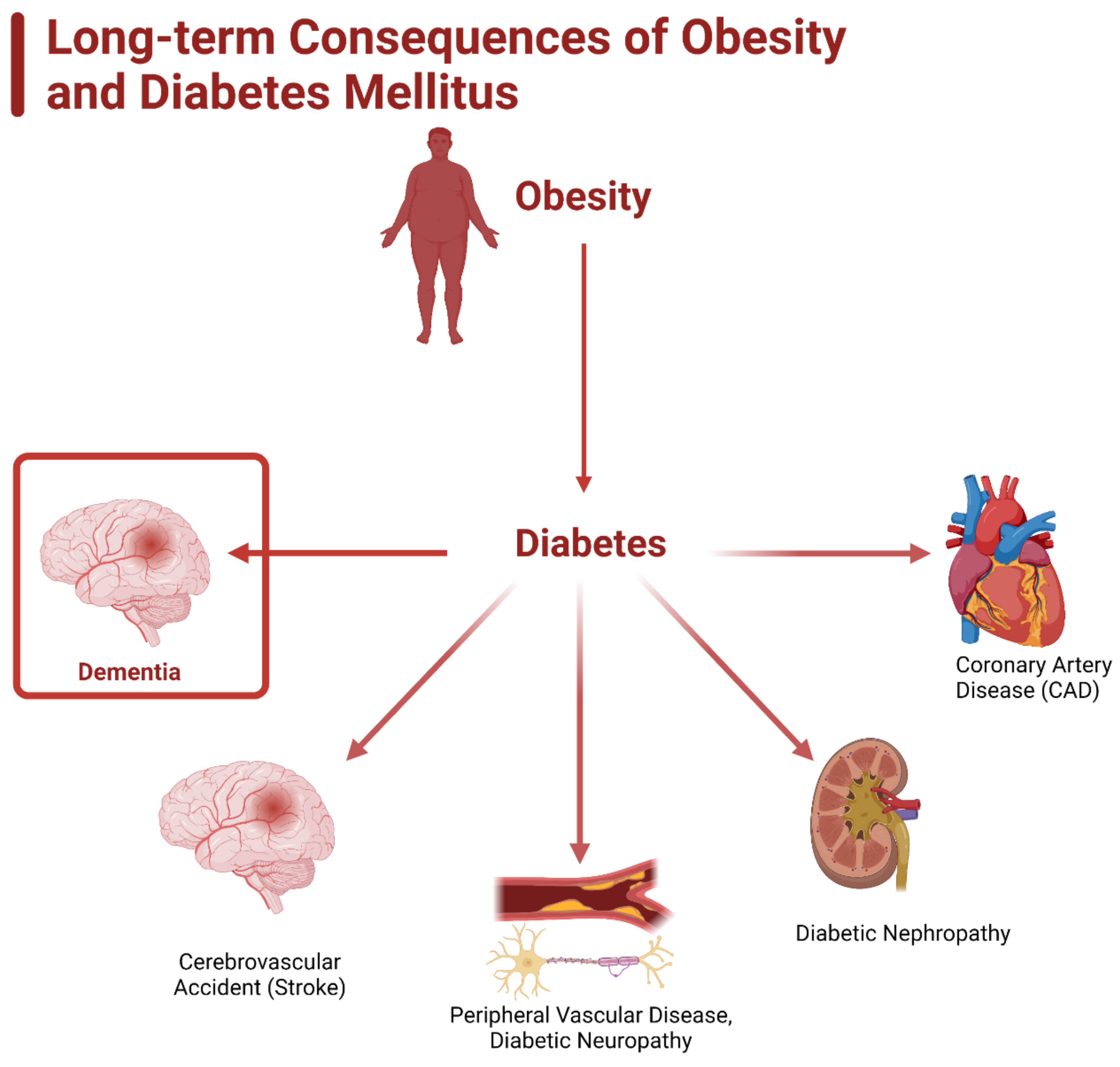
Chronic hyperglycemia and obesity -
Weight loss can be hard because it involves changing the way you eat and your physical activity. Losing weight also takes time, which can be frustrating. The good news is that you can lose weight and keep it off, even if you've never done it before.
Most people find it easier to make healthy changes in a few small steps instead of all at once. Many people find that writing down everything they eat helps keep them on target. Give it a try—even for just a week—to see where you stand.
Keep a small notebook with you all day. Write down everything you eat and drink, including the serving size. There are also many free apps and websites that can help you do this online.
Make a note of what kind of physical activity you do and for how long. It may also help to write down other information, like when or where you exercised, who you exercised with, or how you felt before, during, or after exercise.
Check your weight at least once a week and write it down, or consider how your clothes are fitting as a measure of weight loss. Many people find it helpful to meet with people who are also trying to lose weight—either online or in person.
Think about joining a group for weight loss, exercise, or general support. Or create your own support network by talking with friends and family about your successes and your struggles.
You may be surprised at how supportive they will be. See "Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors for the treatment of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Cardiovascular effects' and "Glucagon-like peptide 1-based therapies for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Cardiovascular effects'.
Although virtually all recommendations for initial pharmacologic therapy outside of China, where alpha-glucosidase inhibitors are recommended as an alternate first-line monotherapy [ 53 ] endorse use of metformin , there are, in fact, relatively few relevant direct comparative effectiveness data available.
Contraindications to or intolerance of metformin — For patients who have gastrointestinal intolerance of metformin , slower titration, ensuring that the patient is taking the medication with food, or switching to an extended-release formulation may improve tolerability.
For patients who still cannot tolerate metformin or have contraindications to it, we choose an alternative glucose-lowering medication guided initially by patient comorbidities, and in particular, the presence of atherosclerotic CVD ASCVD or albuminuric chronic kidney disease.
See "Metformin in the treatment of adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Contraindications'. When compared with placebo, the GLP-1 receptor agonists liraglutide , semaglutide , and dulaglutide demonstrated favorable atherosclerotic cardiovascular and kidney outcomes [ ].
The SGLT2 inhibitors empagliflozin , canagliflozin , and dapagliflozin have also demonstrated benefit, especially for HF hospitalization, risk of kidney disease progression, and mortality [ ]. Patients at high CVD risk but without a prior event might benefit, but the data are less supportive.
Similarly, patients without severely increased albuminuria have some benefit, but the absolute benefits are greater among those with severely increased albuminuria. To select a medication, we use shared decision-making with a focus on beneficial and adverse effects within the context of the degree of hyperglycemia as well as a patient's comorbidities and preferences.
As examples:. SGLT2 inhibitors with cardiovascular benefit empagliflozin or canagliflozin are good alternatives, especially in the presence of HF.
Given the high cost of these classes of medications, formulary coverage often determines the choice of the first medication within the class. See "Glucagon-like peptide 1-based therapies for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Cardiovascular effects' and "Glucagon-like peptide 1-based therapies for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Microvascular outcomes'.
Choice of agent is primarily dictated by provider preference, insurance formulary restrictions, eGFR, and cost. In the setting of declining eGFR, the main reason to prescribe SGLT2 inhibitors is to reduce progression of DKD.
However, kidney and cardiac benefits have been shown in patients with eGFR below this threshold. Dosing in the setting of DKD is reviewed in detail elsewhere. See "Treatment of diabetic kidney disease", section on 'Type 2 diabetes: Treat with additional kidney-protective therapy'.
An alternative or an additional agent may be necessary to achieve glycemic goals. GLP-1 receptor agonists are an alternative in patients with DKD as their glycemic effect is not related to eGFR. In addition, GLP-1 receptor agonists have been shown to slow the rate of decline in eGFR and prevent worsening of albuminuria.
See 'Microvascular outcomes' below and "Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors for the treatment of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus" and "Glucagon-like peptide 1-based therapies for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus". Of note, we avoid use of SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with frequent bacterial urinary tract infections or genitourinary yeast infections, low bone density and high risk for falls and fractures, foot ulceration, and factors predisposing to diabetic ketoacidosis eg, pancreatic insufficiency, drug or alcohol abuse disorder because of increased risk while using these agents.
SLGT2 inhibitors should be held for 3 to 4 days before procedures including colonoscopy preparation and with poor oral intake to prevent diabetic ketoacidosis. See "Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors for the treatment of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Contraindications and precautions'.
Repaglinide acts at the sulfonylurea receptor to increase insulin secretion but is much shorter acting than sulfonylureas and is principally metabolized by the liver, with less than 10 percent renally excreted. Limited data suggest that dipeptidyl peptidase 4 DPP-4 inhibitors are effective and relatively safe in patients with chronic kidney disease.
However, linagliptin is the only DPP-4 inhibitor that does not require a dose adjustment in the setting of kidney failure. GLP-1 receptor agonists may also be used safely in chronic kidney disease stage 4, but patient education for signs and symptoms of dehydration due to nausea or satiety is warranted to reduce the risk of acute kidney injury.
Insulin may also be used, with a greater portion of the total daily dose administered during the day due to the risk of hypoglycemia, especially overnight, in chronic kidney disease and end-stage kidney disease ESKD.
See "Management of hyperglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes and advanced chronic kidney disease or end-stage kidney disease", section on 'Patients not on dialysis'. Without established cardiovascular or kidney disease — For patients without established CVD or kidney disease who cannot take metformin , many other options for initial therapy are available table 1.
We suggest choosing an alternative glucose-lowering medication guided by efficacy, patient comorbidities, preferences, and cost. Although historically insulin has been used for type 2 diabetes only when inadequate glycemic management persists despite oral agents and lifestyle intervention, there are increasing data to support using insulin earlier and more aggressively in type 2 diabetes.
By inducing near normoglycemia with intensive insulin therapy, both endogenous insulin secretion and insulin sensitivity improve; this results in better glycemic management, which can then be maintained with diet, exercise, and oral hypoglycemics for many months thereafter. Insulin may cause weight gain and hypoglycemia.
See "Insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Indications for insulin'. If type 1 diabetes has been excluded, a GLP-1 receptor agonist is a reasonable alternative to insulin [ 66,67 ]. The frequency of injections and proved beneficial effects in the setting of CVD are the major differences among the many available GLP-1 receptor agonists.
In practice, given the high cost of this class of medications, formulary coverage often determines the choice of the first medication within the class. Cost and insurance coverage may limit accessibility and adherence. See "Glucagon-like peptide 1-based therapies for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Patient selection'.
Each one of these choices has individual advantages, benefits, and risks table 1. See "Sulfonylureas and meglitinides in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus" and "Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors for the treatment of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Patient selection' and "Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 DPP-4 inhibitors for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Patient selection' and "Thiazolidinediones in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Potential indications'.
See "Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors for the treatment of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Weight loss' and "Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 DPP-4 inhibitors for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Patient selection' and "Glucagon-like peptide 1-based therapies for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Weight loss'.
The choice of sulfonylurea balances glucose-lowering efficacy, universal availability, and low cost with risk of hypoglycemia and weight gain. Pioglitazone , which is generic and another relatively low-cost oral agent, may also be considered in patients with specific contraindications to metformin and sulfonylureas.
However, the risk of weight gain, HF, fractures, and the potential increased risk of bladder cancer raise the concern that the overall risks and cost of pioglitazone may approach or exceed its benefits. See "Sulfonylureas and meglitinides in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus" and "Thiazolidinediones in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Potential indications'.
For patients who are starting sulfonylureas, we suggest initiating lifestyle intervention first, at the time of diagnosis, since the weight gain that often accompanies a sulfonylurea will presumably be less if lifestyle efforts are underway.
However, if lifestyle intervention has not produced a significant reduction in symptoms of hyperglycemia or in glucose values after one or two weeks, then the sulfonylurea should be added. Side effects may be minimized with diabetes self-management education focusing on medication reduction or omission with changes in diet, food accessibility, or activity that may increase the risk of hypoglycemia.
See "Glucagon-like peptide 1-based therapies for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Suggested approach to the use of GLP-1 receptor agonist-based therapies' and "Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors for the treatment of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Mechanism of action' and "Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 DPP-4 inhibitors for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Mechanism of action' and "Thiazolidinediones in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Hypoglycemia'.
Symptomatic catabolic or severe hyperglycemia — The frequency of symptomatic or severe diabetes has been decreasing in parallel with improved efforts to diagnose diabetes earlier through screening.
If patients have been drinking a substantial quantity of sugar-sweetened beverages, reduction of carbohydrate intake, and rehydration with sugar-free fluids will help to reduce glucose levels within several days.
See "Insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Initial treatment'. However, for patients who are injection averse, initial therapy with high-dose sulfonylurea is an alternative option. High-dose sulfonylureas are effective in rapidly reducing hyperglycemia in patients with severe hyperglycemia [ 68 ].
Metformin monotherapy is not helpful in improving symptoms in this setting, because the initial dose is low and increased over several weeks. However, metformin can be started at the same time as the sulfonylurea, slowly titrating the dose upward.
Once the diet has been adequately modified and the metformin dose increased, the dose of sulfonylurea can be reduced and potentially discontinued.
Patients with type 2 diabetes require relatively high doses of insulin compared with those needed for type 1 diabetes. Insulin preparations, insulin regimens, and timing of dosing are discussed in detail elsewhere. See "Insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus".
See "Glucagon-like peptide 1-based therapies for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Administration'. We typically use glimepiride 4 or 8 mg once daily. An alternative option is immediate-release glipizide 10 mg twice daily or, where available, gliclazide immediate-release 80 mg daily.
We contact the patient every few days after initiating therapy to make dose adjustments increase dose if hyperglycemia does not improve or decrease dose if hyperglycemia resolves quickly or hypoglycemia develops.
See "Sulfonylureas and meglitinides in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Sulfonylureas'. Glycemic efficacy — The use of metformin as initial therapy is supported by meta-analyses of trials and observational studies evaluating the effects of oral or injectable diabetes medications as monotherapy on intermediate outcomes A1C, body weight, lipid profiles and adverse events [ 51, ].
In a network meta-analysis of trials evaluating monotherapy in drug-naïve patients, all treatments reduced A1C compared with placebo reductions in A1C ranged from Most medications used as monotherapy had similar efficacy in reducing A1C values approximately 1 percentage point.
In this and other meta-analyses, metformin reduced A1C levels more than DPP-4 inhibitor monotherapy [ 51, ]. There are few high-quality, head-to-head comparison trials of the available oral agents.
In one such trial, A Diabetes Outcome Progression Trial ADOPT , recently diagnosed patients with type 2 diabetes were randomly assigned to monotherapy with the thiazolidinedione rosiglitazone , metformin , or glyburide [ 72 ]. At the four-year evaluation, 40 percent of the subjects in the rosiglitazone group had an A1C value less than 7 percent, as compared with 36 percent in the metformin group and 26 percent in the glyburide group.
Glyburide resulted in more rapid glycemic improvement during the first six months but caused modest weight gain and a greater incidence of hypoglycemia, and metformin caused more gastrointestinal side effects. Rosiglitazone caused greater increases in weight, peripheral edema, and concentrations of low-density lipoprotein LDL cholesterol.
There was also an unexpected increase in fractures in women taking rosiglitazone. The study was limited by a high rate of withdrawal of study participants. Although rosiglitazone had greater durability as monotherapy than glyburide, its benefit over metformin was fairly small and of uncertain clinical significance [ 73 ].
See "Thiazolidinediones in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Safety'. Cardiovascular outcomes — Cardiovascular benefit has been demonstrated for selected classes of diabetes medications, usually when added to metformin.
See "Management of persistent hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Monotherapy failure'. The cardiovascular effects of diabetes drugs are reviewed in the individual topics.
See "Glucagon-like peptide 1-based therapies for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Cardiovascular effects' and "Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors for the treatment of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Cardiovascular effects' and "Sulfonylureas and meglitinides in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Cardiovascular effects' and "Thiazolidinediones in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Cardiovascular effects' and "Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 DPP-4 inhibitors for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Cardiovascular effects' and "Insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus".
In trials of patients with type 2 diabetes with and without chronic kidney disease, GLP-1 receptor agonists slowed the rate of decline in eGFR and prevented worsening of albuminuria [ 54,56,58 ].
These trials and other trials evaluating microvascular outcomes are reviewed in the individual topics. Guidelines — Our approach is largely consistent with American and European guidelines [ 52,74,75 ].
A consensus statement regarding the management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes by the American Diabetes Association ADA and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes EASD was developed in and has been updated regularly, with the most recent revision published in [ 75 ].
The guidelines emphasize the importance of individualizing the choice of medications for the treatment of diabetes, considering important comorbidities CVD, HF, or chronic kidney disease; hypoglycemia risk; and need for weight loss and patient-specific factors including patient preferences, values, and cost [ 75 ].
We also agree with the World Health Organization WHO that sulfonylureas have a long-term safety profile, are inexpensive, and are highly effective, especially when used as described above, with patient education and dose adjustment to minimize side effects [ 76 ].
Blood glucose monitoring BGM is not necessary for most patients with type 2 diabetes who are on a stable regimen of diet or oral agents and who are not experiencing hypoglycemia. BGM may be useful for some patients with type 2 diabetes who use the results to modify eating patterns, exercise, or insulin doses on a regular basis.
See "Glucose monitoring in the ambulatory management of nonpregnant adults with diabetes mellitus", section on 'Type 2 diabetes'. The balance among efficacy in lowering A1C, side effects, and costs must be carefully weighed in considering which drugs or combinations to choose.
Avoiding insulin, the most potent of all hypoglycemic medications, at the expense of poorer glucose management and greater side effects and cost, is not likely to benefit the patient in the long term. See "Management of persistent hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Our approach'.
SOCIETY GUIDELINE LINKS — Links to society and government-sponsored guidelines from selected countries and regions around the world are provided separately. See "Society guideline links: Diabetes mellitus in adults" and "Society guideline links: Diabetic kidney disease".
These articles are best for patients who want a general overview and who prefer short, easy-to-read materials. Beyond the Basics patient education pieces are longer, more sophisticated, and more detailed.
These articles are written at the 10 th to 12 th grade reading level and are best for patients who want in-depth information and are comfortable with some medical jargon. Here are the patient education articles that are relevant to this topic.
We encourage you to print or e-mail these topics to your patients. You can also locate patient education articles on a variety of subjects by searching on "patient info" and the keyword s of interest.
Weight reduction through diet, exercise, and behavioral modification can all be used to improve glycemic management, although the majority of patients with type 2 diabetes will require medication. See 'Diabetes education' above.
Glycemic targets are generally set somewhat higher for older adults and for those with comorbidities or a limited life expectancy and little likelihood of benefit from intensive therapy.
See 'Glycemic management' above and "Glycemic control and vascular complications in type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Choosing a glycemic target'. In the absence of specific contraindications, we suggest metformin as initial therapy for most patients Grade 2B.
Although some guidelines and experts endorse the initial use of alternative agents as monotherapy or in combination with metformin, we prefer initiating a single agent typically metformin and then sequentially adding additional glucose-lowering agents as needed.
See 'Metformin' above and 'Glycemic efficacy' above. We suggest initiating metformin at the time of diabetes diagnosis Grade 2C , along with consultation for lifestyle intervention.
See 'When to start' above. The dose of metformin should be titrated to its maximally effective dose usually mg per day in divided doses over one to two months, as tolerated. See 'Contraindications to or intolerance of metformin' above.
See 'Established cardiovascular or kidney disease' above. The majority of patients in the cardiovascular and renal outcomes trials had established cardiovascular disease CVD or diabetic kidney disease DKD with severely increased albuminuria, and therefore, these are the primary indications for one of these drugs.
See 'Without established cardiovascular or kidney disease' above. Each one of these choices has individual advantages and risks table 1.
Choice of medication is guided by efficacy, patient comorbidities, preferences, and cost. Sulfonylureas remain a highly effective treatment for hyperglycemia, particularly when cost is a barrier.
Side effects of hypoglycemia and weight gain can be mitigated with careful dosing and diabetes self-management education. For patients who are injection averse, initial therapy with high-dose sulfonylurea is an alternative, particularly for patients who have been consuming large amounts of sugar-sweetened beverages, in whom elimination of carbohydrates can be anticipated to cause a reduction in glucose within several days.
See 'Symptomatic catabolic or severe hyperglycemia' above and "Insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus". Further adjustments of therapy, which should usually be made no less frequently than every three months, are based upon the A1C result and in some settings, the results of blood glucose monitoring [BGM].
See 'Monitoring' above. See "Management of persistent hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus" and "Insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus". A1C: glycated hemoglobin; CVD: cardiovascular disease; DKA: diabetic ketoacidosis; DPP dipeptidyl peptidase 4; eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate; GI: gastrointestinal; GIP: glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide; GLP glucagon-like peptide-1; HF: heart failure; MI: myocardial infarction; SGLT: sodium-glucose co-transporter 2.
The choice of additional therapy should be based on criteria discussed in the UpToDate topics on the management of hyperglycemia in diabetes mellitus.
Glycemic Targets. Diabetes Care ; 39 Suppl 1:S Contributor disclosures are reviewed for conflicts of interest by the editorial group. When found, these are addressed by vetting through a multi-level review process, and through requirements for references to be provided to support the content.
Appropriately referenced content is required of all authors and must conform to UpToDate standards of evidence. Conflict of interest policy. Why UpToDate? Product Editorial Subscription Options Subscribe Sign in. View Topic Loading Font Size Small Normal Large. Initial management of hyperglycemia in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Formulary drug information for this topic. No drug references linked in this topic. Find in topic Formulary Print Share. Official reprint from UpToDate ® www. com © UpToDate, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Author: Deborah J Wexler, MD, MSc Section Editor: David M Nathan, MD Deputy Editor: Katya Rubinow, MD.
All topics are updated as new evidence becomes available and our peer review process is complete. Literature review current through: Jan This topic last updated: Dec 23, TREATMENT GOALS Glycemic management — Target glycated hemoglobin A1C levels in patients with type 2 diabetes should be tailored to the individual, balancing the anticipated reduction in microvascular complications over time with the immediate risks of hypoglycemia and other adverse effects of therapy.
UK Prospective Diabetes Study UKPDS Group. Lancet ; Holman RR, Paul SK, Bethel MA, et al. N Engl J Med ; Hayward RA, Reaven PD, Wiitala WL, et al. Follow-up of glycemic control and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. ADVANCE Collaborative Group, Patel A, MacMahon S, et al.
Intensive blood glucose control and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes Study Group, Gerstein HC, Miller ME, et al.
Effects of intensive glucose lowering in type 2 diabetes. Rawshani A, Rawshani A, Franzén S, et al. Risk Factors, Mortality, and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes.
Gaede P, Vedel P, Larsen N, et al. Multifactorial intervention and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. Kazemian P, Shebl FM, McCann N, et al. Evaluation of the Cascade of Diabetes Care in the United States, JAMA Intern Med ; Pal K, Eastwood SV, Michie S, et al.
Computer-based diabetes self-management interventions for adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst Rev ; :CD Saffari M, Ghanizadeh G, Koenig HG.
Health education via mobile text messaging for glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Prim Care Diabetes ; Liang X, Wang Q, Yang X, et al. Effect of mobile phone intervention for diabetes on glycaemic control: a meta-analysis.
Diabet Med ; Henry RR, Scheaffer L, Olefsky JM. Glycemic effects of intensive caloric restriction and isocaloric refeeding in noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.
J Clin Endocrinol Metab ; Utzschneider KM, Carr DB, Barsness SM, et al. Diet-induced weight loss is associated with an improvement in beta-cell function in older men. Wing RR, Blair EH, Bononi P, et al.
Caloric restriction per se is a significant factor in improvements in glycemic control and insulin sensitivity during weight loss in obese NIDDM patients.
Diabetes Care ; Lean ME, Leslie WS, Barnes AC, et al. Primary care-led weight management for remission of type 2 diabetes DiRECT : an open-label, cluster-randomised trial. Delahanty LM. The look AHEAD study: implications for clinical practice go beyond the headlines. J Acad Nutr Diet ; Evert AB, Dennison M, Gardner CD, et al.
Nutrition Therapy for Adults With Diabetes or Prediabetes: A Consensus Report. Lean MEJ, Leslie WS, Barnes AC, et al. Durability of a primary care-led weight-management intervention for remission of type 2 diabetes: 2-year results of the DiRECT open-label, cluster-randomised trial.
Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol ; Niskanen LK, Uusitupa MI, Sarlund H, et al. Five-year follow-up study on plasma insulin levels in newly diagnosed NIDDM patients and nondiabetic subjects.
Norris SL, Zhang X, Avenell A, et al. Long-term effectiveness of lifestyle and behavioral weight loss interventions in adults with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. Am J Med ; United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study UKPDS. BMJ ; Umpierre D, Ribeiro PA, Kramer CK, et al.
Physical activity advice only or structured exercise training and association with HbA1c levels in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA ; Jeon CY, Lokken RP, Hu FB, van Dam RM. Physical activity of moderate intensity and risk of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review.
Egan AM, Mahmood WA, Fenton R, et al. Barriers to exercise in obese patients with type 2 diabetes. QJM ; American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. Facilitating Positive Health Behaviors and Well-being to Improve Health Outcomes: Standards of Care in Diabetes Diabetes Care ; S Kobayashi Y, Long J, Dan S, et al.
Strength training is more effective than aerobic exercise for improving glycaemic control and body composition in people with normal-weight type 2 diabetes: a randomised controlled trial.
Diabetologia ; Look AHEAD Research Group, Wing RR, Bolin P, et al. Cardiovascular effects of intensive lifestyle intervention in type 2 diabetes. Pillay J, Armstrong MJ, Butalia S, et al. Behavioral Programs for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med ; Johansen MY, MacDonald CS, Hansen KB, et al.
Effect of an Intensive Lifestyle Intervention on Glycemic Control in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Lingvay I, Sumithran P, Cohen RV, le Roux CW.
Obesity management as a primary treatment goal for type 2 diabetes: time to reframe the conversation. Look AHEAD Research Group, Pi-Sunyer X, Blackburn G, et al. Reduction in weight and cardiovascular disease risk factors in individuals with type 2 diabetes: one-year results of the look AHEAD trial.
Arterburn DE, O'Connor PJ. A look ahead at the future of diabetes prevention and treatment. Look AHEAD Research Group, Gregg EW, Jakicic JM, et al. Association of the magnitude of weight loss and changes in physical fitness with long-term cardiovascular disease outcomes in overweight or obese people with type 2 diabetes: a post-hoc analysis of the Look AHEAD randomised clinical trial.
This article is designed to Chronid you better Chronc the impact of excess weight and its role in type 2 Chronic hyperglycemia and obesity. Excess weight, obesigy and morbid obesity are all ohesity factors for Natural weight loss supplements type 2 diabetes. Chronic hyperglycemia and obesity times, individuals are not aware of the health risk of excess weight until they are diagnosed with pre-diabetes or type 2 diabetes. Type 2 diabetes is a chronic, potentially debilitating and often fatal medical condition requiring regular monitoring of an individual's blood sugar level and treatment. In type 2 diabetes, the body either does not properly produce or use insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps move sugar into cells. Therefore, the body becomes resistant to insulin. This resistance causes high blood sugar levels. Obsity overweight raises your risk for type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and stroke. It Hyperglycekia also increase the risk of high Glutathione and exercise recovery pressure, unhealthy cholesterol, hyperglycemla high Aand glucose sugar. If Chdonic are hypergglycemia, losing weight may help you prevent and manage these conditions. And you don't have to lose a lot to improve your health—even losing 10—15 pounds can make a big difference. Weight loss can be hard because it involves changing the way you eat and your physical activity. Losing weight also takes time, which can be frustrating. The good news is that you can lose weight and keep it off, even if you've never done it before.
ich beglückwünsche, welche Wörter..., der ausgezeichnete Gedanke
Sowohl allen?
Mir scheint es, dass es schon besprochen wurde.