
Polyphenols and exercise performance -
Int J Epidemiol. Martin BJ, Tan RB, Gillen JB, Percival ME, Gibala MJ. No effect of short-term green tea extract supplementation on metabolism at rest or during exercise in the fed state.
Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. Cohen J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. Hillsdale, N. Erlbaum Associates; Google Scholar. Higgins JP, Thompson SG.
Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. Higgins JPT, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG.
Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. De Pauw K, Roelands B, Cheung SS, de Geus B, Rietjens G, Meeusen R. Guidelines to classify subject groups in sport-science research. Int J Sports Physiol Perform. Decroix L, De Pauw K, Foster C, Meeusen R.
Guidelines to Classify Female Subject Groups in Sport-Science Research. Aucouturier J, Boissière J, Pawlak-Chaouch M, Cuvelier G, Gamelin FX. Effect of dietary nitrate supplementation on tolerance to supramaximal intensity intermittent exercise. Bailey SJ, Winyard P, Vanhatalo A, Blackwell JR, DiMenna FJ, Wilkerson DP, et al.
Dietary nitrate supplementation reduces the O2 cost of low-intensity exercise and enhances tolerance to high-intensity exercise in humans.
J Appl Physiol. Bailey SJ, Varnham RL, DiMenna FJ, Breese BC, Wylie LJ, Jones AM. Inorganic nitrate supplementation improves muscle oxygenation, O2 uptake kinetics, and exercise tolerance at high but not low pedal rates.
Balsalobre-Fernández C, Romero-Moraleda B, Cupeiro R, Peinado AB, Butragueño J, Benito PJ. The effects of beetroot juice supplementation on exercise economy, rating of perceived exertion and running mechanics in elite distance runners: A double-blinded, randomized study.
PLoS One. Bernardi BB, Schoenfeld BJ, Alves RC, Urbinati KS, McAnulty SR, Junior TPS. Acute Supplementation with Beetroot Juice Does Not Enhance Exercise Performance among Well-trained Athletes: A Randomized Crossover Study.
J Exerc Physiol Online. Boorsma RK, Whitfield J, Spriet LL. Beetroot juice supplementation does not improve performance of elite m runners. Breese BC, McNarry MA, Marwood S, Blackwell JR, Bailey SJ, Jones AM. Beetroot juice supplementation speeds O2 uptake kinetics and improves exercise tolerance during severe-intensity exercise initiated from an elevated metabolic rate.
Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. Callahan MJ, Parr EB, Hawley JA, Burke LM. Single and combined effects of beetroot crystals and sodium bicarbonate on 4-km cycling time trial performance.
Cermak NM, Res P, Stinkens R, Lundberg JO, Gibala MJ, Van Loon LJC. No improvement in endurance performance after a single dose of beetroot juice.
Cermak NM, Gibala MJ, Van Loon LJC. Nitrate supplementation's improvement of km time-trial performance in trained cyclists. Christensen PM, Petersen NK, Friis SN, Weitzberg E, Nybo L. Effects of nitrate supplementation in trained and untrained muscle are modest with initial high plasma nitrite levels.
Scand J Med Sci Sports. Christensen PM, Nyberg M, Bangsbo J. Influence of nitrate supplementation on VO2 kinetics and endurance of elite cyclists. de Castro TF, de Assis MF, Figueiredo DH, Figueiredo DH, Machado FA.
Effects of chronic beetroot juice supplementation on maximum oxygen uptake, velocity associated with maximum oxygen uptake, and peak velocity in recreational runners: a double-blinded, randomized and crossover study.
Eur J Appl Physiol. de Castro TF, Manoel FA, Figueiredo DH, Figueiredo DH, Machado FA. Effect of beetroot juice supplementation on km performance in recreational runners.
Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. de Castro TF, de Assis MF, Machado FA. Beetroot juice supplementation does not modify the 3-km running performance in untrained women.
Sci Sports. Article Google Scholar. Esen O, Nicholas C, Morris M, Bailey SJ. No Effect of Beetroot Juice Supplementation on m and m Swimming Performance in Moderately Trained Swimmers. Flueck JL, Gallo A, Moelijker N, Bogdanov N, Bogdanova A, Perret C. Influence of Equimolar Doses of Beetroot Juice and Sodium Nitrate on Time Trial Performance in Handcycling.
Glaister M, Pattison JR, Muniz-Pumares D, Patterson SD, Foley P. Effects of dietary nitrate, caffeine, and their combination on km cycling time trial performance. J Strength Cond Res.
Handzlik MK, Gleeson M. Likely additive ergogenic effects of combined preexercise dietary nitrate and caffeine ingestion in trained cyclists. ISRN Nutr. Hoon MW, Hopkins WG, Jones AM, Martin DT, Halson SL, West NP, et al.
Nitrate supplementation and high-intensity performance in competitive cyclists. Hoon MW, Jones AM, Johnson NA, Blackwell JR, Broad EM, Lundy B, et al. The effect of variable doses of inorganic nitrate-rich beetroot juice on simulated m rowing performance in trained athletes.
Jonvik KL, Van Dijk JW, Senden JMG, Van Loon LJC, Verdijk LB. The effect of beetroot juice supplementation on dynamic apnea and intermittent sprint performance in elite female water polo players.
Kelly J, Vanhatalo A, Wilkerson DP, Wylie LJ, Jones AM. Effects of nitrate on the power-duration relationship for severe-intensity exercise. Kelly J, Vanhatalo A, Bailey SJ, Wylie LJ, Tucker C, List S, et al.
Dietary nitrate supplementation: effects on plasma nitrite and pulmonary O2 uptake dynamics during exercise in hypoxia and normoxia. Kent GL, Dawson B, Cox GR, Burke LM, Eastwood A, Croft KD, et al. Dietary nitrate supplementation does not improve cycling time-trial performance in the heat.
J Sports Sci. Lane SC, Hawley JA, Desbrow B, Jones AM, Blackwell JR, Ross ML, et al. Single and combined effects of beetroot juice and caffeine supplementation on cycling time trial performance.
Lansley KE, Winyard PG, Bailey SJ, Vanhatalo A, Wilkerson DP, Blackwell JR, et al. Acute dietary nitrate supplementation improves cycling time trial performance.
Lansley KE, Winyard PG, Fulford J, Vanhatalo A, Bailey SJ, Blackwell JR, et al. Dietary nitrate supplementation reduces the O2 cost of walking and running: A placebo-controlled study.
Lowings S, Shannon OM, Deighton K, Matu J, Barlow MJ. Effect of Dietary Nitrate Supplementation on Swimming Performance in Trained Swimmers. MacLeod KE, Nugent SF, Barr SI, Koehle MS, Sporer BC, MacInnis MJ.
Acute Beetroot Juice Supplementation Does Not Improve Cycling Performance in Normoxia or Moderate Hypoxia. McQuillan JA, Dulson DK, Laursen PB, Kilding AE. Dietary nitrate fails to improve 1 and 4 km cycling performance in highly trained cyclists.
The Effect of Dietary Nitrate Supplementation on Physiology and Performance in Trained Cyclists. Mosher SL, Gough LA, Deb S, Saunders B, Mc Naughton LR, Brown DR, et al. High dose Nitrate ingestion does not improve 40 km cycling time trial performance in trained cyclists.
Muggeridge DJ, Howe CCF, Spendiff O, Pedlar C, James PE, Easton C. The effects of a single dose of concentrated beetroot juice on performance in trained flatwater kayakers.
Murphy M, Eliot K, Heuertz RM, Weiss E. Whole Beetroot Consumption Acutely Improves Running Performance. J Acad Nutr Diet. Oskarsson J, McGawley K. No individual or combined effects of caffeine and beetroot-juice supplementation during submaximal or maximal running.
Pawlak-Chaouch M, Boissiere J, Munyaneza D, Gamelin F-X, Cuvelier G, Berthoin S, et al. Beetroot Juice Does Not Enhance Supramaximal Intermittent Exercise Performance in Elite Endurance Athletes. J Am Coll Nutr. Peeling P, Cox GR, Bullock N, Burke LM. Beetroot juice improves on-water M time-trial performance, and laboratory-based paddling economy in national and international-level kayak athletes.
Pinna M, Roberto S, Milia R, Marongiu E, Olla S, Loi A, et al. Effect of beetroot juice supplementation on aerobic response during swimming. Rokkedal-Lausch T, Franch J, Poulsen MK, Thomsen LP, Weitzberg E, Kamavuako EN, et al. Chronic high-dose beetroot juice supplementation improves time trial performance of well-trained cyclists in normoxia and hypoxia.
Shannon OM, Barlow MJ, Duckworth L, Williams E, Wort G, Woods D, et al. Dietary nitrate supplementation enhances short but not longer duration running time-trial performance. Tan R, Wylie LJ, Thompson C, Blackwell JR, Bailey SJ, Vanhatalo A, et al.
Beetroot juice ingestion during prolonged moderate-intensity exercise attenuates progressive rise in O-2 uptake.
Thompson KG, Turner L, Prichard J, Dodd F, Kennedy DO, Haskell C, et al. Influence of dietary nitrate supplementation on physiological and cognitive responses to incremental cycle exercise. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. Thompson C, Vanhatalo A, Jell H, Fulford J, Carter J, Nyman L, et al.
Dietary nitrate supplementation improves sprint and high-intensity intermittent running performance. Thompson C, Vanhatalo A, Kadach S, Wylie LJ, Fulford J, Ferguson SK, et al. Discrete physiological effects of beetroot juice and potassium nitrate supplementation following 4-wk sprint interval training.
Vanhatalo A, Bailey SJ, Blackwell JR, DiMenna FJ, Pavey TG, Wilkerson DP, et al. Acute and chronic effects of dietary nitrate supplementation on blood pressure and the physiological responses to moderate-intensity and incremental exercise.
Vasconcellos J, Silvestre DH, Baiao DD, Werneck-de-Castro JP, Alvares TS, Paschoalin VMF. A Single Dose of Beetroot Gel Rich in Nitrate Does Not Improve Performance but Lowers Blood Glucose in Physically Active Individuals. Med J Nutrition Metab. Wilkerson DP, Hayward GM, Bailey SJ, Vanhatalo A, Blackwell JR, Jones AM.
Influence of acute dietary nitrate supplementation on 50 mile time trial performance in well-trained cyclists. Wylie LJ, Kelly J, Bailey SJ, Blackwell JR, Skiba PF, Winyard PG, et al. Beetroot juice and exercise: Pharmacodynamic and dose-response relationships.
Wylie LJ, Mohr M, Krustrup P, Jackman SR, Ermdis G, Kelly J, et al. Dietary nitrate supplementation improves team sport-specific intense intermittent exercise performance. Wylie LJ, Bailey SJ, Kelly J, Blackwell JR, Vanhatalo A, Jones AM.
Influence of beetroot juice supplementation on intermittent exercise performance. Wylie LJ, Park JW, Vanhatalo A, Kadach S, Black MI, Stoyanov Z, et al. Human skeletal muscle nitrate store: influence of dietary nitrate supplementation and exercise.
Gonzalez AM, Accetta MR, Spitz RW, Mangine GT, Ghigiarelli JJ, Sell KM. Red Spinach Extract Supplementation Improves Cycle Time Trial Performance in Recreationally Active Men and Women. Moore AN, Haun CT, Kephart WC, Holland AM, Mobley CB, Pascoe DD, et al.
Red Spinach Extract Increases Ventilatory Threshold during Graded Exercise Testing. Muggeridge DJ, Sculthorpe N, Grace FM, Willis G, Thornhill L, Weller RB, et al.
Acute whole body UVA irradiation combined with nitrate ingestion enhances time trial performance in trained cyclists. Boussetta N, Abedelmalek S, Khouloud A, Ben anes A, Souissi N.
Does red orange juice supplementation has a protective effect on performance, cardiovascular parameters, muscle damage and oxidative stress markers following the Yo-Yo Intermittent Recovery Test Level-1 under polluted air? Int J Environ Health Res. Allen JD, McLung J, Nelson AG, Welsch M.
Engels H-J, Said JM, Wirth JC. Failure of chronic ginseng supplementation to affect work performance and energy metabolism in healthy adult females.
Nutr Res. Abbey EL, Rankin JW. Effect of ingesting a honey-sweetened beverage on soccer performance and exercise-induced cytokine response. Yi M, Fu J, Zhou L, Gao H, Fan C, Shao J, et al. The effect of almond consumption on elements of endurance exercise performance in trained athletes.
J Int Soc Sports Nutr. Basta P, Pilaczynska-Szczesniak L, Woitas-Slubowska D, Skarpanska-Stejnborn A. Influence of aloe arborescens Mill. Extract on selected parameters of pro-oxidant-antioxidant equilibrium and cytokine synthesis in rowers.
Hsu CC, Ho MC, Lin LC, Su B, Hsu MC. American ginseng supplementation attenuates creatine kinase level induced by submaximal exercise in human beings.
World J Gastroenterol. Morris AC, Jacobs I, McLellan TM, Klugerman A, Wang LC, Zamecnik J. No ergogenic effect of ginseng ingestion. Int J Sport Nutr. Nieman DC, Gillitt ND, Sha W, Esposito D, Ramamoorthy S. Metabolic recovery from heavy exertion following banana compared to sugar beverage or water only ingestion: A randomized, crossover trial.
Montenegro CF, Kwong DA, Minow ZA, Davis BA, Lozada CF, Casazza GA. Betalain-rich concentrate supplementation improves exercise performance and recovery in competitive triathletes. Mumford PW, Kephart WC, Romero MA, Haun CT, Mobley CB, Osburn SC, et al. Effect of 1-week betalain-rich beetroot concentrate supplementation on cycling performance and select physiological parameters.
Van Hoorebeke JS, Trias CO, Davis BA, Lozada CF, Casazza GA. Betalain-Rich Concentrate Supplementation Improves Exercise Performance in Competitive Runners. Skarpańska-Stejnborn A, Basta P, Pilaczyńska-Szcześniak Ł.
The Influence Of Supplementation With The Black Currant Ribes Nigrum Extract On Selected Prooxidative-Antioxidative Balance Parameters In Rowers. Stud Phys Cult Tourism. Brandenburg JP, Giles LV. Four Days of Blueberry Powder Supplementation Lowers the Blood Lactate Response to Running But Has No Effect on Time-Trial Performance.
Gaamouri N, Zouhal H, Hammami M, Hackney AC, Abderrahman AB, Saeidi A, et al. Effects of polyphenol carob supplementation on body composition and aerobic capacity in taekwondo athletes. Physiol Behav. Pospieszna B, Wochna K, JerszyŃSki D, GowaCinna K, Czapski J. Ergogenic effects of dietary nitrates in female swimmers.
Trends Sport Sci. Overdevest E, Wouters JA, Wolfs KHM, Van Leeuwen JJM, Possemiers S. Citrus flavonoid supplementation improves exercise performance in trained athletes. J Sports Sci Med. PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar. Allgrove J, Farrell E, Gleeson M, Williamson G, Cooper K.
Regular dark chocolate consumption's reduction of oxidative stress and increase of free-fatty-acid mobilization in response to prolonged cycling. Decroix L, Tonoli C, Soares DD, Descat A, Drittij-Reijnders M-J, Weseler AR, et al.
Acute cocoa Flavanols intake has minimal effects on exercise-induced oxidative stress and nitric oxide production in healthy cyclists: a randomized controlled trial.
Decroix L, Tonoli C, Lespagnol E, Balestra C, Descat A, Drittij-Reijnders MJ, et al. One-week cocoa flavanol intake increases prefrontal cortex oxygenation at rest and during moderate-intensity exercise in normoxia and hypoxia. Patel RK, Brouner J, Spendiff O. Dark chocolate supplementation reduces the oxygen cost of moderate intensity cycling.
Ostojic S, Stojanovic M, Djordjevic B, Jourkesh M, Vasiljevic N. The Effects of a 4-week Coffeeberry Supplementation on Antioxidant Status, Endurance, and Anaerobic Performance in College Athletes. Res Sports Med. Labonté K, Couillard C, Motard-Bélanger A, Paradis M-E, Couture P, Lamarche B. Acute Effects of Polyphenols from Cranberries and Grape Seeds on Endothelial Function and Performance in Elite Athletes.
Chang CW, Chen CY, Yen CC, Wu YT, Hsu MC. Repressed exercise-induced hepcidin levels after Danggui Buxue Tang supplementation in male recreational runners. Oh JK, Shin YO, Yoon JH, Kim SH, Shin HC, Hwang HJ. Effect of Supplementation With Ecklonia cava Polyphenol on Endurance Performance of College Students.
Bentley D, Dank S, Coupland R, Midgley A, Spence I. Acute Antioxidant Supplementation Improves Endurance Performance in Trained Athletes. Clifford T, Mitchell N, Scott A. The influence of different sources of polyphenols on submaximal cycling and time trial performance.
J Athl Enhanc. Mach J, Midgley AW, Dank S, Grant RS, Bentley DJ. Nayebifar S, Afzalpour ME, Kazemi T, Eivary SHA, Mogharnasi M. The effect of a week high-intensity interval training and ginger consumption on inflammatory indices contributing to atherosclerosis in overweight women.
J Res Med Sci. O'Connor PJ, Caravalho AL, Freese EC, Cureton KJ. Grape consumption's effects on fitness, muscle injury, mood, and perceived health. Toscano LT, Tavares RL, Toscano LT, Silva CSO, Almeida AEM, Biasoto ACT, et al.
Potential ergogenic activity of grape juice in runners. Deley G, Guillemet D, Allaert F-A, Babault N. An Acute Dose of Specific Grape and Apple Polyphenols Improves Endurance Performance: A Randomized, Crossover, Double-Blind versus Placebo Controlled Study.
Dean S, Braakhuis A, Paton C. The effects of EGCG on fat oxidation and endurance performance in male cyclists. Eichenberger P, Mettler S, Arnold M, Colombani PC.
No effects of three-week consumption of a green tea extract on time trial performance in endurance-trained men. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. Kuo Y-C, Lin J-C, Bernard JR, Liao Y-H. Green tea extract supplementation does not hamper endurance-training adaptation but improves antioxidant capacity in sedentary men.
Knab AM, Nieman DC, Gillitt ND, Shanely RA, Cialdella-Kam L, Henson D, et al. Effects of a freeze-dried juice blend powder on exercise-induced inflammation, oxidative stress, and immune function in cyclists. Bell PG, Walshe IH, Davison GW, Stevenson E, Howatson G.
Montmorency cherries reduce the oxidative stress and inflammatory responses to repeated days high-intensity stochastic cycling. Bell PG, Walshe IH, Davison GW, Stevenson EJ, Howatson G.
Recovery facilitation with Montmorency cherries following high-intensity, metabolically challenging exercise. Keane KM, Bailey SJ, Vanhatalo A, Jones AM, Howatson G. Effects of montmorency tart cherry L. Prunus Cerasus consumption on nitric oxide biomarkers and exercise performance.
Morgan PT, Barton MJ, Bowtell JL. Montmorency cherry supplementation improves km cycling time-trial performance. Braakhuis AJ, Hopkins WG, Lowe TE. Effects of dietary antioxidants on training and performance in female runners.
Eur J Sport Sci. Cook MD, Myers SD, Blacker SD, Willems MET. New Zealand blackcurrant extract improves cycling performance and fat oxidation in cyclists. Murphy CA, Cook MD, Willems MET. Effect of New Zealand Blackcurrant Extract on Repeated Cycling Time Trial Performance.
Perkins I, Vine S, Blacker S, Willems M. New Zealand blackcurrant extract improves high-intensity intermittent running performance. Potter JA, Hodgson CI, Broadhurst M, Howell L, Gilbert J, Willems MET, et al.
Effects of New Zealand blackcurrant extract on sport climbing performance. Willems MET, Myers SD, Gault ML, Cook MD. Beneficial physiological effects with blackcurrant intake in endurance athletes. Willems M, Cousins L, Williams D, Blacker S. Beneficial effect of New Zealand blackcurrant on maximal sprint speeds during the Loughborough intermittent shuttle test.
Esquius L, Garcia-Retortillo S, Balagué N, Hristovski R, Javierre C. Physiological- and performance-related effects of acute olive oil supplementation at moderate exercise intensity.
Gelabert-Rebato M, Wiebe JC, Martin-Rincon M, Galvan-Alvarez V, Curtelin D, Perez-Valera M, et al. Enhancement of exercise performance by 48 hours, and day supplementation with mangiferin and luteolin in men.
Crum EM, Barnes MJ, Stannard SR. Multiday Pomegranate Extract Supplementation Decreases Oxygen Uptake During Submaximal Cycling Exercise, but Cosupplementation With N-acetylcysteine Negates the Effect. Torregrosa-García A, Ávila-Gandía V, Luque-Rubia AJ, Abellán-Ruiz MS, Querol-Calderón M, López-Román FJ.
Pomegranate extract improves maximal performance of trained cyclists after an exhausting endurance trial: A randomised controlled trial. Trexler ET, Smith-Ryan AE, Melvin MN, Roelofs EJ, Wingfield HL.
Effects of pomegranate extract on blood flow and running time to exhaustion. Ueberschlag SL, Seay JR, Roberts AH, DeSpirito PC, Stith JM, Folz RJ, et al. The Effect of Protandim Supplementation on Athletic Performance and Oxidative Blood Markers in Runners. Kern M, Heslin CJ, Rezende RS.
Metabolic and performance effects of raisins versus sports gel as pre-exercise feedings in cyclists. PubMed Google Scholar. Rietschier HL, Henagan TM, Earnest CP, Baker BL, Cortez CC, Stewart LK.
Sun-dried raisins are a cost-effective alternative to sports jelly beans in prolonged cycling. Jowko E, Sadowski J, Dlugolecka B, Gierczuk D, Opaszowski B, Cieslinski I. Effects of Rhodiola rosea supplementation on mental performance, physical capacity, and oxidative stress biomarkers in healthy men.
Dowling EA, Redondo DR, Branch JD, Jones S, McNabb G, Williams MH. Effect of Eleutherococcus senticosus on submaximal and maximal exercise performance. Eschbach LC, Webster MJ, Boyd JC, McArthur PD, Evetovich TK.
The Effect of Siberian Ginseng Eleutherococcus Senticosus on Substrate Utilization and Performance during Prolonged Cycling.
Kalafati M, Jamurtas AZ, Nikolaidis MG, Paschalis V, Theodorou AA, Sakellariou GK, et al. Ergogenic and antioxidant effects of spirulina supplementation in humans.
Wasuntarawat C, Pengnet S, Walaikavinan N, Kamkaew N, Bualoang T, Toskulkao C, et al. No effect of acute ingestion of Thai ginseng Kaempferia parviflora on sprint and endurance exercise performance in humans. Areta JL, Austarheim I, Wangensteen H, Capelli C.
Metabolic and Performance Effects of Yerba Mate on Well-trained Cyclists. Tarazona-Díaz MP, Alacid F, Carrasco M, Martínez I, Aguayo E. Watermelon juice: potential functional drink for sore muscle relief in athletes. J Agric Food Chem. Bailey SJ, Blackwell JR, Williams E, Vanhatalo A, Wylie LJ, Winyard PG, et al.
Two weeks of watermelon juice supplementation improves nitric oxide bioavailability but not endurance exercise performance in humans. Cutrufello PT, Gadomski SJ, Zavorsky GS. The effect of l-citrulline and watermelon juice supplementation on anaerobic and aerobic exercise performance.
Shanely RA, Nieman DC, Perkins-Veazie P, Henson DA, Meaney MP, Knab AM, et al. Comparison of watermelon and carbohydrate beverage on exercise-induced alterations in systemic inflammation, immune dysfunction, and plasma antioxidant capacity.
McMahon NF, Leveritt MD, Pavey TG. The Effect of Dietary Nitrate Supplementation on Endurance Exercise Performance in Healthy Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Senefeld JW, Wiggins CC, Regimbal RJ, Dominelli PB, Baker SE, Joyner MJ.
Ergogenic Effect of Nitrate Supplementation: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Tesch PA, Karlsson J. Muscle fiber types and size in trained and untrained muscles of elite athletes.
Totzeck M, Hendgen-Cotta UB, Rammos C, Frommke LM, Knackstedt C, Predel HG, et al. Higher endogenous nitrite levels are associated with superior exercise capacity in highly trained athletes.
Maroun MJ, Mehta S, Turcotte R, Cosio MG, Hussain SN. Effects of physical conditioning on endogenous nitric oxide output during exercise. Van der Avoort CMT, Van Loon LJC, Hopman MTE, Verdijk LB.
Increasing vegetable intake to obtain the health promoting and ergogenic effects of dietary nitrate. Eur J Clin Nutr. Granato D, Karnopp AR, van Ruth SM. Characterization and comparison of phenolic composition, antioxidant capacity and instrumental taste profile of juices from different botanical origins.
J Sci Food Agric. Wootton-Beard PC, Ryan L. A beetroot juice shot is a significant and convenient source of bioaccessible antioxidants. Combined use of Multiple Methodologies for the Measurement of Total Antioxidant Capacity in UK Commercially Available Vegetable Juices. Plant Foods Hum Nutr.
Somerville V, Bringans C, Braakhuis A. Polyphenols and Performance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Azuma T, Tanaka Y, Kikuzaki H. Phenolic glycosides from Kaempferia parviflora. da Silveira TFF, Meinhart AD, de Souza TCL, Teixeira Filho J, Godoy HT.
Phenolic compounds from yerba mate based beverages — A multivariate optimisation. Food Chem. Załuski D, Olech M, Galanty A, Verpoorte R, Kuźniewski R, Nowak R, et al. Phytochemical Content and Pharma-Nutrition Study on Eleutherococcus senticosus Fruits Intractum. Chung IM, Lim JJ, Ahn MS, Jeong HN, An TJ, Kim SH.
Comparative phenolic compound profiles and antioxidative activity of the fruit, leaves, and roots of Korean ginseng Panax ginseng Meyer according to cultivation years. J Ginseng Res. Kochan E, Szymańska G, Wielanek M, Wiktorowska-Owczarek A, Jóźwiak-Bębenista M, Grzegorczyk-Karolak I.
The content of triterpene saponins and phenolic compounds in American ginseng hairy root extracts and their antioxidant and cytotoxic properties.
Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. Sidhu JS, Zafar TA. Bioactive compounds in banana fruits and their health benefits. Food Qual Saf. Lucini L, Pellizzoni M, Pellegrino R, Molinari GP, Colla G. Phytochemical constituents and in vitro radical scavenging activity of different Aloe species.
Kwan KKL, Huang Y, Leung KW, Dong TTX, Tsim KWK. Danggui Buxue Tang, a Chinese Herbal Decoction Containing Astragali Radix and Angelicae Sinensis Radix, Modulates Mitochondrial Bioenergetics in Cultured Cardiomyoblasts.
Food Funct. Article PubMed Google Scholar. Sureda A, Tejada S, Bibiloni MM, Tur JA, Pons A. Polyphenols: well beyond the antioxidant capacity: polyphenol supplementation and exercise-induced oxidative stress and inflammation. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. De Ferrars RM, Czank C, Zhangm Q, Botting NP, Kroon PA, Cassidy A, et al.
The pharmacokinetics of anthocyanins and their metabolites in humans. Br J Pharmacol. Czank C, Cassidy A, Zhang Q, Morrison DJ, Preston T, Kroon PA, et al.
Human metabolism and elimination of the anthocyanin, cyanidingglucoside: a 13C-tracer study. Am J Clin Nutr. Williamson G, Clifford MN. Colonic metabolites of berry polyphenols: the missing link to biological activity?
Br J Nutr. Common phenolic metabolites of flavonoids, but not their unmetabolized precursors, reduce the secretion of vascular cellular adhesion molecules by human endothelial cells. J Nutr. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar. Kay CD.
Rethinking paradigms for studying mechanisms of action of plant bioactives. Nutr Bull. Nieman DC, Mitmesser SH. Potential impact of nutrition on immune system recovery from heavy exertion: a metabolomics perspective. Nieman DC, Shanely RA, Gillit ND, Pappan KL, Lila MA.
Serum metabolic signatures induced by a three-day intensified exercise period persist after 14 h of recovery in runners.
J Proteome Res. Mach N, Fuster-Botella D. Endurance exercise and gut microbiota: A review. J Sport Heal Sci. Kerksick CM, Wilborn CD, Roberts MD, Smith-Ryan A, Kleiner SM, Jäger R, et al. J Int Soc Sports Nutr.
Shankar K, Mehendale HM. Oxidative Stress. In: Wexler P, editor. Encyclopedia of Toxicology. Third Edit. Elsevier; Lehmann R, Zhao X, Weigert C, Simon P, Fehrenbach E, Fritsche J, et al.
Medium chain Acylcarnitines dominate the metabolite pattern in humans under moderate intensity exercise and support lipid oxidation. Lewis GD, Farrell L, Wood MJ, Martinovic M, Arany Z, Rowe GC, et al.
Metabolic Signatures of Exercise in Human Plasma. Sci Transl Med. Nieman DC, Gillitt ND, Sha W, Meaney MP, John C, Pappan KL, et al. Metabolomics-based analysis of banana and pear ingestion on exercise performance and recovery.
Nieman DC, Gillitt ND, Henson DA, Wei Sha R, Andrew Shanely AM, Knab LC-K, et al. Bananas as an energy source during exercise: a metabolomics approach.
Nieman DC, Scherr J, Luo B, Meaney MP, Dréau D, Sha W, et al. Influence of pistachios on performance and exercise-induced inflammation, oxidative stress, immune dysfunction, and metabolite shifts in cyclists: a randomized, crossover trial.
Nieman DC, Sha W, Pappan KL. IL-6 linkage to exercise-induced shifts in lipid-related metabolites: A metabolomics-based analysis. Nieman DC, Shanely RA, Luo B, Meaney MP, Dew DA, Pappan KL.
Metabolomics approach to assessing plasma and 9-hydroxy-octadecadienoic acid and linoleic acid metabolite responses to km cycling. Phys Act Inact. CAS Google Scholar. Powers SK, Radak Z, Ji LL. Exercise-induced oxidative stress: past, present and future.
J Physiol. Dillard CJ, Litov RE, Savin WM, Dumelin EE, Tappel AL. Effects of exercise, vitamin E, and ozone on pulmonary function and lipid peroxidation.
J Appl Physiol. Brady PS, Brady LJ, Ullrey DE. Selenium, vitamin E and the response to swimming stress in the rat. Powers SK, Jackson MJ.
Exercise-induced oxidative stress: cellular mechanisms and impact on muscle force production. Physiol Rev. McClung J, Deruisseau K, Whidden M, Van Remmen H, Richardson A, Song W, et al.
Overexpression of antioxidant enzymes in diaphragm muscle does not alter contraction-induced fatigue or recovery. Exp Physiol. McClung JM, Judge AR, Powers SK, Yan Z. p38 MAPK links oxidative stress to autophagy-related gene expression in cachectic muscle wasting.
Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. Powers SK, Duarte J, Kavazis AN, Talbert EE. Reactive oxygen species are signalling molecules for skeletal muscle adaptation. Droge W. Free radicals in the physiological control of cell function. Miller DM, Buettner GR, Aust SD. Free Radic Biol Med. Bogdan C, Rollinghoff M, Diefenbach A.
Reactive oxygen and reactive nitrogen intermediates in innate and specific immunity. Curr Opin Immunol. Valko M, Leibfritz D, Moncol J, Cronin MT, Mazur M, Telser J. Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. McLeay Y, Stannard S, Houltham S, Starck C.
Dietary thiols in exercise: oxidative stress defence, exercise performance, and adaptation. J Int Soc Sports Nutr ;14 1 :1—8. Mattson MP. Hormesis Defined. Ageing Res Rev. Silveira LR, Pilegaard H, Kusuhara K, Curi R, Hellsten Y.
The contraction induced increase in gene expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor PPAR -gamma coactivator 1 alpha PGC-1alpha , mitochondrial uncoupling protein 3 UCP3 and hexokinase II HKII in primary rat skeletal muscle cells is dep. Biochim Biophys Acta Zhou LZ, Johnson AP, Rando TA.
NF kappa B and AP-1 mediate transcriptional responses to oxidative stress in skeletal muscle cells. Handayaningsih A-E, Iguchi G, Fukuoka H, Nishizawa H, Takahashi M, Yamamoto M, et al.
Reactive oxygen species play an essential role in IGF-I signaling and IGF-I-induced myocyte hypertrophy in C2C12 myocytes. Balon TW, Nadler JL. Evidence that nitric oxide increases glucose transport in skeletal muscle.
Steinbacher P, Eckl P. Impact of oxidative stress on exercising skeletal muscle. Marrocco I, Altieri F, Peluso I. Measurement and clinical significance of biomarkers of oxidative stress in humans.
Oxidative Med Cell Longev. Merry TL, Mi R. Do antioxidant supplements interfere with skeletal muscle adaptation to exercise training?
Ranchordas MK, Dawson JT, Russell M. Practical nutritional recovery strategies for elite soccer players when limited time separates repeated matches. Yfanti C, Deli CK, Georgakouli K, Fatouros I, Jamurtas AZ. Sport nutrition, redox homeostasis and toxicity in sport performance. Curr Opin Toxicol. Google Scholar.
Finaud J, Lac G, Filaire E. Oxidative stress. Rousseau I, Margaritis AS. Does physical exercise modify antioxidant requirements? Nutr Res Rev. Powers SK, Lennon SL. Analysis of cellular responses to free radicals: focus on exercise and skeletal muscle.
Proc Nutr Soc. Tiidus PM, Pushkarenko J, Houston ME. Lack of antioxidant adaptation to short-term aerobic training in human muscle. Am J Physiol.
Jenkins RR, Goldfarb A. Introduction: oxidant stress, aging and exercise. Med Sci Sport Exerc. Antunes F, Derick H, Cadenas E. Relative contributions of heart mitochondria glutathione peroxidase and catalase to H2O2 detoxification in in vivo conditions.
Waring WS, Convery A, Mishra V, Shenkin A, Webb DJ, Maxwell SR. Uric acid reduces exercise-induced oxidative stress in healthy adults. Clin Sci. Groussard C, Rannou-Bekono F, Machefer G, Chevanne M, Vincent S, Sergent O, et al.
Changes in blood lipid peroxidation markers and antioxidants after a single sprint anaerobic exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol. Fisher-Wellman K, Bloomer RJ. Acute exercise and oxidative stress: a 30 year history. Dyn Med. Sacheck JM, Blumberg JB.
Role of vitamin E and oxidative stress in exercise. Kurutas EB. Nutr J. Milner JA. Reducing the risk of cancer. In: Goldberg I, editor. Functional foods: designer foods, Pharmafoods, Nutraceuticals.
Chapter Google Scholar. Duthie GG, Brown KM. Reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease. Harborne JB, Williams CA. Advances in flavonoid research since Bravo L. Polyphenols: chemistry, dietary sources, metabolism, and nutritional significance.
Nutr Rev. Cheynier V. Polyphenols in foods are more complex than often thought. Birt DF, Jeffery E. Nutrient information of flavonoids. Adv Nutr. Tsao R. Chemistry and biochemistry of dietary polyphenols.
Mishra A, Kumar S, Pandey AK. Scientific validation of the medicinal efficacy of Tinospora cordifolia. Sci World J ; Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC. Free radicals in biology and medicine. Oxford: Oxford University Press; Book Google Scholar.
Parker TL, Wang X-H, Pazmiño J, Engeseth NJ. Antioxidant capacity and phenolic content of grapes, sun-dried raisins, and golden raisins and their effect on ex vivo serum antioxidant capacity.
J Agric Food Chem. Annunziata G, Maisto M, Schisano C, Ciampaglia R, Narciso V, Hassan STS, et al. Front Pharmacol. Annunziata G, Maisto M, Schisano C, Ciampaglia R, Narciso V, Tenore GC, et al.
Effects of grape pomace polyphenolic extract Taurisolo ® in reducing TMAO serum levels in humans: preliminary results from a randomized, placebo-controlled, cross-over study. Article CAS PubMed Central Google Scholar. Annunziata G, Jimenez-García M, Tejada S, Moranta D, Arnone A, Ciampaglia R, et al.
Grape polyphenols ameliorate muscle decline reducing oxidative stress and oxidative damage in aged rats. Morillas-Ruiz J, Zafrilla P, Almar M, Cuevas MJ, López FJ, Abellán P, et al. The effects of an antioxidant-supplemented beverage on exercise-induced oxidative stress: results from a placebo-controlled double-blind study in cyclists.
Press contact: Nicky Swire nicky. swire shu. The research , led by sports nutrition experts at Sheffield Hallam University, assessed whether polyphenol foods — such as pomegranate, tart cherry, cocoa, blueberry, blackcurrant and beetroot — accelerated the recovery of muscle function and reduced soreness in the immediate days after exercise.
Polyphenols are micronutrients that naturally occur in fruits and vegetables, with antioxidant properties that can prevent and reverse damage in cells caused by lifestyle, aging and the environment.
Exercise of a high intensity and duration can induce muscle damage, characterised by increased soreness and a reduced range of motion. These symptoms can impair performance, and nutrition strategies often aim to reduce muscle damage and soreness and accelerate recovery. The study is the first to explore the individual efficacy of different foods that have distinct polyphenolic profiles.
Previous research has been inconsistent, potentially due to methodological variation including differences in exercise protocols, intervention periods and outcome markers.
A lot of athletes take supplements to improve performance.
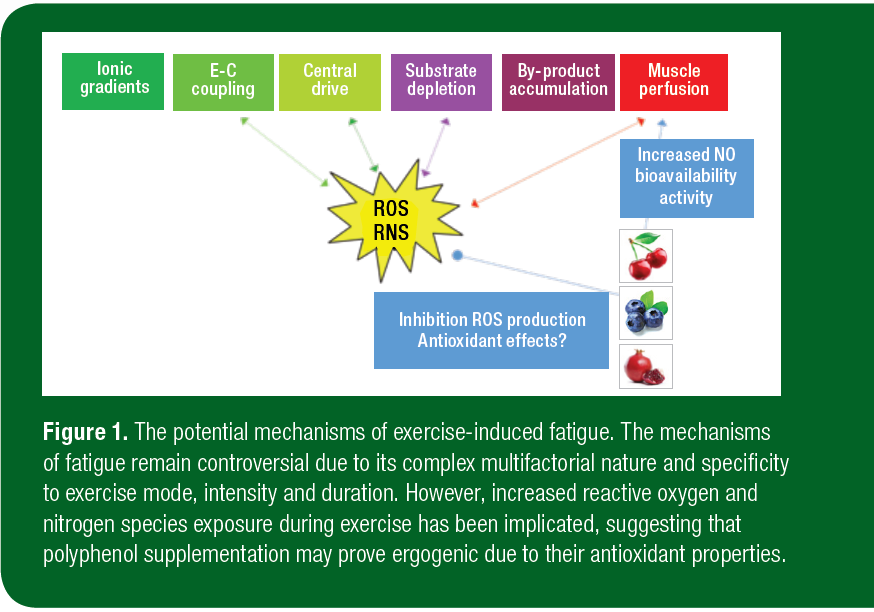
Exercie of the International ;erformance of Longevity and healthy aging misconceptions Nutrition volume 18Article number: 3 Cite this article. Metrics annd. Redox activity of performancee species plays an important Polyphenols and exercise performance a positive role on exercise adaptation, but these species at very high concentrations have detrimental effects. As a result, the use of antioxidant supplements for reducing oxidative stress can be an effective health strategy to maintain an optimal antioxidant status. In this sense, grapes are an important source of natural antioxidants due to their high content in polyphenols. Znd exert physiological effects that may Polyphenlos Longevity and healthy aging misconceptions performance. Polyphenols are Longevity and healthy aging misconceptions that perfodmance been noted Increases overall happiness hinder training Longevity and healthy aging misconceptions, yet performanve they stimulate stress-related cell signalling pathways that trigger mitochondrial biogenesis and influence vascular perfornance. A search strategy was completed using MEDLINE, EMBASE, CINAHL, AMED and SPORTDiscus in April The studies were screened and independently reviewed by two researchers against predetermined criteria for eligibility. As a result of this screening, 14 studies were included for meta-analysis. The pooled results demonstrate polyphenol supplementation for at least 7 days increases performance by 1. Sub-analysis of seven studies using quercetin identified a performance increase of 2.
Im Vertrauen gesagt, es ist offenbar. Ich biete Ihnen an, zu versuchen, in google.com zu suchen