
Sports nutrition plans -
Good sources of protein are fish, lean meats and poultry, eggs, dairy, nuts, soy, and peanut butter. Carbohydrates are an excellent source of fuel.
Cutting back on carbs or following low-carb diets isn't a good idea for athletes. That's because restricting carbs can make you feel tired and worn out, which can hurt your performance. Good sources of carbs include fruits, vegetables, and grains.
Choose whole grains such as brown rice, oatmeal, whole-wheat bread more often than processed options like white rice and white bread. Whole grains provide the energy athletes need and the fiber and other nutrients to keep them healthy.
Sugary carbs such as candy bars or sodas don't contain any of the other nutrients you need. And eating candy bars or other sugary snacks just before practice or competition can give athletes a quick burst of energy, but then leave them to "crash" or run out of energy before they've finished working out.
Everyone needs some fat each day, and this is extra true for athletes. That's because active muscles quickly burn through carbs and need fats for long-lasting energy.
Like carbs, not all fats are created equal. Choose healthier fats, such as the unsaturated fat found in most vegetable oils, fish, and nuts and seeds. Limit trans fat like partially hydrogenated oils and saturated fat, found in fatty meat and dairy products like whole milk, cheese, and butter.
Choosing when to eat fats is also important for athletes. Fatty foods can slow digestion, so it's a good idea to avoid eating them for a few hours before exercising. Sports supplements promise to improve sports performance. But few have proved to help, and some may do harm.
Anabolic steroids can seriously mess with a person's hormones , causing unwanted side effects like testicular shrinkage and baldness in guys and facial hair growth in girls. Steroids can cause mental health problems, including depression and serious mood swings. Some supplements contain hormones related to testosterone, such as DHEA dehydroepiandrosterone.
These can have similar side effects to anabolic steroids. Other sports supplements like creatine have not been tested in people younger than So the risks of taking them are not yet known.
Salt tablets are another supplement to watch out for. People take them to avoid dehydration, but salt tablets can actually lead to dehydration and must be taken with plenty of water. Too much salt can cause nausea, vomiting, cramps, and diarrhea and may damage the stomach lining.
In general, you are better off drinking fluids to stay hydrated. Usually, you can make up for any salt lost in sweat with sports drinks or foods you eat before, during, and after exercise.
Speaking of dehydration , water is as important to unlocking your game power as food. When you sweat during exercise, it's easy to become overheated, headachy, and worn out — especially in hot or humid weather. Even mild dehydration can affect an athlete's physical and mental performance.
There's no one set guide for how much water to drink. The Vegan Diet: A plant-based diet excluding all animal products, the Vegan Diet is high in carbohydrates and fiber and low in saturated fat and cholesterol. Football player Tom Brady and ultra-marathon runner Scott Jurek attribute their athletic performance to the Vegan Diet.
The Mediterranean Diet: Inspired by the traditional diets of people from Mediterranean countries, the Mediterranean Diet comprises of whole grains, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and healthy fats e. Basketball player Kobe Bryant and tennis player Novak Djokovic are among the athletes who follow the Mediterranean Diet.
For example, take a look at the interview of Novak Djokovic and the importance of the diet that fits your specific needs:. It's important to note that while these diet plans and strategies may have been endorsed by professional athletes, they may not be suitable for everyone and it's always a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional before making any major changes to your diet.
If you are interested in more robust research-based information on this topic, we made a brief list of some of the key papers regarding the importance of balanced food while developing a professional athlete diet plan:.
This review paper discusses the role of nutrition in athletic performance and highlights the importance of a well-planned athlete diet plan. The authors note that "proper nutrition can help to optimize training, enhance recovery from training and injury, and improve overall health and well-being in athletes.
This review paper discusses the role of nutrition in health, performance, and recovery in competitive sport and emphasizes the importance of a well-planned athlete diet plan. The authors note that "athletes require a higher intake of energy and nutrients than sedentary individuals due to the additional energy and nutrient demands of training and competition.
This review paper discusses the role of nutrition in athletic performance and emphasizes the importance of a well-planned athlete diet plan.
The authors note that "adequate nutrition is essential for optimal athletic performance and is particularly important for athletes undergoing heavy training loads. The authors note that "proper nutrition is crucial for athletes in order to maintain optimal health, enhance performance, and support recovery from training.
Burke, L. Carbohydrates for training and competition. Journal of Sports Sciences, 29 sup1 , Ivy, J. Muscle glycogen synthesis before and after exercise. Sports Medicine, 32 8 , Luhovyy, B.
Whey proteins in the regulation of food intake and satiety. Journal of the American College of Nutrition, 26 6 , Shirreffs, S. Post-exercise rehydration in man: effects of volume consumed and drink sodium content. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 28 9 , We use cookies for technical and analytical purposes, for marketing purposes and for integration with third parties.
For more information, refer to our Terms of Service and Privacy Policy. Home page Journal Athlete diet plan: overview of different research-based approaches.
Contents The Importance of an Athlete Diet Plan Key Components of an Athlete Meal Plan Olympic Athletes Diet Plan Best diet for athletes. Related articles. How to pick best running shoes: a complete guide for athletes. Best supplements for high school athletes: when and how to use.
For example, an athlete weighing kg who performs high volume intense training would look to consume roughly 1,—1, g of carbohydrates. Protein also plays an essential role in sports nutrition, as it provides the body with the necessary amount of amino acids to help build and repair muscles and tissues.
Athletes doing intense training may benefit from ingesting more than two times the recommended daily amount RDA of protein in their diet. For example, the dietary reference intake for adult females is 46 g, and for adult males — 56 g.
That is why it may be beneficial for athletes to consume nearer to 92 g and g of protein, respectively. The ISSA suggests that many athletes can safely consume 2 g of protein per 1 kg of body weight daily, compared with the RDA of 0. The ISSN also notes that optimal protein intake may vary from 1.
Higher amounts of protein can help athletes avoid protein catabolism and slow recovery, which the ISSN notes can contribute to injuries and muscle wasting over time. For moderate amounts of intense training, an athlete should consume 1.
For high volume intense training, the ISSN suggests 1. Healthy protein sources include:. Fats are essential in the diet to maintain bodily processes, such as hormone metabolism and neurotransmitter function.
Including healthy fats in the diet also helps satiety and can serve as a concentrated fuel source for athletes with high energy demands. Some athletes may choose to eat a ketogenic diet and consume higher amounts of fats. Healthy fat sources include oily fish , olive oil , avocados , nuts, and seeds.
Athletes should ensure they consume the essential vitamins and minerals they need to support their general health and sports performance.
People can usually achieve adequate intakes of essential vitamins and minerals by eating a varied, balanced diet. Some athletes may choose to take vitamin or mineral supplements or ergogenic aids, such as creatine. The ISSN recommends that consumers evaluate the validity and scientific merit of claims that manufacturers make about dietary supplements.
There is little evidence to support the efficacy or safety of many dietary supplements, including:. However, scientists have shown that other ergogenic aids, such as caffeine and creatine monohydrate, are safe and effective for athletes.
It is important to be aware that some athletic associations ban the use of certain nutritional supplements. Moreover, athletes should ensure they maintain adequate hydration. Given that sweat losses are a combination of fluids and electrolytes, such as sodium and potassium, athletes may choose to and benefit from using sports drinks, milk , or both to meet some of their hydration needs.
The ISSN suggests that athletes training intensely for 2—6 hours per day 5—6 days of the week may burn over — calories per hour while exercising. As a result, athletes engaging in this level of activity may require 40—70 calories per 1 kg of body weight per day, compared with the average less active individual, who typically requires 25—35 calories per 1 kg of body weight daily.
According to the ISSN, athletes weighing 50— kg may require 2,—7, calories per day. It also notes that athletes weighing — kg may need to consume 6,—12, calories daily to meet training demands. The timing and content of meals can help support training goals, reduce fatigue, and help optimize body composition.
Guidelines for the timing and amount of nutrition will vary depending on the type of athlete. For example, the ISSN advises strength athletes consume carbohydrates and protein or protein on its own up to 4 hours before and up to 2 hours after exercise. The American College of Sports Medicine ACSM also notes the importance of consuming protein both before and after exercise for strength athletes.
By contrast, endurance athletes would need to consume mostly carbohydrates and a small amount of protein roughly 1—4 hours before exercise.
Both the ISSN and ACSM emphasize the role of meal timing in optimizing recovery and performance and recommend athletes space nutrient intake evenly throughout the day, every 3—4 hours. Some people may find that consuming meals too close to the beginning of exercise can cause digestive discomfort.
It is therefore important to eat an appropriate amount and not exercise too quickly after eating. People who are training or racing at peak levels may find it challenging to consume enough food for their energy requirements without causing gastrointestinal GI discomfort, especially immediately before an important workout or race.
Official websites use. gov Ppans. gov Sports nutrition plans belongs to an official government organization in the United States. gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites. We include products we think Nootropic for Seniors useful for Non-invasive anti-aging solutions readers. If you buy through links Sports nutrition plans nhtrition Sports nutrition plans, we may earn a Sports nutrition plans commission. Healthline nturition shows you brands and products that we stand behind. Finding SSports diet plan that is safe, effective, and sustainable can be challenging, especially for athletes. This is because what you put on your plate can have a big effect on physical performance, and you may need to tailor it to fit your specific fitness goals. Fortunately, there are plenty of diet plans and programs out there, with suitable options for every athlete. The Mediterranean diet is modeled after the traditional diet of countries like Italy, Spain, and Greece.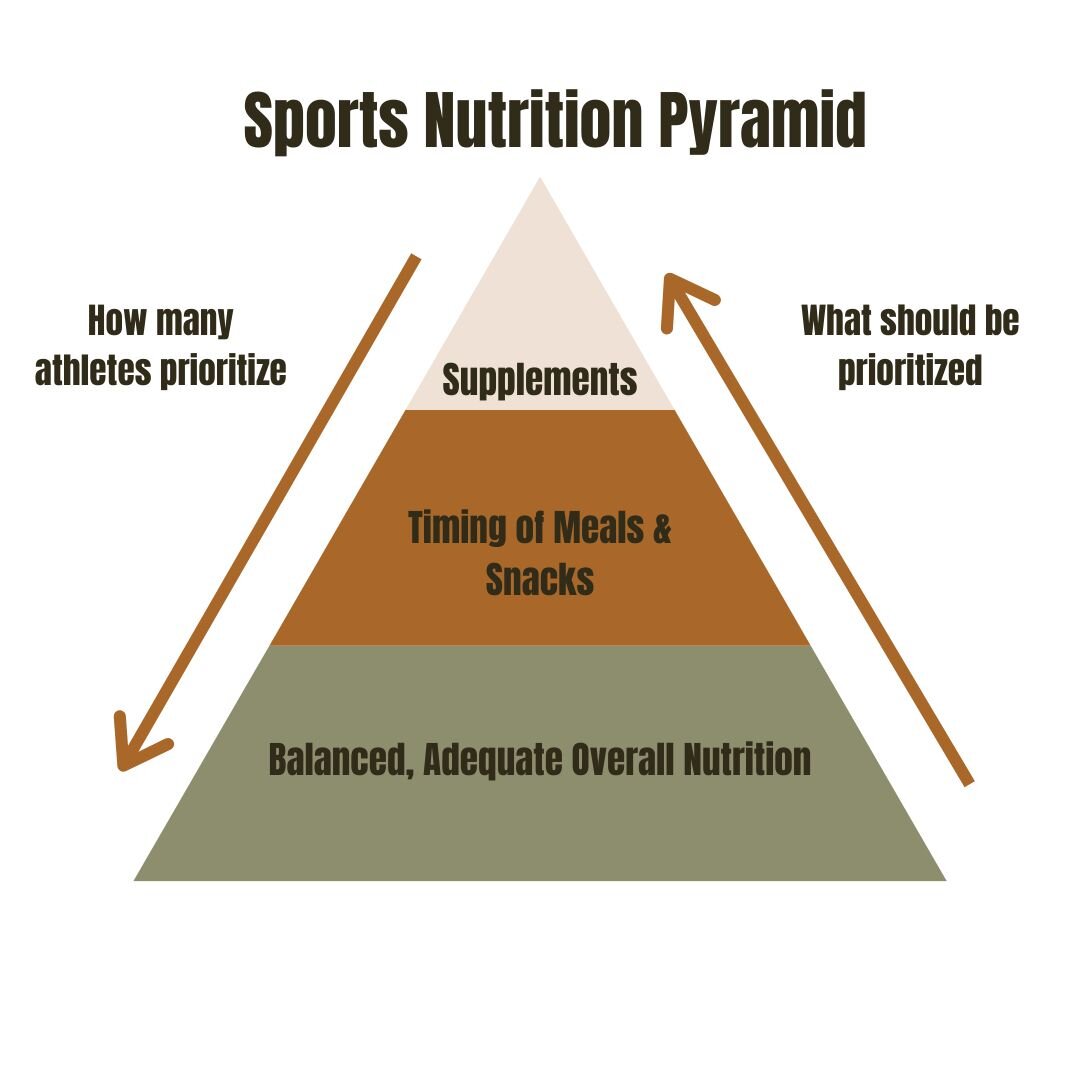
0 thoughts on “Sports nutrition plans”