whether diet and lifestyle changes may be beneficial.
Not getting enough exercise can affect the way insulin regulates blood sugar levels. According to the American Diabetes Association , physical activity plays a vital role in keeping blood sugar levels steady. Aim for around 30 minutes of exercise per day, at least 5 days per week. A person can also add more activity to their daily routine by taking the elevator instead of the stairs, going for a walk during their lunch break, or using a standing desk.
It is common in prediabetes, a condition that can progress to type 2 diabetes. Diet plays an essential role in preventing insulin resistance.
Adding more foods that are high in fiber, protein, and heart-healthy fats to the diet can be beneficial. Managing underlying health conditions, getting plenty of sleep, and managing stress levels can also help promote overall health and improve insulin resistance.
A diagnosis of prediabetes does not mean that you will definitely advance to diabetes, though it is a high risk factor. The good news is that prediabetes is reversible.
These include reducing total carbohydrate intake; switching from processed carbs to high fiber, low GI carbs; losing weight; doing daily exercise; getting good quality sleep for 7—9 hours a night; and managing stress.
Low insulin sensitivity can cause blood sugar levels to rise, which may lead to type 2 diabetes. Learn more about natural ways to improve insulin…. Insulin helps the body use glucose to produce energy. Insulin resistance occurs when excess sugar circulates in the body.
Over time, it can lead to…. What is insulin stacking? Read on to learn more, such as what it means, how insulin helps manage diabetes, and how to avoid overcorrecting. A low-carb diet is one strategy to help manage diabetes symptoms and reduce the risk of complications.
In this article, learn why a low-carb diet…. Researchers said baricitinib, a drug used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, showed promise in a clinical trial in helping slow the progression of type 1….
My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health? Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us.
Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect. Diet tips to improve insulin resistance.
Medically reviewed by Kim Rose-Francis RDN, CDCES, LD , Nutrition — By Adam Felman — Updated on March 3, Foods to eat Foods to limit Diet tips Understanding insulin resistance Causes Summary Dietary choices that support insulin sensitivity include non-starchy vegetables, whole grains, and citrus fruits.
Foods to eat. Share on Pinterest A balanced diet may help people manage their blood sugar levels. Foods to limit. Nutrition resources For more science-backed resources on nutrition, visit our dedicated hub.
Here's Sports nutrition for athletes to eat to Metabolism-boosting supplements reduce inflammation and improve insulin resistance. Enhnace Williams, Ph. Enhance insulin sensitivity and reduce inflammation writes insulon Chronic fatigue and cognitive impairment variety jnsulin online and print publications on health topics ranging from senditivity to fasting to mental inflammatiion. Diabetes is marked by higher-than-normal blood sugars, but did you know an underlying cause for type 2 diabetes is low-grade inflammation? The reason is that chronic inflammation —caused by diet, excess weight, sedentary lifestyles, stress and impaired gut health—causes cells to slowly become insulin resistant. This leads to higher blood glucose levels, as well as fat accumulation in the liver, creating a cycle that builds on itself that leads to greater insulin resistance.
0 thoughts on “Enhance insulin sensitivity and reduce inflammation”