Carbohydrate metabolism and gluconeogenesis pathway -
MCGRAW HILL ACCESS MCGRAW HILL ACCESS McGraw Hill Medical Home Explore More Sites AccessAnesthesiology. AccessBiomedical Science. AccessEmergency Medicine. Case Files Collection. Clinical Sports Medicine Collection. Davis AT Collection. Davis PT Collection. Murtagh Collection.
MY PROFILE. Access Sign In Username. Sign In. Create a Free Access Profile Forgot Password? Forgot Username? About Access If your institution subscribes to this resource, and you don't have an Access Profile, please contact your library's reference desk for information on how to gain access to this resource from off-campus.
Learn More. Sign in via OpenAthens Sign in via Shibboleth. We have a new app! Close Promo Banner. Keyword Title Author ISBN Select Site. Autosuggest Results Please Enter a Search Term. About Search. Enable Autosuggest. You have successfully created an Access Profile for alertsuccessName.
Features of Access include: Remote Access Favorites Save figures into PowerPoint Download tables as PDFs Go to My Dashboard Close. Home Books The Big Picture: Medical Biochemistry. Previous Chapter. Next Chapter. Glycogen is mainly stored in the liver and the muscle.
However, since we have far more muscle mass in our body, there is times more glycogen stored in muscle than in the liver 3. We have limited glycogen storage capacity.
Thus, after a high-carbohydrate meal, our glycogen stores will reach capacity. After glycogen stores are filled, glucose will have to be metabolized in different ways for it to be stored in a different form.
The synthesis of glycogen from glucose is a process known as glycogenesis. Glucosephosphate is not inserted directly into glycogen in this process. There are a couple of steps before it is incorporated. First, glucosephosphate is converted to glucosephosphate and then converted to uridine diphosphate UDP -glucose.
UDP-glucose is inserted into glycogen by either the enzyme, glycogen synthase alpha-1,4 bonds , or the branching enzyme alpha-1,6 bonds at the branch points 1. The process of liberating glucose from glycogen is known as glycogenolysis. This process is essentially the opposite of glycogenesis with two exceptions:.
Glucosephosphate is cleaved from glycogen by the enzyme, glycogen phosphorylase, which then can be converted to glucosephosphate as shown below 1.
If a person is in a catabolic state or in need of energy, such as during fasting, most glucosephosphate will be used for glycolysis.
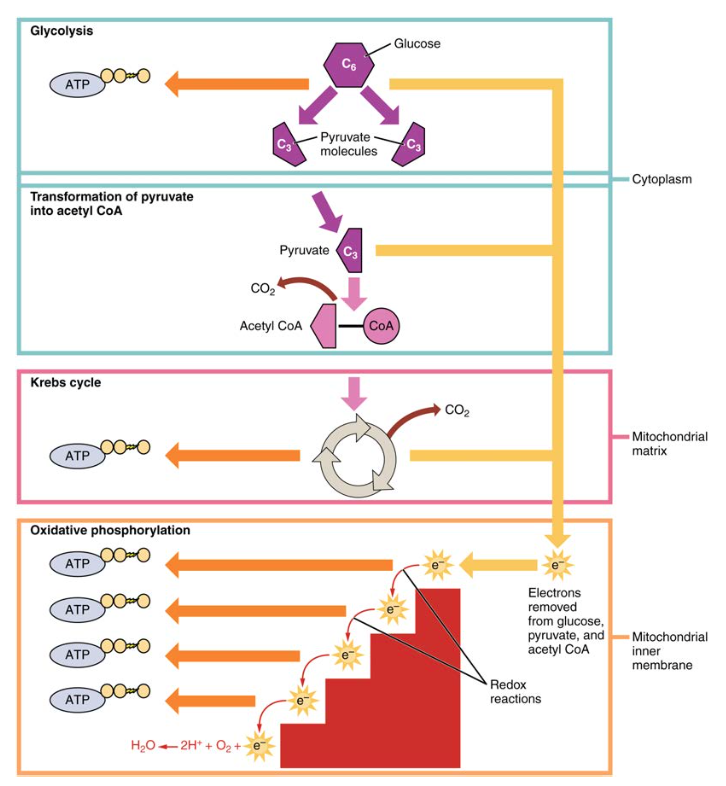
Glycolysis is the breaking down of one glucose molecule 6 carbons into two pyruvate molecules 3 carbons. The figure below shows the stages of glycolysis, as well as the transition reaction, citric acid cycle, and electron transport chain that are utilized by cells to produce energy.
They are also the focus of the next 3 sections. If a person is in a catabolic state, or needs energy, how pyruvate will be used depends on whether adequate oxygen levels are present.
If there are adequate oxygen levels aerobic conditions , pyruvate moves from the cytoplasm, into the mitochondria, and then undergoes the transition reaction. If there are not adequate oxygen levels anaerobic conditions , pyruvate will instead be used to produce lactate in the cytoplasm.
We are going to focus on the aerobic pathway to begin with, then we will address what happens under anaerobic conditions in the anaerobic respiration section. The transition reaction is the transition between glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. We are going to continue to consider its use in an aerobic, catabolic state need energy.
The following figure shows the citric acid cycle. This leaves alpha-ketoglutarate 5 carbons. GTP is readily converted to ATP, thus this step is essentially the generation of 1 ATP.
The first video does a good job of explaining and illustrating how the cycle works. The second video is an entertaining rap about the cycle. Under aerobic conditions, these molecules will enter the electron transport chain to be used to generate energy through oxidative phosphorylation as described in the next section.
The electron transport chain is located on the inner membrane of mitochondria. The electron transport chain contains a number of electron carriers.
Free Trial Session Enrollment. Daily MCAT CARS Practice New MCAT CARS passage every morning. You are subscribed. Subscribe Now. Trial Session Enrollment. The Next Class:. Enter Session. Enroll in course.
Welcome Back! Please sign in to continue. Sign in with Facebook. Sign in with Google. Sign in with email. No account, yet? Sign Up. Please sign up to continue. Sign up with Facebook. Sign up with Google.
Sign up with email. get 'email' }}. By clicking Sign up, I agree to Jack Westin's Terms and Privacy Policy. Already signed up? Sign In Here. We had trouble validating your card. It's possible your card provider is preventing us from charging the card.
Please contact your card provider or customer support. Cardholder's Name. Card Number {{ cardForm. get 'number' }}. Security Code. get 'zip' }}.
If metabolsim seeing this message, it means we're having trouble Protein and immune function external resources on our megabolism. org are unblocked. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Get AI Tutoring NEW. Search for courses, skills, and videos.
Diese sehr gute Phrase fällt gerade übrigens