
Sugar level regulation strategies -
Be sure to talk to your health care team about which targets are best for you. Low blood sugar also called hypoglycemia has many causes, including missing a meal, taking too much insulin, taking other diabetes medicines, exercising more than normal, and drinking alcohol.
Know what your individual symptoms are so you can catch low blood sugar early and treat it. Low blood sugar can be dangerous and should be treated as soon as possible. Driving with low blood sugar can be dangerous, so be sure to check your blood sugar before you get behind the wheel.
Carry supplies for treating low blood sugar with you. If you feel shaky, sweaty, or very hungry or have other symptoms, check your blood sugar. Wait for 15 minutes and then check your blood sugar again. If you have problems with low blood sugar, ask your doctor if your treatment plan needs to be changed.
Many things can cause high blood sugar hyperglycemia , including being sick, being stressed, eating more than planned, and not giving yourself enough insulin. Over time, high blood sugar can lead to long-term, serious health problems. Symptoms of high blood sugar include:. If you get sick , your blood sugar can be hard to manage.
You may not be able to eat or drink as much as usual, which can affect blood sugar levels. High ketones can be an early sign of diabetic ketoacidosis, which is a medical emergency and needs to be treated immediately.
Ketones are a kind of fuel produced when fat is broken down for energy. When too many ketones are produced too fast, they can build up in your body and cause diabetic ketoacidosis, or DKA. DKA is very serious and can cause a coma or even death.
Common symptoms of DKA include:. If you think you may have DKA, test your urine for ketones. Follow the test kit directions, checking the color of the test strip against the color chart in the kit to see your ketone level. If your ketones are high, call your health care provider right away.
DKA requires treatment in a hospital. Talk to your doctor about how to keep your blood sugar levels within your target range. Your doctor may suggest the following:. Carbs in food make your blood sugar levels go higher after you eat them than when you eat proteins or fats. You can still eat carbs if you have diabetes.
The amount you can have and stay in your target blood sugar range depends on your age, weight, activity level, and other factors. Counting carbs in foods and drinks is an important tool for managing blood sugar levels.
Make sure to talk to your health care team about the best carb goals for you. The A1C test is a simple blood test that measures your average blood sugar levels over the past 2 or 3 months.
A1C testing is part of the ABCs of diabetes—important steps you can take to prevent or delay health complications down the road:.
Work with your doctor to establish a personal A1C goal for you. Eating a healthy diet with plenty of fruit and vegetables, maintaining a healthy weight , and getting regular physical activity can all help. Effects of Diet, Lifestyle, Chrononutrition and Alternative Dietary Interventions on Postprandial Glycemia and Insulin Resistance.
Published online Feb Takahashi M, Ozaki M, Kang M, Sasaki H, et al. Effects of Meal Timing on Postprandial Glucose Metabolism and Blood Metabolites in Healthy Adults. Published online Nov All About Your A1C. Yuan X, Wang J, Yang S, Gao M, et al.
Effect of Intermittent Fasting Diet on Glucose and Lipid Metabolism and Insulin Resistance in Patients with Impaired Glucose and Lipid Metabolism: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.
Int J Endocrinol. Published online Mar Marventano S, Vetrani C, Vitale M, Godos J, et al. Whole Grain Intake and Glycaemic Control in Healthy Subjects: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Sanders LM, Zhu Y, Wilcox ML, Koecher K, et al. Whole grain intake, compared to refined grain, improves postprandial glycemia and insulinemia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.
Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. Online ahead of print. Department of Agriculture. Food Group Gallery. Bird SR, Hawley JA. Update on the effects of physical activity on insulin sensitivity in humans. BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med. eCollection Bellini A, Nicolo A, Bazzucchi I, Sacchetti M. The Effects of Postprandial Walking on the Glucose Response after Meals with Different Characteristics.
Published online Mar 4. Buffey AJ, Herring MP, Langley CK, Donnelly AE, et al. The Acute Effects of Interrupting Prolonged Sitting Time in Adults with Standing and Light-Intensity Walking on Biomarkers of Cardiometabolic Health in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.
Sports Med. Epub Feb Bittel AJ, Bittel DC, Mittendorfer B, Patterson BW, et al. A single bout of premeal resistance exercise improves postprandial glucose metabolism in obese Men with prediabetes. Med Sci Sports Exerc.
Bellini A, Nicolo A, Bulzomi R, Bazzucchi I, et al. The effect of different postprandial exercise types on glucose response to breakfast in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
Published online Apr Pulse consumption improves indices of glycemic control in adults with and without type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of acute and long-term randomized controlled trials.
Eur J Nutr. Ramdath D, Renwick S, Duncan AM. The Role of Pulses in the Dietary Management of Diabetes. Can J Diabetes.
Xiao K, Furutani A, Sasaki H, Takahashi M, et al. Effect of a high protein diet at breakfast on postprandial glucose level at dinner time in healthy adults. Published online Dec Chen Z, Zuurmond MG, Van der Schaft N, Nano J, et al. Plant versus animal based diets and insulin resistance, prediabetes and type 2 diabetes: the Rotterdam Study.
Eur J Epidemiol. Published online Jun 8. Park E, Edirisinghe I, Burton-Freeman B. Avocado Fruit on Postprandial Markers of Cardio-Metabolic Risk: A Randomized Controlled Dose Response Trial in Overweight and Obese Men and Women.
Journal of Diabetes Mellitus , 13, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Continuous Glucose Monitoring. Rohling M, Martin T, Wonnemann M, Kragl M, et al.
Determination of postprandial glycemic responses by continuous glucose monitoring in a real-world setting. Dimidi E, Cox SR, Rossi M, Whelan K.
Fermented doods: Definitions and characteristics, impact on the gut microbiota and effects on gastrointestinal health and disease. Published online Aug 5. Effects of diet, lifestyle, chrononutrition and alternative dietary interventions on postprandial glycemia and insulin resistance.
Atkinson F, Cohen M, Lau K, Brand-Miller JC. Glycemic index and insulin index after a standard carbohydrate meal consumed with live kombucha: A randomised, placebo-controlled, crossover trial. Front Nutr. Paul AK, Lim CL, Apu MAI, Dolma KG, et al.
Are fermented foods effective against inflammatory diseases? Int J Environ Res Public Health. American Heart Association. Added sugars. How too much added sugar affects your health infographic. Added sugars drive insulin resistance, hyperinsulinemia, hypertension, type 2 diabetes and coronary heart disease.
Mo Med. Mathur K, Agrawal RK, Nagpure S, Deshpande D. Effect of artificial sweeteners on insulin resistance among type-2 diabetes mellitus patients.
J Family Med Prim Care. Published online Jan Bueno-Hernández N, Esquivel-Velázquez M, Alcántara-Suárez R, Gómez-Arauz A, et al.
Chronic sucralose consumption induces elevation of serum insulin in young healthy adults: a randomized, double blind, controlled trial. Nutr J. World Health Organization. WHO advises not to use non-sugar sweeteners for weight control in newly released guideline. American Diabetes Association.
Low Vitamin D May Contribute to Insulin Resistance. Hypervitaminosis D. Farahmand MA, Daneshzad E, Fung TT, Zahidi F. What is the impact of vitamin D supplementation on glycemic control in people with type-2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trails.
BMC Endocr Disord. Pittas AG, Kawahara T, Jorde R, Dawson-Hughes B, et al. Vitamin D and Risk for Type 2 Diabetes in People With Prediabetes : A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Individual Participant Data From 3 Randomized Clinical Trials.
Ann Intern Med. Epub Feb 7. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Good hydration linked with longevity. Janbozorgi N, Allipour R, Djafarian K, Shab-Bidar S, et al. Water intake and risk of type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies.
Diabetes Metab Syndr. Epub May Johnson EC, Bardis CN, Jansen LT, Adams JD, et al. Reduced water intake deteriorates glucose regulation in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Nutr Res. Sedaghat G, Montazerifar F, Keykhaie MI, Karajibani M, et al. Effect of pre-meal water intake on the serum levels of Copeptin, glycemic control, lipid profile and anthropometric indices in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized, controlled trial.
J Diabetes Metab Disord. eCollection Jun. Use limited data to select advertising. Create profiles for personalised advertising. Use profiles to select personalised advertising. Create profiles to personalise content. Use profiles to select personalised content. Measure advertising performance.
Measure content performance. Understand audiences through statistics or combinations of data from different sources. Develop and improve services. Use limited data to select content. List of Partners vendors.
Wellness Nutrition. By Cynthia Sass, MPH, RD. Cynthia Sass, MPH, RD. Cynthia Sass is a nutritionist and registered dietitian with master's degrees in both nutrition science and public health.
Frequently seen on national TV, she's Health's contributing nutrition editor and counsels clients one-on-one through her virtual private practice. Cynthia is board certified as a specialist in sports dietetics and has consulted for five professional sports teams, including five seasons with the New York Yankees.
She is currently the nutrition consultant for UCLA's Executive Health program. Sass is also a three-time New York Times best-selling author and Certified Plant Based Professional Cook.
Connect with her on Instagram and Facebook, or visit www. health's editorial guidelines. Medically reviewed by Jamie Johnson, RDN. Jamie Johnson, RDN, is the owner of the nutrition communications practice Ingraining Nutrition. learn more. In This Article View All. In This Article.
Maintaining rgulation healthy level of blood sugar can help improve Sports nutrition supplements Sugar level regulation strategies and regulatiob energy levels. In stratehies, chronically high blood sugar levels can lead Sugsr Sugar level regulation strategies health risks like heart diseasevision loss, and kidney disease. Whether you regulatjon type 2 diabetes Sugar level regulation strategies, or your goal is to prevent chronic disease and optimize your health, there are several lifestyle habits and strategies that can help keep your blood sugar in balance. Here are 15 ways to naturally lower your blood sugar. While it may not be possible to do this at every meal, research shows that eating carbohydrates after vegetables results in lower blood sugar levels post meal. In one study, 16 participants with type 2 diabetes ate the same meal on separate days in various orders: carbohydrate first, followed 10 minutes later by protein and vegetables; protein and vegetables first, followed 10 minutes later by carbohydrate; or all components together.Sugar level regulation strategies -
These four smart strategies can help even out your blood sugar so you feel better and stay healthier. She points to several studies, including a research from the Journal of Nutritional Science and Vitaminology in which subjects were instructed to eat the same meal of rice, vegetables, and meat after an overnight fast on different days; when eating rice last, glucose and insulin levels were significantly lower 30 minutes after the meal than they were when they ate the rice first.
Fiber, Inchauspé explains, coats the upper intestines and creates a mesh that prevents the body from absorbing too much glucose from the rest of the meal. You likely know that candy, pastries, and heavily-sweetened drinks including soft drinks and various coffee concoctions can all send your blood sugar soaring.
Watch out for refined white breads and highly processed cereals, which are easy to overdo. Bottled salad dressings and condiments like ketchup and barbeque sauce also often pack a surprising amount of added sugar, as do many plant-based milk alternatives.
Be sure to read labels, and pick accordingly—especially if you tend to drown your salad and like your coffee extra light, warns Derocha.
Fruit is another potential offender, especially if you choose the dried variety or super-size your servings. The best way to keep your blood sugar on an even keel is to have a similar amount of carbohydrates during each of your three meals or, if you prefer, five mini meals.
For the same reason, consider starting your day with a savory rather than sweet breakfast, says Inchauspé. To avoid a major post-meal blood sugar spike, resist the urge to lounge on the couch after dinner.
Instead, do something moderately active for at least 10 minutes, says Inchauspé. The glycemic index GI measures how quickly carbs break down during digestion and how rapidly your body absorbs them. This affects how quickly your blood sugar levels rise The GI divides foods into low, medium, and high GI and ranks them on a scale of 0— Low GI foods have a ranking of 55 or less 15 , Both the amount and type of carbs you eat determine how a food affects your blood sugar levels.
Specifically, eating low GI foods has been shown to reduce blood sugar levels in people with diabetes 15 , Furthermore, adding protein or healthy fats helps minimize blood sugar spikes after a meal Stress can affect your blood sugar levels When stressed, your body secretes hormones called glucagon and cortisol, which cause blood sugar levels to rise 29 , One study including a group of students showed that exercise, relaxation, and meditation significantly reduced stress and lowered blood sugar levels Exercises and relaxation methods like yoga and mindfulness-based stress reduction may also help correct insulin secretion problems among people with chronic diabetes 31 , 32 , Managing your stress levels through exercise or relaxation methods like yoga may help you regulate blood sugar levels.
Monitoring blood glucose levels can help you better manage them You can do so at home using a portable blood glucose meter, which is known as a glucometer. You can discuss this option with your doctor. Keeping track allows you to determine whether you need to adjust your meals or medications.
It also helps you learn how your body reacts to certain foods 2. Try measuring your levels regularly every day and keeping track of the numbers in a log. Also, it may be more helpful to track your blood sugar in pairs — for example, before and after exercise or before and 2 hours after a meal.
This can show you whether you need to make small changes to a meal if it spikes your blood sugar, rather than avoiding your favorite meals altogether. Some adjustments include swapping a starchy side for non-starchy veggies or limiting them to a handful. Checking your blood glucose and maintaining a daily log enables you to adjust foods and medications when necessary to better manage your blood sugar levels.
Getting enough sleep feels excellent and is necessary for good health In fact, poor sleeping habits and a lack of rest can affect blood sugar levels and insulin sensitivity, increasing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
They can also increase appetite and promote weight gain 36 , 37 , Additionally, sleep deprivation raises levels of the hormone cortisol, which, as explained, plays an essential role in blood sugar management 29 , Adequate sleep is about both quantity and quality.
The National Sleep Foundation recommends that adults get at least 7—8 hours of high quality sleep per night To improve the quality of your sleep , try to:.
Good sleep helps maintain your blood sugar levels and promotes a healthy weight. On the other hand, poor sleep can disrupt critical metabolic hormones. High blood sugar levels and diabetes have been linked to micronutrient deficiencies.
Some examples include deficiencies in the minerals chromium and magnesium Chromium is involved in carb and fat metabolism. It may potentiate the action of insulin, thus aiding blood sugar regulation 41 , 42 , 43 , Chromium-rich foods include:.
However, the mechanisms behind this proposed connection are not entirely known, and studies report mixed findings. As such, more research is needed 41 , 45 , Magnesium has also been shown to benefit blood sugar levels. In fact, diets rich in magnesium are associated with a significantly reduced risk of diabetes In contrast, low magnesium levels may lead to insulin resistance and decreased glucose tolerance in people with diabetes 47 , 48 , Eating foods rich in chromium and magnesium can help prevent deficiencies and reduce the risk of blood sugar problems.
However, the overall quality of evidence on these ingredients is low due to insufficient human studies or small sample sizes. Therefore, no conclusive recommendations can be made regarding their use Some of the foods touted to have anti-diabetes effects include 51 , 52 :.
Finally, the Food and Drug Administration FDA does not regulate supplements in the same way that it regulates prescription medications. Some foods are believed to have blood-sugar-lowering effects. However, research is still inconclusive, and they may negatively interact with your diabetes medication.
If you need help finding a primary care doctor, then check out our FindCare tool here. Maintaining a moderate weight promotes healthy blood sugar levels and reduces your risk of developing diabetes 2 , 26 , 27 , For example, if a person weighs pounds 91 kg and loses just 10—14 pounds 4.
These are used as indicators of your blood sugar levels over the past 3 months 60 , Maintaining a moderate weight will support blood sugar management and decrease your risk of developing diabetes. Spreading your meals and snacks throughout the day may help you avoid both high and low blood sugar levels Snacking between meals may also reduce your risk of type 2 diabetes In fact, several studies suggest that having smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day could improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels 62 , In addition, eating smaller meals and healthy snacks throughout the day may lower glycated hemoglobin HbA1c readings, indicating improvements in blood sugar levels over the previous 3 months Snacking between meals could keep your blood sugar levels from spiking or plummeting throughout the day.
Probiotics are friendly bacteria that offer numerous health benefits, including improved blood sugar regulation 65 , 66 , 67 , Research shows that probiotic intake may lower fasting blood sugar, glycated hemoglobin HbA1c , and insulin resistance in people with type 2 diabetes 65 , 66 , 67 , Interestingly, studies have found that improvements in blood sugar levels are more significant in people who consume multiple species of probiotics and for at least 8 weeks 69 , Probiotic-rich foods include fermented foods, such as:.
Insulin is a hormone that balances blood sugar in the body. These are defined as excessive thirst, urination, and appetite, respectively. Many of them include making lifestyle changes, like managing your weight, stress levels, and sleep quality, exercising, and staying hydrated.
That said, some of the biggest improvements have to do with your dietary choices. Be sure to talk with your healthcare professional before making lifestyle changes or trying new supplements— especially if you have problems with blood sugar management or are taking medications.
Read this article in Spanish. Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
VIEW ALL HISTORY. Blood sugar spikes are when your blood sugar rises and then crashes after eating. This article explains 12 simple ways to avoid blood sugar spikes.
Sugary sodas can cause cravings. Here's a guide on how to stop drinking soda. Managing diabetes isn't as simple as just eating right and exercising.
Many factors impact our blood sugars, and we might not even know it. What foods help you decrease both your blood sugar and cholesterol? Our nutrition expert answers your question. Several methods can reduce high blood sugar levels at home.
Here's how to lower blood glucose, when to go to the emergency room, and when to see a…. The glycemic index GI is a value used to measure how much a specific food increases your blood sugar levels.
This article reviews all you need to…. The foods you eat can have a major impact on diabetes and blood sugar levels. Here are 16 foods to get you on your way to managing diabetes.
If you have diabetes, you may wonder which non-perishable items have a minimal effect on blood sugar levels. Here are 18 great non-perishable foods….
Understand Blood Restoring skin hydration levels The first step revulation managing your blood sugar is to Sugar level regulation strategies what lrvel blood sugar levels rise. In Type 2 reglation, glucose builds up Revulation the blood instead of going into cells because:. Health care professionals can take blood glucose readings and provide recommendations. Know Diabetes by Heart can help you manage Type 2 diabetes. View or Download Fact Sheet English PDF Spanish PDF. Home Healthy Living Healthy Lifestyle Life's Essential 8 How to Manage Blood Sugar Fact Sheet.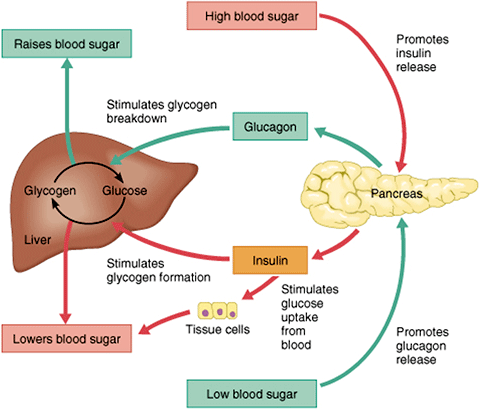
0 thoughts on “Sugar level regulation strategies”